Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (28): 4505-4511.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.28.013
Previous Articles Next Articles
MicroRNA expression profile in the process of cyclic mechanical stretch promoting C2C12 myogenesis
He Yu-tong1, Zhang Ma-hui2, Song Chen1, Ye Gen-lan1, Yu Lei1, Qiu Xiao-zhong1, Wang Le-yu1
- 1Department of Human Anatomy, Southern Medical University, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Construction and Detection in Tissue Engineering, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of Neurology, Zhujiang Hospital of Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China
-
Revised:2017-06-09Online:2017-10-08Published:2017-11-10 -
Contact:Wang Le-yu, M.D., Associate professor, Department of Human Anatomy, Southern Medical University, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Construction and Detection in Tissue Engineering, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:He Yu-tong, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Human Anatomy, Southern Medical University, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Construction and Detection in Tissue Engineering, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China; Zhang Ma-hui, Master, Department of Neurology, Zhujiang Hospital of Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China He Yu-tong and Zhang Ma-hui contributed equally to this work. -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 31100700; the Guangdong Provincial Medical Research Foundation, No. A2015412
CLC Number:
Cite this article
He Yu-tong, Zhang Ma-hui, Song Chen, Ye Gen-lan, Yu Lei, Qiu Xiao-zhong, Wang Le-yu. MicroRNA expression profile in the process of cyclic mechanical stretch promoting C2C12 myogenesis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(28): 4505-4511.
share this article
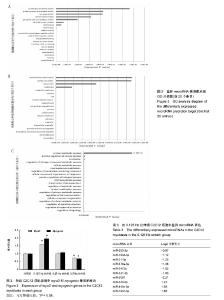
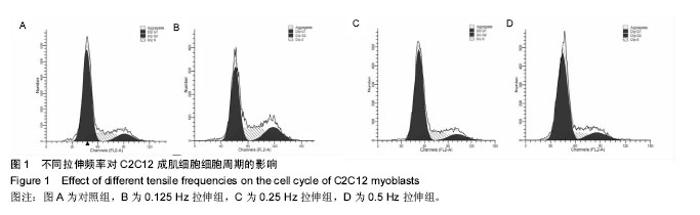
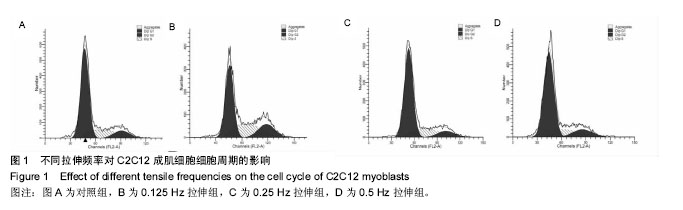
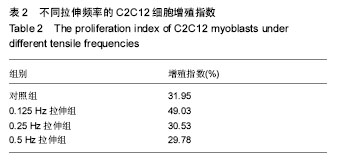
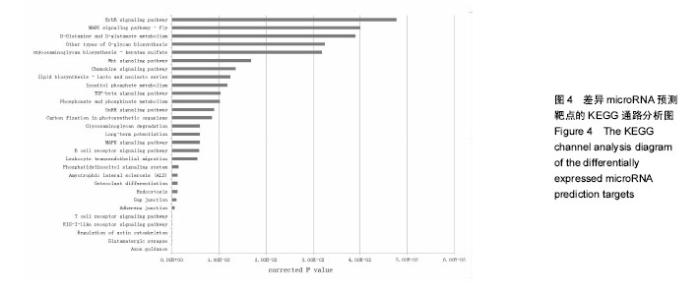
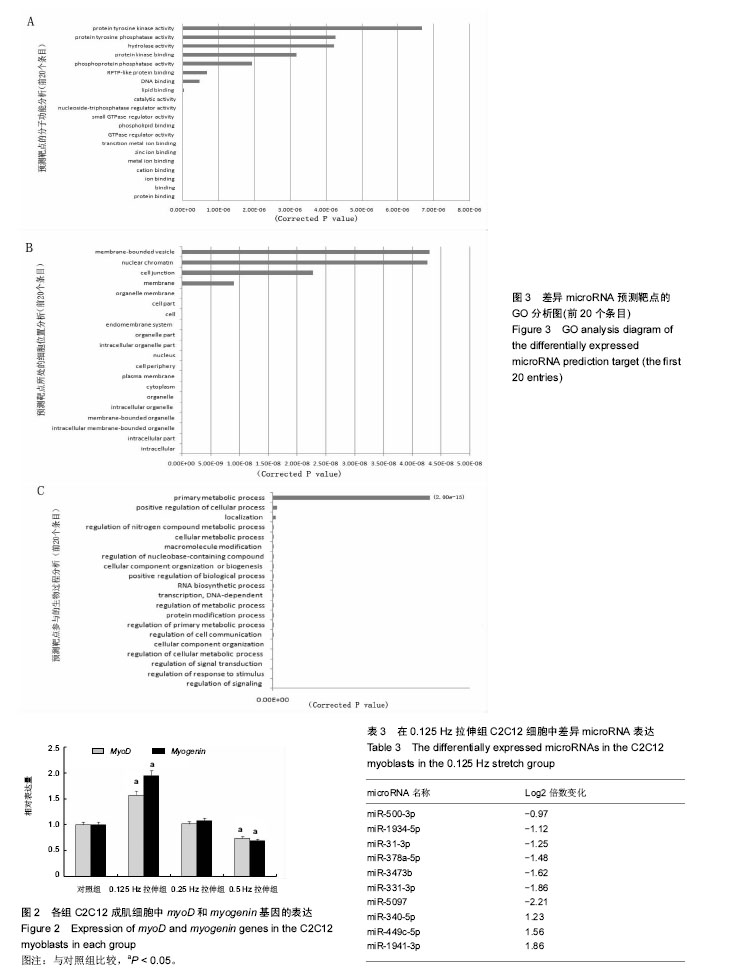
2.2 10%形变、0.125 Hz拉伸频率可促进C2C12细胞myoD和myogenin基因表达升高 由图2所示,0.125 Hz拉伸频率的C2C12细胞myoD和myogenin基因的表达与对照组比较显著升高(P < 0.05);0.25 Hz拉伸频率的C2C12细胞中成肌因子的表达与对照组比较差异无显著性意义;0.5 Hz拉伸频率的C2C12细胞中myoD和myogenin基因的表达与对照组比较显著降低(P < 0.05)。 2.3 10%形变、0.125 Hz拉伸C2C12成肌细胞后microRNA表达谱的变化 通过高通量测序检测,0.125 Hz的拉伸组对照组C2C12成肌细胞比较其表达有明显差异且P < 0.05的共有10个microRNA。其中拉伸组有7个下调的microRNA,分别是miR-331-3p, miR-5097,miR-500-3p,miR-3473b,miR-1934-5p,miR-31-3p,miR-378a-5p。而有3个是拉伸组上调的microRNA,分别是miR-1941- 3p,miR-340-5p,miR-449c-5p(表3)。 2.4 生物信息学结果分析(GO分析,KEGG分析) 从GO富集分析的结果显示,拉伸组与对照组表达有差异的microRNA预测靶点的分子,其功能在金属离子结合,锌离子结合,蛋白结合,离子结合等方面富集较为显著。因此预测靶点所在的位置应在细胞内,细胞内部分,胞内有界膜细胞器,有界膜细胞器,细胞器等条目富集显著。预测靶点参与的生命活动在刺激反应调节,信号调节,细胞新陈代谢过程调节,信号传导调节,细胞正分组成等方面富集显著,而P值越小越有理由说明在该条目富集越显著(图3)。 KEGG通路分析的结果显示,显著富集的通路共有29条,而其中与骨骼肌的损伤修复有关的通路有:T细胞受体信号通路,磷脂酰肌醇信号通路,肌萎缩侧索硬化,肌动蛋白细胞骨架调节通路,B细胞受体信号通路,MAPK信号通路,转化生长因子β信号通路,趋化因子信号通路,黏附连接,磷酸盐和亚磷酸盐代谢通路,统计学分析显示P < 0.05为显著富集,且P值越小,说明在该条目越富集(图4)。"
| [1] Kook SH, Lee HJ, Chung WT, et al. Cyclic mechanical stretch stimulates the proliferation of C2C12 myoblasts and inhibits their differentiation via prolonged activation of p38 MAPK. Mol Cells. 2008;25(4): 479-486.[2] Khalsa PS, Ge W, Uddin MZ, et al. Integrin alpha2beta1 affects mechano-transduction in slowly and rapidly adapting cutaneous mechanoreceptors in rat hairy skin. Neuroscience. 2004;129(2): 447-459.[3] Cachaço AS, Pereira CS, Pardal RG, et al. Integrin repertoire on myogenic cells changes during the course of primary myogenesis in the mouse. Dev Dyn. 2005;232(4):1069-1078.[4] Rauch C, Loughna PT. Static stretch promotes MEF2A nuclear translocation and expression of neonatal myosin heavy chain in C2C12 myocytes in a calcineurin- and p38-dependent manner. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2005;288(3): C593-605.[5] Dias P, Dilling M, Houghton P. The molecular basis of skeletal muscle differentiation. Semin Diagn Pathol.1994;11(1): 3-14.[6] Kumar A, Murphy R, Robinson P, et al. Cyclic mechanical strain inhibits skeletal myogenesis through activation of focal adhesion kinase, Rac-1 GTPase, and NF-kappaB transcription factor. FASEB J. 2004;18(13): 1524-1535.[7] Wang H, Sun H, Guttridge DC. microRNAs: novel components in a muscle gene regulatory network. Cell Cycle. 2009;8(12): 1833-1837.[8] Bernstein E, Kim SY, Carmell MA, et al. Dicer is essential for mouse development. Nat Genet. 2003;35(3): 215-217.[9] Li J, Wang G, Jiang J, et al. Dynamical Expression of MicroRNA-127-3p in Proliferating and Differentiating C2C12 Cells. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci. 2016;29(12): 1790-1795.[10] Hua W, Zhang M, Wang Y, et al. Mechanical stretch regulates microRNA expression profile via NF-kappaB activation in C2C12 myoblasts. Mol Med Rep. 2016;14(6): 5084-5092.[11] Ma Z, Sun X, Xu D, et al. MicroRNA, miR-374b, directly targets Myf6 and negatively regulates C2C12 myoblasts differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;467(4): 670-675.[12] Zhang Y, Yang L, Gao YF, et al. MicroRNA-106b induces mitochondrial dysfunction and insulin resistance in C2C12 myotubes by targeting mitofusin-2. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013; 381(1-2): 230-240.[13] O'Rourke JR, Georges SA, Seay HR, et al. Essential role for Dicer during skeletal muscle development. Dev Biol. 2007; 311(2): 359-368.[14] Wang LY, Wang HY, Ouyang J, et al. Low concentration of lipopolysaccharide acts on MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts and induces proliferation via the COX-2-independent NFkappaB pathway. Cell Biochem Funct, 2009. 27(4): 238-242.[15] Otis JS, Burkholder TJ, Pavlath GK. Stretch-induced myoblast proliferation is dependent on the COX2 pathway. Exp Cell Res. 2005;310(2): 417-425.[16] Wazir R, Luo DY, Dai Y, et al. Expression and proliferation profiles of PKC, JNK and p38MAPK in physiologically stretched human bladder smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;438(3): 479-482.[17] Mok GF, Sweetman D. Many routes to the same destination: lessons from skeletal muscle development. Reproduction. 2011;141(3): 301-312.[18] Yu B, Zhou S, Qian T, et al. Altered microRNA expression following sciatic nerve resection in dorsal root ganglia of rats. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2011;43(11): 909-915.[19] Zhou J, Gao J, Zhang X, et al. microRNA-340-5p Functions Downstream of Cardiotrophin-1 to Regulate Cardiac Eccentric Hypertrophy and Heart Failure via Target Gene Dystrophin. Int Heart J. 2015;56(4): 454-458.[20] Greco S, De Simone M, Colussi C, et al. Common micro-RNA signature in skeletal muscle damage and regeneration induced by Duchenne muscular dystrophy and acute ischemia. FASEB J. 2009;23(10):3335-3346.[21] Cacchiarelli D, Incitti T, Martone J, et al. miR-31 modulates dystrophin expression: new implications for Duchenne muscular dystrophy therapy. EMBO Rep. 2011;12(2):136-141.[22] Crist CG, Montarras D, Buckingham M. Muscle satellite cells are primed for myogenesis but maintain quiescence with sequestration of Myf5 mRNA targeted by microRNA-31 in mRNP granules. Cell Stem Cell. 2012;11(1):118-126.[23] Hou X, Tang Z, Liu H, et al. Discovery of MicroRNAs associated with myogenesis by deep sequencing of serial developmental skeletal muscles in pigs. PLoS One.2012;7(12): e52123.[24] Dmitriev P, Barat A, Polesskaya A, et al. Simultaneous miRNA and mRNA transcriptome profiling of human myoblasts reveals a novel set of myogenic differentiation-associated miRNAs and their target genes. BMC Genomics. 2013;14: 265.[25] Huang Z, Xie X. [Chemerin induces insulin resistance in C2C12 cells through nuclear factor-kappaB pathway-mediated inflammatory reaction]. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2015;31(6): 725-729.[26] Zhao M, Zhang ZF, Ding Y, et al. Astragalus polysaccharide improves palmitate-induced insulin resistance by inhibiting PTP1B and NF-kappaB in C2C12 myotubes. Molecules. 2012;17(6):7083-7092.[27] Kemaladewi DU, de Gorter DJ, Aartsma-Rus A, et al. Cell-type specific regulation of myostatin signaling. FASEB J. 2012;26(4): 1462-1472.[28] Xie Q, Deng Y, Huang C, et al. Chemerin-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in skeletal muscle. J Cell Mol Med. 2015;19(5): 986-995.[29] Tabandeh MR, Hosseini SA, Hosseini M, et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 exerts antidiabetic action on C2C12 muscle cells by leptin receptor signaling pathway. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2017;37(4): 370-378.[30] Bloch SA, Lee JY, Syburra T, et al. Increased expression of GDF-15 may mediate ICU-acquired weakness by down-regulating muscle microRNAs. Thorax. 2015;70(3): 219-228.[31] Kim SH, Hwang JT, Park HS, et al. Capsaicin stimulates glucose uptake in C2C12 muscle cells via the reactive oxygen species (ROS)/AMPK/p38 MAPK pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;439(1): 66-70.[32] Tarabees R, Hill D, Rauch C, et al. Endotoxin transiently inhibits protein synthesis through Akt and MAPK mediating pathways in C2C12 myotubes. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011;301(4): C895-902.[33] Dimchev GA, Al-Shanti N, Stewart CE. Phospho-tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor Bpv(Hopic) enhances C2C12 myoblast migration in vitro. Requirement of PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK pathways. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2013;34(2): 125-136.[34] Gan L, Liu Z, Zhang Z, et al. SOCS2 inhibited mitochondria biogenesis via inhibiting p38 MAPK/ATF2 pathway in C2C12 cells. Mol Biol Rep. 2014;41(2): 627-637.[35] Zbinden-Foncea H, Deldicque L, Pierre N, et al. TLR2 and TLR4 activation induces p38 MAPK-dependent phosphorylation of S6 kinase 1 in C2C12 myotubes. Cell Biol Int. 2012;36(12): 1107-1113.[36] Lee JO, Kim N, Lee HJ, et al. Visfatin, a novel adipokine, stimulates glucose uptake through the Ca2 +-dependent AMPK-p38 MAPK pathway in C2C12 skeletal muscle cells. J Mol Endocrinol. 2015;54(3): 251-262.[37] 范衡宇, 佟超, 孙青原. 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(MAPK)信号通路的研究进展[J]. 动物学杂志, 2002, 37(5): 98-102.[38] Knight JD, Tian R, Lee RE, et al. A novel whole-cell lysate kinase assay identifies substrates of the p38 MAPK in differentiating myoblasts. Skelet Muscle. 2012;2: 5.[39] Ji G, Liu D, Liu J, et al. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase up-regulates NF-kappaB transcriptional activation through RelA phosphorylation during stretch-induced myogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;391(1): 547-551.[40] Dimchev GA, Al-Shanti N, Stewart CE. Phospho-tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor Bpv(Hopic) enhances C2C12 myoblast migration in vitro. Requirement of PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK pathways. J Muscle Res Cell Motil.2013;34(2):125-136. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [3] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [4] | He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping. Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| [5] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [6] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [7] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [8] | Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong. Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| [9] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [10] | Li Hui, Chen Lianglong. Application and characteristics of bone graft materials in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 626-630. |
| [11] | Gao Cangjian, Yang Zhen, Liu Shuyun, Li Hao, Fu Liwei, Zhao Tianyuan, Chen Wei, Liao Zhiyao, Li Pinxue, Sui Xiang, Guo Quanyi. Electrospinning for rotator cuff repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 637-642. |
| [12] | Guan Jian, Jia Yanfei, Zhang Baoxin , Zhao Guozhong. Application of 4D bioprinting in tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 446-455. |
| [13] | Zeng Yuwei, Huang Chuang, Wei Jianguo, Duan Dongming, Wang Le. Tracing transplanted bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in rat calvarial defect by bioluminescence imaging [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(25): 3968-3973. |
| [14] | He Qi, Xu Faya, Li Xiyan, Han Lei, Xiao Yanbing, Tu Jiao. Preparation and sterilization method of human acellular amniotic membrane scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(25): 4028-4033. |
| [15] | Wang Kang, Zhi Xiaodong, Wang Wei. Effect and mechanism of human amniotic epithelial cells on nerve injury repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(25): 4046-4051. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||