Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (30): 4769-4774.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.30.003
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of zinc-containing magnesium alloys on proliferation of human osteosarcoma U2OS cells in vitro
- Department of Orthopedics, China Meitan General Hospital, Beijing 100028, China
-
Received:2017-05-09Online:2017-10-28Published:2017-11-07 -
Contact:Yang Wan-shi, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, China Meitan General Hospital, Beijing 100028, China -
About author:Zhao Xiao-kui, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, China Meitan General Hospital, Beijing 100028, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhao Xiao-kui, He Bao-hua, Shao Nan, Zhang Sheng-guo, Yang Wan-shi.
share this article
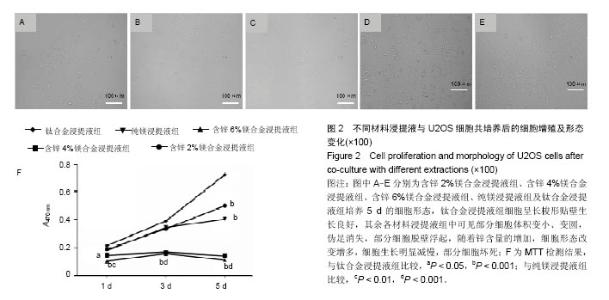
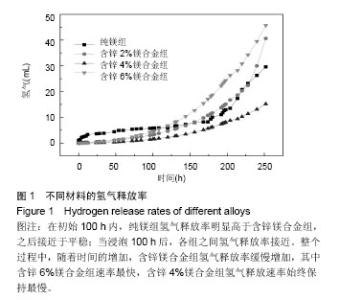
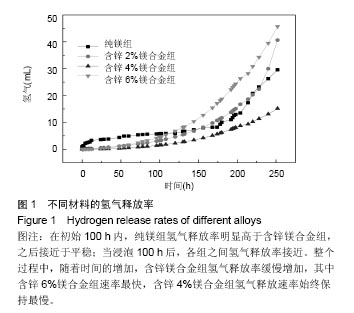
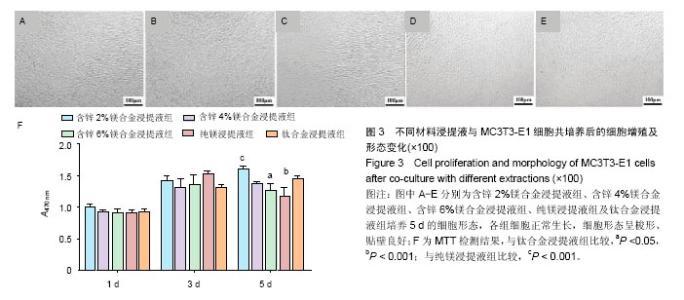
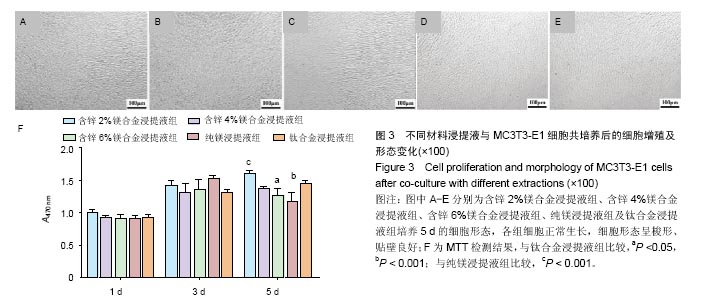
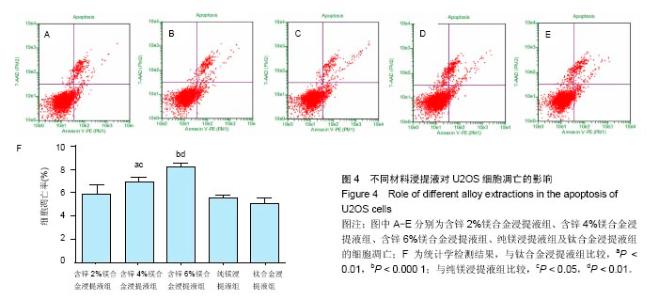
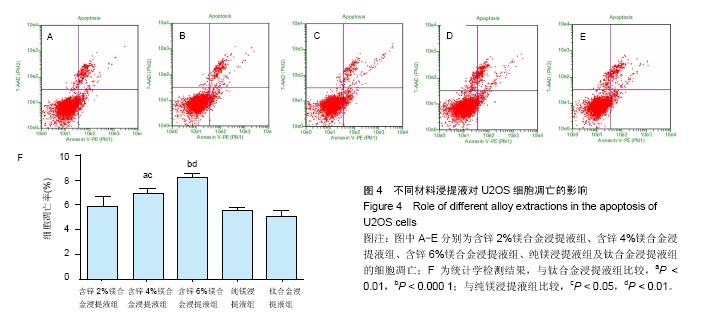
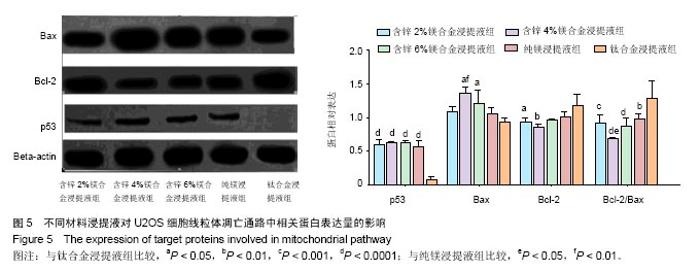
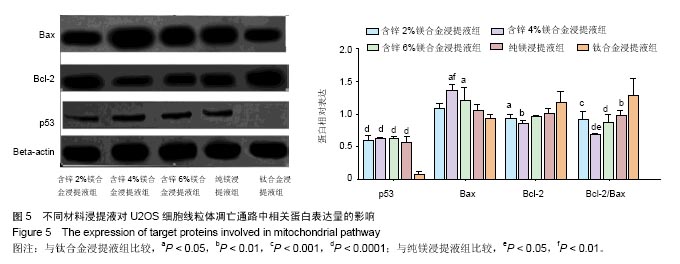
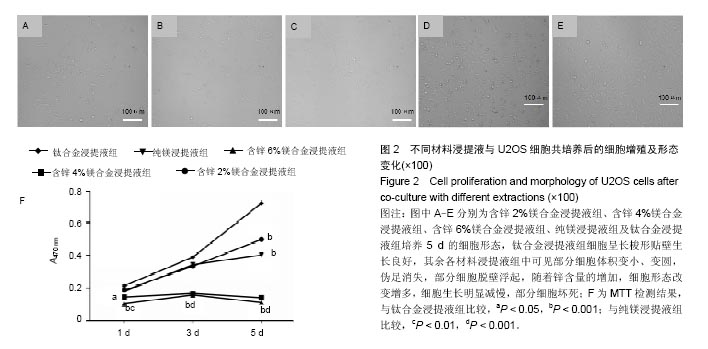
2.2 材料浸提液对U2OS及MC3T3-E1细胞形态学及增殖的影响 U2OS细胞:共培养5 d后,倒置显微镜下观察(图2A-E)发现,钛合金浸提液组细胞呈长梭形贴壁生长良好,其余各材料浸提液组中可见部分细胞体积变小、变圆,伪足消失,部分细胞脱壁浮起,随着锌含量的增加,细胞形态改变增多,细胞生长明显减慢,部分细胞坏死。MTT实验结果表明(图2F),各材料浸提液组中U2OS细胞增殖均受到抑制,并且呈现明显的时间和剂量依赖性,当培养1,3 d时,含锌4%、6%镁合金浸提液组的细胞增殖低于纯镁浸提液组、钛合金浸提液组(P < 0.05);培养5 d时,含锌镁合金浸提液组、纯镁浸提液组细胞增殖低于钛合金浸提液组 (P < 0.05),含锌4%、6%镁合金浸提液组的细胞增殖低于纯镁浸提液组(P < 0.05)。"
| [1]Nan M,Yangmei C,Bangcheng Y.Magnesium metal--a potential biomaterial with antibone cancer properties.J Biomed Mater Res A.2014;102(8):2644-2651. [2]Rad MP,Fattahi Masoum SH,Layegh P,et al.Primary Osteosarcoma of the Sternum: A case Report and Review of the Literature.Arch Bone J Surg.2014;2(4):272-275. [3]殷实.生物材料植入体内引发肿瘤的机制研究[J].科技信息, 2010, 24(3):384-385.[4]Schoen FJ,奚廷斐,王春仁.生物材料引起的感染、肿瘤和钙化[J].国外医学:生物医学工程分册, 1989,12(1):29-35.[5]Guo Y,Liu W,Ma S,et al.A preliminary study for novel use of two Mg alloys(WE43 and Mg3Gd).J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2016; 27(5):82.[6]Li Z,Gu X,Lou S,et al.The development of binary Mg-Ca alloys for use as biodegradable materials within bone. Biomaterials. 2008;29(10):1329-1344.[7]Zhang S,Zhang X,Zhao C,et al.Research on an Mg-Zn alloy as a degradable biomaterial. Acta Biomater.2010;6(2):626-640.[8]Li Z,Gu X,Lou S,et al.The development of binary Mg-Ca alloys for use as biodegradable materials within bone.Biomaterials. 2008;29(10):1329-1344.[9]Gu XN,Xie XH,Li N,et al.In vitro and in vivo studies on a Mg-Sr binary alloy system developed as a new kind of biodegradable metal.Acta Biomater.2012;8(6):2360-2374.[10]Li Y,Liu L,Wan P,et al.Biodegradable Mg-Cu alloy implants with antibacterial activity for the treatment of osteomyelitis: In vitro and in vivo evaluations.Biomaterials.2016;106:250-263.[11]Tie D,Feyerabend F,Müller WD,et al.Antibacterial biodegradable Mg-Ag alloys.Eur Cell Mater.2013;25:284-298.[12]Neel, E.A., et al.Characterisation of antibacterial copper releasing degradable phosphate glass fibres.Biomaterials. 2005;26(15):2247-2254.[13]Chen Y, Xia J,Fan G,et al.Biodegradable Mg-6Zn Alloy Down-Regulation the NF- B Signaling Pathway of Intestinal Epithelial Cells.J Biomater Tissue Eng.2016;6(7):531-537.[14]Zhang S,Zhang X,Zhao C,et al.Research on an Mg–Zn alloy as a degradable biomaterial.Acta Biomaterialia.2010;6:626-640.[15]Chen Y,Yan J,Zhao C,et al.In vitro and in vivo assessment of the biocompatibility of an Mg-6Z(n) alloy in the bile.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2014;25(2):471-480.[16]Barahuie F,Hussein MZ,Abd Gani S,et al.Anticancer nanodelivery system with controlled release property based on protocatechuate–zinc layered hydroxide nanohybrid.Int J Nanomedicine. 2014;9:3137-4319. [17]Song Y,Guan R,Lyu F,et al.In vitro cytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles and zinc oxide nanoparticles to human epithelial colorectal adenocarcinoma (Caco-2) cells.Mutat Res. 2014;769: 113-118.[18]Chyan W,Zhang DY,Lippard SJ,et al.Reaction-based fluorescent sensor for investigating mobile Zn2+ in mitochondria of healthy versus cancerous prostate cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014; 111(1):143-148. [19]Wandzilak A,Czyzycki M,Wrobel P,et al.The oxidation states and chemical environments of iron and zinc as potential indicators of brain tumour malignancy grade - preliminary results.Metallomics. 2013;5(11):1547-1553. [20]Bornapour M, Muja N,Shum-Tim D,et al.Biocompatibility and biodegradability of Mg-Sr alloys: the formation of Sr-substituted hydroxyapatite.Acta Biomater. 2013;9(2):5319-5330.[21]Ahamed M1,Akhtar MJ,Raja M,et al.ZnO nanorod-induced apoptosis in human alveolar adenocarcinoma cells via p53, survivin and bax/bcl-2 pathways: role of oxidative stress. Nanomedicine.2011;7(6):904-913.[22]Chiche J,Brahimi-Horn MC,Pouyssegur J.Tumour hypoxia induces a metabolic shift causing acidosis: a common feature in cancer.J Cell Mol Med.2010;14(4):771-794.[23]李文辉,张岩,陶海荣,等.镁锌合金在体外对MC3T3一E1细胞增殖、分化和矿化的影响[J].中华实验外科杂志, 2010,26(6):819-822.[24]Herman-Antosiewicz A,Singh SV.Signal transduction pathways leading to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis induction in cancer cells by Allium vegetable-derived organosulfur compounds: a review. Mutat Res.2004;555(1-2):121-131.[25]Roth W,Reed JC.Apoptosis and cancer: when BAX is TRAILing away.Nat Med.2002;8(3):216-218.[26]Kang N,Zhang JH,Qiu F,et al.Inhibition of EGFR signaling augments oridonin-induced apoptosis in human laryngeal cancer cells via enhancing oxidative stress coincident with activation of both the intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways. Cancer Lett.2010;294(2):147-158.[27]Pan JS,Hong MZ,Ren JL.Reactive oxygen species: A double-edged sword in oncogenesis.World J Gastroenterol. 2009;15(14):1702-1707.[28]Wang X,Liu JZ,Hu JX,et al.ROS-activated p38 MAPK/ERK-Akt cascade plays a central role in palmitic acid-stimulated hepatocyte proliferation.Free Radic Biol Med.2011;51(2):539-551.[29]Orzo?ek A,Wysocki P,Strze?ek J,et al.Superoxide dismutase (SOD) in boar spermatozoa: purification, biochemical properties and changes in activity during semen storage (16 degrees C) in different extenders.Reprod Biol. 2013;13(1):34-40. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [3] | Zhang Yujie, Yang Jiandong, Cai Jun, Zhu Shoulei, Tian Yuan. Mechanism by which allicin inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of rat vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1080-1084. |
| [4] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [5] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [6] | Deng Shuang, Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Zhang Jianchao, Yuan Lingyan . Effects of exercise preconditioning on myocardial protection and apoptosis in a mouse model of myocardial remodeling due to early stress overload [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 717-723. |
| [7] | Yang Sidi, Wang Qian, Xu Nuo, Wang Ronghan, Jin Chuanqi, Lu Ying, Dong Ming. Biodentine enhances the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts through upregulating bone morphogenetic protein-2 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 516-520. |
| [8] | Chen Shuo, Xiao Dongqin, Li Xingping, Ran Bin, Shi Feng, Zhang Chengdong, Deng Li, Huang Nanxiang, Liu Kang, Feng Gang, Duan Ke. Preparation and characterization of tantalum functional coating on titanium implant [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 546-552. |
| [9] | He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping. Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| [10] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [11] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [12] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [13] | Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong. Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| [14] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [15] | Li Hui, Chen Lianglong. Application and characteristics of bone graft materials in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 626-630. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||