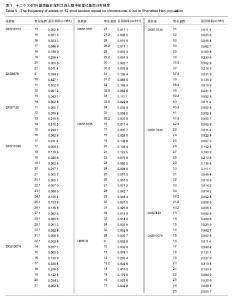
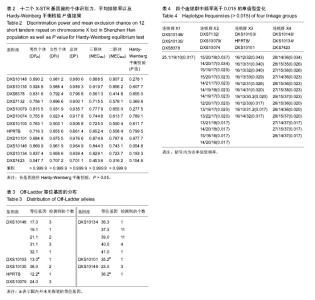
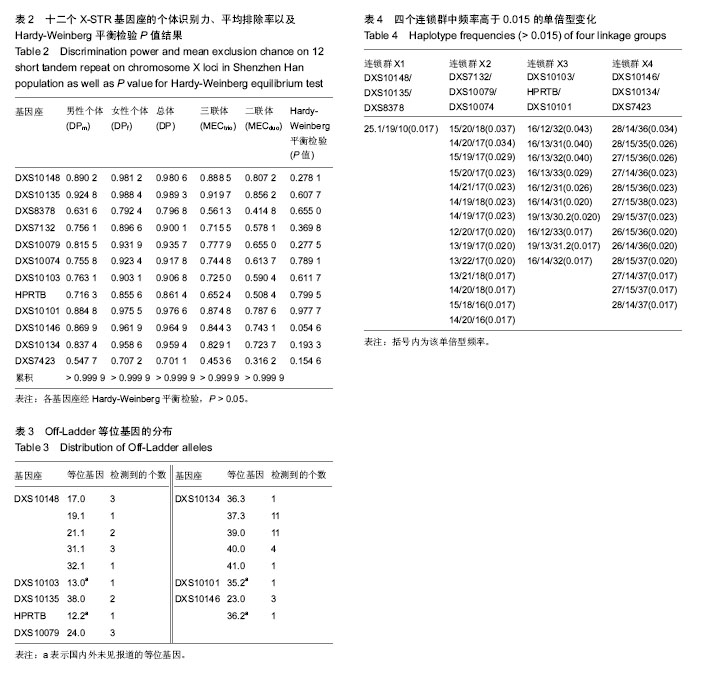
| [1] 李莉,刘俊宏,柳燕,等.常染色体STR和X染色体STR联合应用于姑侄和叔侄关系鉴定[J].中国司法鉴定,2012,62(3):62-66.[2] 唐泽英,陆惠玲,刘秋玲.常染色体及X染色体STR用于同胞鉴定1例[J].中国法医学杂志,2010,25(4):291-292.[3] 阙庭志,赵书民,李成涛.多种遗传标记在同父异母半同胞关系鉴定中的综合应用[J].法医学杂志,2010,26(4):279-300.[4] 林源,赵珍敏,李莉.应用多种 STR 技术对基因嵌合体进行亲权鉴定分析[J].中国司法鉴定,2011,6(6):35-53.[5] 张胤鸣,刘素娟,吴小青,等.X-STR分型用于祖孙关系鉴定1例[J].法医学杂志,2012,28(3):236-237.[6] 刘秋玲,吕德坚,赵虎.X染色体STR荧光复合扩增体系的建立及多态性[J].国际遗传学杂志,2010,33(3):129-133.[7] 张素华,朱如心,李莉,等.Investigator Argus X-12试剂盒在华东汉族人群中的法医学应用评估[J].法医学杂志,2011,27(5): 365-368.[8] 曾祥培,任峥,陈文静,等.Investigator Argus X-12扩增体系在广东汉族人群的遗传多态性[J].中华医学遗传学杂志,2011, 28(2): 230-234.[9] Guo F. Population genetic data for 12 X-STR loci in the Northern Han Chinese and StatsX package as tools for population statistics on X-STR. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2017;26:e1-e8.[10] 任峥,曾祥培,陈文静,等.十二个X染色体STR基因座荧光标记复合扩增体系的法医学应用[J].中山大学学报(医学科学版),2011, 32(1):109-115.[11] Sun M, Zhang Y, Zhang X, et al. Genetic polymorphisms of 12 X STR loci in Shaanxi Han population from China. Leg Med (Tokyo). 2017;26:76-78. [12] Inturri S, Menegon S, Amoroso A, et al. Linkage and linkage disequilibrium analysis of X-STRs in Italian families. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2011;5:152-154. [13] Zidkova A, Capek P, Horinek A, et al. Investigator Argus X-12 study on the population of Czech Republic: comparison of linked and unlinked X-STRs for kinship analysis. Electrophoresis. 2014;35:1989-1992. [14] 叶乾素,唐剑频,陈祖聪,等.12个X染色体短串联重复序列基因座的连锁不平衡和连锁分析[J].中华医学遗传学杂志,2014,31(6): 782-785. [15] Nothnagel M, Szibor R, Vollrath O, et al. Collaborative genetic mapping of 12 forensic short tandem repeat (STR) loci on the human X chromosome. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2012;6(6): 778-784. [16] Walsh PS, Metzger DA, Higushi R. Chelex 100 as a medium for simple extraction of DNA for PCR-based typing from forensic material. Bio Tech. 2013;54(3):134-139. [17] 林敏,刘琼珊,黄以兰,等.福建畲族X染色体12个STR基因座的群体遗传学研究[J].中国计划生育学杂志,2011,19(10): 628-631. [18] Meng HT, Shen CM, Zhang YD, et al. Chinese Xibe population genetic composition according to linkage groups of X-chromosomal STRs: population genetic variability and interpopulation comparisons. Ann Hum Biol. 2017;5:1-8. [19] He G, Li Y, Zou X, Li P, et al. Forensic characteristics and phylogenetic analyses of the Chinese Yi population via 19 X-chromosomal STR loci. Int J Legal Med. 2017. doi: 10.1007/s00414-017-1563-0. [20] Chuncao Deng, Feng, Jienan Li, et al. Forensic parameters of 19 X-STR polymorphisms in two Chinese populations. Int J Legal Med, 2017. doi: 10.1007/s00414-017-1538-1. [21] Shrivastava P, Jain T, Gupta U, et al. Genetic polymorphism study on 12 X STR loci of investigator Argus XSTR kit in Bhil tribal population of Madhya Pradesh, India. Legal Med. 2015; 17:214-217. [22] Elakkary S, Hoffmeister-MLlerich S, SchμLze C, et al. Genetic polymorphisms of twelve X-STRs of the investigator ArgusX-12 kit and additional six X-STR centromere region loci in an Egyptian population sample. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2014;11:26-30. [23] Jeong Eun Sim, Hwan Young Lee, Woo Ick Yang, et al. Population genetic study of four closely-linked X-STR triosin Koreans. Mol Biol Rep. 2010;37:333-337. [24] Liu YS, Meng HT, Mei T, et al. Genetic diversity and haplotypic structure of Chinese Kazak ethnic group revealed by 19 STRs on the X chromosome. Gene. 2017;600:64-69. [25] Pasino S, Caratti S, Del Pero M, et al. Allele and haplotype diversity of X-chromosomal STRs in Ivory Coast. Int J Legal Med. 2011;125:749-752. [26] 吕德坚,刘秋玲.X染色体STR的法医学应用进展[J].中国法医学杂志,2002,17(4):252-255. [27] 吕德坚,陆慧玲.共显性遗传标记亲权排除率的计算[J].中国法医学杂志,2001,16(1):48-50.[28] 任云星,梁景青.X染色体STR基因座的法医学研究进展[J].遗传, 2006,28(10):1316-1320. [29] Phillips C, Ballard D, Gill P, et al. The recombination landscape around forensic STRs: accurate measurement of genetic distances between syntenic STR pairs using HapMap high density SNP data. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2012;6(3): 354-365. [30] Kling D. Curiosities of X chromosomal markers and haplotypes. Int J Legal Med. 2017. doi: 10.1007/s00414-017- 1612-8. [31] Liu OL, Li ZD, Li CT, et al. X chromosomal recombination-A family study analyzing 26 X-STR Loci in Chinese Han three-generation pedigrees. Electrophoresis. 2013;34(20-21): 3016-3022. [32] 吴强,陈丽云,张学君.X染色体上脆性X智力低下基因1敲除模型小鼠针刺长强穴学习记忆及海马CA1区γ-氨基丁酸A型受体α1亚基表达的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(49):7964-7968. |