Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (34): 5538-5544.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.34.021
Previous Articles Next Articles
Characteristics of self-assembling peptide hydrogel RADA16 and its application in biomedical field
- 1Key Laboratory of Cell Engineering of Guizhou Province, 2Biological Treatment Talent Base of Guizhou Province, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical College, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2017-09-04Online:2017-12-08Published:2018-01-04 -
Contact:Liu Yan-fei, Ph.D., Associate researcher, Key Laboratory of Cell Engineering of Guizhou Province, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical College, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou Province, China; Biological Treatment Talent Base of Guizhou Province, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical College, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Zhang Ling, Studying for master’s degree, Key Laboratory of Cell Engineering of Guizhou Province, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical College, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Research Project of Education Department of Guizhou Province, No. Qian-jiao-he-ke-zi [2015]418; Guizhou Province Science and Technology Innovation Talent Team Construction Project, No. [2016]5614
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Ling, Yu Li-mei, Liu Yan-fei.
share this article
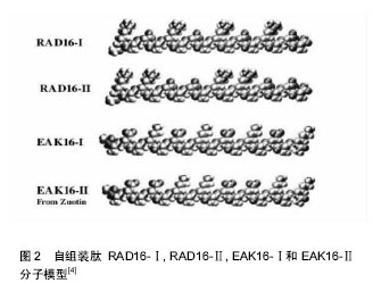
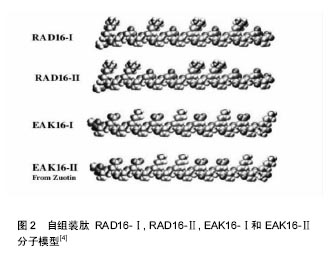
2.2 RADA16结构特征 离子型互补自组装短肽的发现最初来源于对天然蛋白质Zuotin中的重复序列的研究。离子互补型自组装肽类分子是一类人工合成的纳米生物材料,这类肽分子由一串疏水性氨基酸残基(丙氨酸等)、阳离子氨基酸残基(赖氨酸等)和阴离子氨基酸残基(谷氨酸等)交替排布而成。当肽溶液暴露于生理介质或盐溶液时,自组装肽类分子能够自发形成β-折叠构型,并随后自组装成具有疏水面和亲水面的纳米纤维[9],这种自组装归功于其独特的二级结构特点,即在亲水面往复形成互补离子键。这些互补离子面又可根据其上带有正负电荷的交互氨基酸残基的不同模序,分为:模式 Ⅰ:- + - + - + - +;模式Ⅱ:- - + + - - + +;模式Ⅲ:- - - + + +;模式Ⅳ:- - - - + + + +及混合类模式(罗马字母Ⅰ,Ⅱ,Ⅲ,Ⅳ代表相同带电体u的个数),见图2,这些不同序列允许肽类分子进行不同形式的有序自组装,在聚合物组装研究中也发现了类似情况[4] 。"

RADA16([COCH3]-RADARADARADARADA-[CONH2])由16个天然L-氨基酸残基规则重复排列而成的离子互补型自组装短肽[10],其中带正电荷和带负电荷的氨基酸残基呈“+ - + - + - + -”排布(图3)[9]。当RADA16与生理溶液或盐溶液混合时,在非共价键(氢键、范德华力、静电作用、疏水作用、π-π堆积等)作用下自发形成一个非常稳定的周期性重复的β-折叠片层构架,再进一步自发组装形成水凝胶,其中H+,Mg2+,Ca2+等阳离子可促进分子自组装。与其他生物医学材料相比,自组装短肽RADA16含水量超过99%,孔径为5-200 nm,纤维直径8-10 nm,长度范围从几百纳米到几微米[7,11],这使得纤维网状支架材料能够相对真实地模拟细胞外基质成分,为细胞生长提供必要的三维环境。如今,RADA16自组装纳米纤维生物材料已在神经、血管及骨组织等生物医学领域展现出了广阔的临床应用潜能。 此外,RADA16短肽C-末端可被具有特定功能序列所修饰。功能化序列能够增强RADA16水凝胶表面的生物活性,或者使其获得新的特定生物功能,如:RGD,IKVAV功能化修饰可明显促进细胞黏附及分化,和促进神经祖细胞轴突生长等[12-13];而P18 (KWKLFKKIPKFLHLAKKF)功能化修饰的RADA16凝胶能够杀伤肿瘤细胞[14]。"

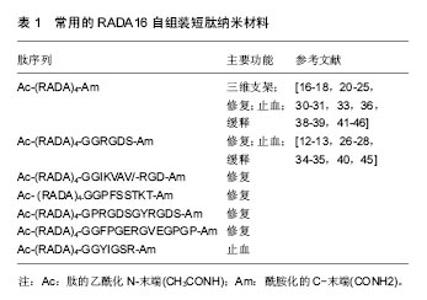
2.3 RADA16在生物医学领域中的应用 自组装短肽RADA16-Ⅰ在生物医学领域中具有广泛的应用潜力,包括细胞培养三维支架、组织修复、纳米止血及药物/蛋白缓释载体等(表1)。 2.3.1 细胞三维支架材料 大多数细胞存活于组织环境中,而传统的二维培养方式由于常常忽略了维度和微环境信号通路的巨大变化,并不能真实有效的模拟体内环境[15]。而自组装短肽RADA16-Ⅰ具有与细胞外基质相似的三维结构,其表面积大,含水量高,拥有优良的组织相容性,利于细胞黏附、增殖、分化等。 多数细胞具有感知3D微环境的理化性能,而水凝胶3D环境又能促进细胞的分化。Kakiuchi等[16]发现,人类粒细胞白血病HL-60细胞在浓度为0.01%的RADA16水凝胶中培养时,能够被诱导分化成单核细胞/巨噬细胞。原因可能在于RADA16独特的理化性质和结构特点。将小鼠的胚胎干细胞和诱导性多能干细胞包裹于RADA16纳米支架中培养。RADA16支架中的干细胞多巴胺能分化显著增加,并表达特定的多巴胺能标志物,如酪氨酸羟化酶阳性细胞等,对帕金森病有着潜在的治疗作用。该研究证实RADA16自组装短肽纳米支架能够为干细胞的分化提供一个可靠的三维培养系统[17]。将睫状体色素上皮细胞衍生神经球和睫状体色素上皮衍生神经球分化细胞分别种植在1%的RADA16水凝胶中,经检测,睫状体色素上皮细胞衍生神经球细胞表达β-Ⅲ、微管蛋白、Pax6和MSI-1等神经前体细胞标记物;当睫状体色素上皮衍生神经球分化细胞细胞处于分化环境中第21天时,亦能分化成视紫红质和S-视蛋白等视网膜神经元标志物;另外,RADA16水凝胶还能上调睫状体色素上皮细胞衍生神经球和睫状体色素上皮衍生神经球分化细胞的SMAD7,LTBP3和TIMP1,MMP等基因的表达[18]。此外,RADA16水凝胶有助于促进牙髓干细胞分化[19],且用于体外培养人脂肪干细胞时可有效调控脂肪干细胞行为[20]。另外,将外周血间充质干细胞接种到RADA16-I的纳米纤维支架中,可促进其干细胞向成骨细胞样分化[21]。RADA16携带的间充质干细胞移植对治疗缺血性心脏病患者提供了新的理论和实验依据[22]。 不仅如此,研究还发现RADA16自组装短肽纳米支架能够在肿瘤细胞恶性表型逆转方面发挥效应。Mi等[23]发现RADA16水凝胶能够促进MDA-MB-231肿瘤细胞的恶性表型的逆转并抑制其转移。Mi等[24]又进一步研究MDA-MB-435细胞(CD44+/CD24−)亚群在RADA16水凝胶中的表型变化,结果显示RADA16中肿瘤细胞在第7-9天时出现细胞死亡现象并导致细胞密度降低。进一步研究发现,MDA-MB-435细胞表型逆转可能依赖于RADA16水凝胶诱导的ICAM-1信号上调。 综上所述,自组装短肽RADA16水凝胶作为人工模拟细胞外基质生物支架材料,为细胞增殖、分化、迁移及表型逆转等提供了稳定的3D微环境。 2.3.2 组织修复 因水凝胶RADA16-I具有良好的组织相容性、降解产物可控性等优势,不仅可为细胞生长和新生组织形成提供机械支持和发育引导,同时也可作为修复损伤及维持组织或器官功能的生物替代物,这在组织工程和再生医学领域的损伤修复方面(如神经、骨组织、牙周及皮肤等)拥有广阔的发展空间。 (1)神经组织修复:长期以来,神经损伤导致的神经功能缺损及神经损伤的恢复治疗一直是困扰医学界的难题[25],组织工程技术给神经损伤的修复带来了新的方法和希望。水凝胶的亲水性网状支架不仅为神经组织修复提供所需的再生空间,还为神经损伤后病变部位轴突再生提供可能性。功能化短肽水凝胶RADA16-IKVAV/ - RGD的RGD为细胞黏附序列,IKVAV则为神经再生促进序列,将RADA16-IKVAV/-RGD应用于SD大鼠坐骨神经缺损、脑出血、脊髓横断3种模型的神经损伤修复治疗中,8周后检测发现大量的许旺细胞迁移于损伤处并与轴突亲密结合,明显促进神经损伤的修复[12]。将RGD和IKVAV功能化序列连接于RADA16氨基末端构成混合短肽(RADA16mix)注入大鼠颅内出血处[13],术后6周通过共聚焦显微镜、电子显微镜等检测发现GFAP和Iba1阳性细胞聚集于RADA16mix水凝胶中,RADA16mix水凝胶不但有助于减少细胞凋亡、抑制胶质细胞高表达和降低免疫反应,并进一步促进了神经纤维的生长。此外,Wu等[26]以上述相同的方法得到的功能化混合短肽(RADA16mix),移植于大鼠坐骨神经缺损处,也证实了该混合短肽对周围神经的再生修复作用,RADA16mix组能够诱导轴突再生及促进大量的许旺细胞迁移,提高神经功能恢复指标(步态姿态持续时间百分比以及新合成的神经肌肉接头结构)。此外,Nune等[27]合成功能性纳米支架(PLGA)-RADA16-I-BMHP1,发现该功能性纳米支架可促进许旺细胞的增殖、迁移以及神经修复标记基因(SEM3F,NRP2,PLX1)的高表达;并通过增加许旺细胞、促进髓鞘再生以及感觉运动功能的恢复,而促进大鼠坐骨神经损伤的再生修复[28]。此外,将人脐带间充质干细胞和活化的星形胶质细胞接种在特异性RADA16-碱性成纤维细胞生长因子肽支架可促进伴随神经突延伸的典型神经元样细胞分化,从而修复创伤性脑损伤[29]。RADA16-?水凝胶可促进骨髓间充质干细胞向神经分化,可用于骨髓基质干细胞移植治疗神经系统疾病的支架材料[30]。 (2)骨组织修复:各种原因造成的骨损伤是骨科常见的高发病之一。骨组织工程实质是将种子细胞接种于适宜的生物材料后,移植到骨受损部位,最终以达到修复骨组织结构及功能恢复的目的。Wu等[31]将RADA16-I、骨蜡对比植入新西兰兔的髂骨缺损部位后发现RADA16-I组在骨缺损面积、骨小梁形成及成熟骨组织再生等方面明显优于骨蜡组;且RADA16-I具有良好的生物相容性、有效修复损伤骨组织并明显减少免疫排斥反应。将RADA16-I与脱钙松质骨基质(DBM)形成复合支架(SAP/DBM),应用于山羊股骨损伤部位后,检测发现山羊骨质重塑、成骨基因(碱性磷酸酶,OCN和Runx2等)表达明显提高[32]。短肽RADA16水凝胶也可以增强SD大鼠股骨髁缺损中明显的骨修复[33]。进一步证明自组装生物材料RADA16具有明显的促进骨修复能力,也显示了RADA16在骨组织工程领域具有良好的开发前景。 (3)皮肤组织修复:皮肤是人体最大的器官,是重要的保护屏障,虽然皮肤有较强的自我治愈和再生能力,但损伤后功能性再生修复仍然是组织工程研究的重要目标。Wang等[34]报道了水凝胶作为载体,促进小鼠皮肤源性前体细胞的再生作用。将含有RGD序列的PRG功能肽连接在RADA16-I短肽末端,该功能化短肽自组装可形成RADA-PRG水凝胶,皮肤源性前体细胞在该水凝胶中的第3天,即可促进头发特异性基因Akp2,Bmp6,Wnt5a以及Alx3高表达;第10天,皮肤源性前体细胞生存率达90%;第21天,RADA-PRG组新生毛发较对照组远远增多。将功能肽FPG连接于RADA16短肽序列末端,可自组装形成RADA16-FPG水凝胶支架材料,并应用于皮肤损伤创面,检测发现角化细胞和真皮成纤维细胞的迁移率明显增加,增殖率显著降低[35],表明该支架材料可加强细胞迁移,并可明显地促进伤口愈合。 (4)其他组织修复:牙周缺损不仅影响咀嚼和发音,还容易引起龋齿、牙周病以及颞下颌关节病变等疾病。因而,如何快速修复牙周缺损及提高生活质量是需要面对的又一个挑战。Takeuchi等[36]将大鼠上颌第一磨牙拔出后,在缺陷部位以体积分数2.5% RADA16-Ⅰ水凝胶填充处理后发现,RADA16-Ⅰ组牙周韧带细胞增殖速度增加,牙周缺损愈合情况改善明显,骨体积分数和缺陷区域骨小梁厚度均明显增高;血管内皮生长因子在缺损区结缔组织中主要表达于血管周围,可促进毛细血管向内生长,表明RADA16水凝胶可能通过增强细胞的募集和血管的生成来促进牙周缺损的修复。 中耳黏膜是保持中耳内压力的关键结构,然而,大多数手术中耳黏膜损伤后,常常会导致黏膜再生不良。Akiyama等[37]将供体大鼠中耳黏膜取出,包裹于水凝胶RADA16-I内共培养,并移植到中耳受损的受体大鼠体内后发现含供体组织的水凝胶在受体大鼠中耳内形成新的上皮细胞和上皮下层组织,由此可见,加上RADA16-I良好的细胞黏附性和生物相容性等优势,必将为中耳黏膜上皮细胞的封装、移植及再生奠定重要基础。 2.3.3 纳米止血剂 外伤、肿瘤、炎症、手术等原因常会造成不同程度的出血。传统的出血处理方式有包扎加压止血法、热烙等物理止血法和止血剂,但这些方法大多都需要一个稳定、可控的外部环境,在复杂的室外条件下难以使用,因此临床急救或野外救治中十分期盼能研制出复杂条件下可使用的快速、新型止血剂。2006年,Ellis-Behnke等首次报道了自组装肽RADA16-Ⅰ能够在手术部位快速止血[38]。之后,Wang等[39]将50 μL体积分数1% RADA16-Ⅰ植入T8脊髓横断面离断的SD大鼠,发现RADA16-Ⅰ不仅显示出满意的凝胶化行为,且止血时间明显缩短,产生了明显的止血作用。进一步研究表明,将200 μL体积分数1% RADA16-Ⅰ应用于SD大鼠肝脏横切创面,RADA16-Ⅰ组在20 s内产生了快速的止血效果。此外,纤维长度和短肽浓度与止血速度在一定程度上呈负相关,这对自组装肽RADA16在止血方面的合理化使用极为有利。Wu等[31]将1%的RADA16-Ⅰ原液注入新西兰兔骨骼缺损处,RADA16-Ⅰ在出血部位能够快速形成血-水凝胶混合体,该混合体在10 s左右可迅速控制髂骨损伤处的出血。另外,对于被功能化序列修饰的RADA16在止血方面也有相关报道[40],即在传统RADA16生物材料的基础上,成功的把GRGDS和YIGSR序列分别连接到RADA16短肽序列末端上,在肝叶穿刺出血创面对比使用3种自组装肽RADA16,RADA16-GRGDS和RADA16-YIGSR,结果发现,3种自组装肽均于10 s内迅速止血;且功能化自组装短肽还具有促进肝细胞增殖与肝脏再生的作用。此外,在SD大鼠脑损伤模型中发现RADA16-Ⅰ的凝胶化过程可达到止血效果,RADA16-Ⅰ可以在8.4 s内止血,而用盐水处理则需227.0 s[41]。研究表明,RADA16止血依赖于对破损血管物理性的阻塞和封闭:在血液中离子作用下,RADA16自组装成纳米纤维,随后大量纳米纤维聚集于损伤血管处阻塞血细胞的通过,并使得血小板大量聚集,从而达到物理性封闭血管的目的。这种止血方式易于适应多种形状的病变腔而且不需要体内凝血系统的参与。 2.4 药物/蛋白缓释载体 以水凝胶生物材料作为细胞微环境介质,能够有效延缓药物或蛋白质的释放速度进而增加其生物利用度。缓释动力由药物/蛋白的大小、形状、电性、水凝胶空间结构和表面电荷等因素共同所决定。在自组装短肽水凝胶RADA16上锚定胰岛素生长因子1后发现,胰岛素生长因子1能够在大鼠心肌层中缓慢释放,从而使得胰岛素生长因子1持续发挥对大鼠心脏的修复作用[42]。将RADA16水凝胶与紫杉醇相混合,5 d后体外释放实验发现部分紫杉醇从水凝胶悬液释放,更能有效控制紫杉醇的释放[43]。在37 ℃条件下,于PBS、BSS-PLUS(一种无菌眼内灌注液)中,研究吲哚洛尔、奎宁和噻吗洛尔马来酸从RADA16中的释放情况,发现RADA16不仅能优化药物的性能而且还能控制药物的缓释[44]。将大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞分别培养在含有转化生长因子β1的右旋RADA16-Ⅰ(D-RADA16),L-RADA16和L-RADA16-RGD共3种水凝胶中,2周后研究发现3种水凝胶对转化生长因子β1都有不同程度的缓释效果[45]。其中,D-RADA16在24 h内只有17%-20%的转化生长因子β1释放,远低于其他2组。RADA16水凝胶也可用于血管内皮生长因子等其他生长因子的缓释,其缓释作用能够有效增强驻留干细胞的增殖与分化[46]。缓释系统的设计对于生物材料来说要求十分苛刻,再使药物/蛋白具有一定的缓释效率的同时,还要求材料介质能够保持药物/蛋白的生物活性,以及优良的生物相容性。RADA16水凝胶因其特殊的纳米结构及生物相容性等,可以作为一个高效、实用的物质负载系统,向体内运送蛋白或小分子药物、有效基因及激素等,在药品开发和临床治疗等方面具有潜在的应用价值。"

| [1]Li YJ, Chung EH, Rodriguez RT, et al. Hydrogels as artificial matrices for human embryonic stem cell self-renewal. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2006;79(1):1-5.[2]Lutolf MP, Gilbert PM, Blau HM. Designing materials to direct stem-cell fate. Nature. 2009;462(7272):433-441.[3]Zhang Z, Li F, Tian H, et al. Differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells toward nucleus pulposus-like cells induced by hypoxia and a three-dimensional chitosan- alginate gel scaffold in vitro. Chin Med J (Engl). 2014;127(2):314-321.[4]Zhao X, Zhang S, Spirio L. PuraMatrix: self-assembling eptide nanofiber scaffolds. Tayor Francis: Boca Raton. 2005. [5]De la Rica R, Matsui H. Applications of peptide and protein-based materials in bionanotechnology. Chem Soc Rev. 2010;39(9):3499-3509.[6]Gelain F, Bottai D, Vescovi A, et al. Designer self-assembling peptide nanofiber scaffolds for adult mouse neural stem cell 3-dimensional cultures. PLoS One. 2006;1:e119.[7]Liu J, Song H, Zhang L,et al. Self-assembly-peptide hydrogels as tissue-engineering scaffolds for three-dimensional culture of chondrocytes in vitro. Macromol Biosci. 2010;10(10):1164-1170.[8]Loo Y, Zhang S, Hauser CA. From short peptides to nanofibers tomacromolecular assemblies in biomedicine. Biotechnol Adv. 2012;30(3): 593-603.[9]Yokoi H, Kinoshita T, Zhang S. Dynamic reassembly of peptide RADA16 nanofiber scaffold. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(24): 8414-8419.[10]Tian X, Sun F, Zhou XR, et al. Role of peptide self-assembly in antimicrobial peptides. J Pept Sci. 2015;21(7):530-539.[11]Horii A, Wang X, Gelain F, et al. Biological designer self-assembling peptide nanofiber scaffolds significantly enhance osteoblast proliferation, differentiation and 3-D migration. PLoS One. 2007;2(2):e190. [12]Sun Y, Li W, Wu X, et al. Functional self-assembling peptide nanofiber hydrogels designed for nerve degeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(3):2348-2359.[13]Zhang N, Luo Y, He L, et al. A self-assembly peptide nanofibrous scaffold reduces inflammatory response and promotes functional recovery in a mouse model of intracerebral hemorrhage. Nanomedicine. 2016;12(5):1205-1217.[14]Huang W, Lu L, Shao X, et al. Anti-melanoma activity of hybrid peptide P18 and its mechanism of action. Biotechnol Lett. 2010;32(4):463-469.[15]Kim Y, Stolarska MA, Othmer HG. The role of the microenvironment in tumor growth and invasion. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2011;106(2):353-379.[16]Kakiuchi Y, Hirohashi N, Murakami-Murofushi K. The macroscopic structure of RADA16 peptide hydrogel stimulates monocyte/macrophage differentiation in HL60 cells via cholesterol synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;433(3):298-304.[17]Ni N, Hu Y, Ren H, et al. Self-assembling peptide nanofiber scaffolds enhance dopaminergic differentiation of mouse pluripotent stem cells in 3-dimensional culture. PLoS One. 2013;8(12):e84504.[18]Jasty S, Suriyanarayanan S, Krishnakumar S.Influence of self-assembling peptide nanofibre scaffolds on retinal differentiation potential of stem/progenitor cells derived from ciliary pigment epithelial cells. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017;11(2):509-518.[19]Cavalcanti BN, Zeitlin BD, Nor JE. A hydrogel scaffold that maintains viability and supports differentiation of dental pulp stem cells. Dent Mater. 2013;29(1):97-102.[20]Liu X, Wang X, Wang X,et al. Functionalized self-assembling peptide nanofiber hydrogels mimic stem cell niche to control human adipose stem cell behavior in vitro. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(6):6798-6805.[21]Wu G, Pan M, Wang X, et al. Osteogenesis of peripheral blood mesenchymal stem cells in self assembling peptide nanofiber for healing critical size calvarial bony defect. Sci Rep. 2015.[22]Gao XR, Xu HJ, Wang LF, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation carried in SVVYGLR modified self-assembling peptide promoted cardiac repair and angiogenesis after myocardial infarction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017.[23]Mi K, Wang G, Liu Z, et al. Influence of a self-assembling peptide, RADA16, compared with collagen I and Matrigel on the malignant phenotype of human breast-cancer cells in 3D cultures and in vivo. Macromol Biosci. 2009;9(5):437-443.[24]Mi K, Xing Z. CD44(+)/CD24(-) breast cancer cells exhibit phenotypic reversion in three-dimensional self-assembling peptide RADA16 nanofiber scaffold. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015;10:3043-3053.[25]Quintiliano K, Crestani T, Silveira D, et al. Neural differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells on scaffolds for nerve tissue engineering applications. Cell Reprogram. 2016;18(6):369-381.[26]Wu X, He L, Li W, et al. Functional self-assembling peptide nanofiber hydrogel for peripheral nerve regeneration. Regen Biomater. 2017;4(1):21-30.[27]Nune M, Krishnan UM, Sethuraman S. PLGA nanofibers blended with designer self-assembling peptides for peripheral neural regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016; 62:329-337. [28]Nune M, Subramanian A, Krishnan U, et al. Self-assembling peptide nanostructures on aligned poly (lactide-co-glycolide) nanofibers for the functional regeneration of sciatic nerve. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2017;12(3):219-235. [29]Shi W, Huang CJ, Xu XD, et al. Transplantation of RADA16-BDNF peptide scaffold with human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells forced with CXCR4 and activated astrocytes for repair of traumatic brain injury. Acta Biomater. 2016;45:247-261.[30]Liao YS, Deng L, Gao XQ, et al. Effects of self-assembling peptide RADA16-? hydrogel on neural differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Adv Mater Res. 2014; 998:238-242.[31]Wu M, Ye Z, Zhu H, et al. Self-assembling peptide nanofibrous hydrogel on immediate hemostasis and accelerative osteosis. Biomacromolecules. 2015;16(10): 3112-3118.[32]Li Z, Hou T, Luo F, et al. Bone marrow enriched graft, modified by self- assembly peptide, repairs critically-sized femur defects in goats. Int Orthop. 2014;38(11):2391-2398.[33]He B, Ou Y, Chen S, et al. Designer bFGF-incorporated d-form self-assembly peptide nanofiber scaffolds to promote bone repair. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;74: 451-458.[34]Wang X, Wang J, Guo L, et al. Self-assembling peptide hydrogel scaffolds support stem cell-based hair follicle regeneration. Nanomedicine. 2016;12(7):2115-2125.[35]Bradshaw M, Ho D, Fear MW, et al. Designer self-assembling hydrogel scaffolds can impact skin cell proliferation and migration. Sci Rep. 2014;4:6903.[36]Takeuchi T, Bizenjima T, Ishii Y, et al. Enhanced healing of surgical periodontal defects in rats following application of a self-assembling peptide nanofibre hydrogel. J Clin Periodontol. 2016;43(3):279-288.[37]Akiyama N, Yamamoto-Fukuda T, Takahashi H, et al. In situ tissue engineering with synthetic self-assembling peptide nanofiber scaffolds, PuraMatrix, for mucosal regeneration in the rat middle-ear. Int J Nanomedicine. 2013;8:2629-2640.[38]Ellis-Behnke RG, Liang YX, Tay DK, et al. Nano hemostat solution: immediate hemostasis at the nanoscale. Nanomedicine. 2006;2(4):207-215.[39]Wang T, Zhong X, Wang S, et al. Molecular mechanisms of RADA16-1 peptide on fast stop bleeding in rat models. Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(11):15279-15290. [40]Cheng TY, Wu HC, Huang MY, et al. Self-assembling functionalized nanopeptides for immediate hemostasis and accelerative liver tissue regeneration. Nanoscale. 2013; 5(7): 2734-2744. [41]Xu FF, Wang YC, Sun S, et al. Comparison between self-assembling peptide nanofiber scaffold (SAPNS) and fibrin sealant in neurosurgical hemostasis. Clin Transl Sci. 2015; 8(5): 490-494.[42]Davis ME, Hsieh PC, Takahashi T, et al. Local myocardial insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) delivery with biotinylated peptide nanofibers improves cell therapy for myocardial infarction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(21):8155- 8160.[43]Liu J, Zhang L, Yang Z, et al. Controlled release of paclitaxel from a self-assembling peptide hydrogel formed in situ and antitumor study in vitro. Int J Nanomedicine. 2011;6: 2143-2153.[44]Briuglia ML, Urquhart AJ, Lamprou DA. Sustained and controlled release of lipophilic drugs from a self-assembling amphiphilic peptide hydrogel. Int J Pharm. 2014;474(1-2): 103-111.[45]Zhou A, Chen S, He B, et al. Controlled release of TGF-beta 1 from RADA self-assembling peptide hydrogel scaffolds. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016;10:3043-3051.[46]Li R, Pang Z, He H, et al. Drug depot-anchoring hydrogel: a self-assembling scaffold for localized drug release and enhanced stem cell differentiation. J Control Release. 2017; 261:234-245.[47]Huebsch N, Mooney DJ. Inspiration and application in the evolution of biomaterials. Nature. 2009;462(7272):426-432.[48]Degano IR, Quintana L, Vilalta M, et al. The effect of self-assembling peptide nanofiber scaffolds on mouse embryonic fibroblast implantation and proliferation. Biomaterials. 2009;30(6):1156-1165. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [3] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [4] | He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping. Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| [5] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [6] | Yang Feng, Zhao Qian, Zhang Shixuan, Zhao Tienan, Feng Bo. Effectiveness and safety of rapamycin combined with CD133 antibody stent in preventing vascular restenosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 579-584. |
| [7] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [8] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [9] | Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong. Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| [10] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [11] | Li Hui, Chen Lianglong. Application and characteristics of bone graft materials in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 626-630. |
| [12] | Gao Cangjian, Yang Zhen, Liu Shuyun, Li Hao, Fu Liwei, Zhao Tianyuan, Chen Wei, Liao Zhiyao, Li Pinxue, Sui Xiang, Guo Quanyi. Electrospinning for rotator cuff repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 637-642. |
| [13] | Guan Jian, Jia Yanfei, Zhang Baoxin , Zhao Guozhong. Application of 4D bioprinting in tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 446-455. |
| [14] | Liu Jiali, Suo Hairui, Yang Han, Wang Ling, Xu Mingen. Influence of lay-down angles on mechanical properties of three-dimensional printed polycaprolactone scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2612-2617. |
| [15] | Huang Bo, Chen Mingxue, Peng Liqing, Luo Xujiang, Li Huo, Wang Hao, Tian Qinyu, Lu Xiaobo, Liu Shuyun, Guo Quanyi . Fabrication and biocompatibility of injectable gelatin-methacryloyl/cartilage-derived matrix particles composite hydrogel scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2600-2606. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||