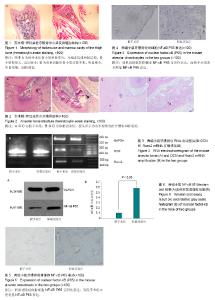
| [1] 肖建德. 实用骨质疏松学[M]. 北京:科学出版社, 2004: 274-276.[2] Pascarella A, Ciatti R, Pascarella F,et al. Treatment of articular cartilage lesions of the knee joint using a modified AMIC technique. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010; 18(4):509-513.[3] Passos JS, Vianna MI, Gomes-Filho IS, et al. Osteoporosis/osteopenia as an independent factor associated with periodontitis in postmenopausal women: a case-control study. Osteoporos Int. 2013;24(4):1275-1283.[4] 刘大勇.VEGF在卵巢切除大鼠实验性牙周炎牙周组织表达的实验研究[D].天津:天津医科大学,2005.[5] Guttridge DC, Mayo MW, Madrid LV, et al. NF-kappaB-induced loss of MyoD messenger RNA: possible role in muscle decay and cachexia. Science. 2000; 289 (5488):2363-2366.[6] Jimi E, Fukushima H. NF-κB signaling pathways and the future perspectives of bone disease therapy using selective inhibitors of NF-κB. Clin Calcium. 2016;26(2):298-304.[7] Huh JE, Jung IT, Choi J, et al. The natural flavonoid galangin inhibits osteoclastic bone destruction and osteoclastogenesis by suppressing NF-κB in collagen-induced arthritis and bone marrow-derived macrophages. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013;698 (1-3): 57-66.[8] Clowes JA, Riggs BL, Khosla S. The role of the immune system in the pathophysiology of osteoporosis. Immunol Rev. 2005;208:207-227.[9] Raisz LG. Pathogenesis of osteoporosis: concepts, conflicts, and prospects. J Clin Invest. 2005;115(12):3318-3325.[10] Weitzmann MN, Pacifici R. Estrogen deficiency and bone loss: an inflammatory tale. J Clin Invest. 2006;116(5): 1186-1194.[11] Haeckel R, Hänecke P. Application of saliva for drug monitoring. An in vivo model for transmembrane transport. Eur J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1996;34(3):171-191.[12] Bettelli E, Korn T, Kuchroo VK. Th17: the third member of the effector T cell trilogy. Curr Opin Immunol. 2007; 19(6): 652-657.[13] Palacios S, Borrego RS, Forteza A. The importance of preventive health care in post-menopausal women. Maturitas. 2005;52 Suppl 1:S53-60.[14] Lai PS, Chua SS, Chan SP. Impact of pharmaceutical care on knowledge, quality of life and satisfaction of postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. Int J Clin Pharm. 2013;35(4): 629-637.[15] Deal C. Potential new drug targets for osteoporosis.Potential new drug targets for osteoporosis. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2009;5(1):20-27.[16] Ogita M, Rached MT, Dworakowski E, et al. Differentiation and proliferation of periosteal osteoblast progenitors are differentially regulated by estrogens and intermittent parathyroid hormone administration. Endocrinology. 2008; 149(11):5713-5723.[17] Liang L, Yu JF, Wang Y, et al. Estrogen regulates expression of osteoprotegerin and RANKL in human periodontal ligament cells through estrogen receptor beta. J Periodontol. 2008; 79(9):1745-1751.[18] Trombelli L, Penolazzi L, Torreggiani E, et al. Effect of hydroxyapatite-based biomaterials on human osteoblast phenotype. Minerva Stomatol. 2010;59(3):103-115.[19] Yao C, Sakata D, Esaki Y, et al. Prostaglandin E2-EP4 signaling promotes immune inflammation through Th1 cell differentiation and Th17 cell expansion. Nat Med. 2009; 15(6):633-640.[20] Hayden MS, Ghosh S. Signaling to NF-kappaB. Genes Dev. 2004;18(18):2195-2224.[21] Bonizzi G, Karin M. The two NF-kappaB activation pathways and their role in innate and adaptive immunity. Trends Immunol. 2004;25(6):280-288.[22] Ghosh S, Karin M. Missing pieces in the NF-kappaB puzzle. Cell. 2002;109 Suppl:S81-96.[23] DiDonato JA, Mercurio F, Karin M. NF-κB and the link between inflammation and cancer. Immunol Rev. 2012;246(1): 379-400. [24] Jimi E, Ghosh S. Role of nuclear factor-kappaB in the immune system and bone. Immunol Rev. 2005;208:80-87.[25] Lee ZH, Kim HH. Signal transduction by receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B in osteoclasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003;305(2):211-214.[26] Soysa NS, Alles N. NF-kappaB functions in osteoclasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;378(1):1-5.[27] Cheng B, Li J, Du J, et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 inhibits osteoclastogenesis by modulating NF-κB and MAPKs pathways. Food Chem Toxicol. 2012;50(5):1610-1615.[28] Chang J, Wang Z, Tang E, et al. Inhibition of osteoblastic bone formation by nuclear factor-kappaB. Nat Med. 2009; 15(6):682-689.[29] Harnish DC. Estrogen receptor ligands in the control of pathogenic inflammation. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2006; 7(11):997-1001.[30] Raisz LG. Pathogenesis of osteoporosis: concepts, conflicts, and prospects. J Clin Invest. 2005;115(12):3318-3325.[31] Urushibara M, Takayanagi H, Koga T, et al. The antirheumatic drug leflunomide inhibits osteoclastogenesis by interfering with receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand-stimulated induction of nuclear factor of activated T cells c1. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50(3):794-804.[32] Yago T, Nanke Y, Ichikawa N, et al. IL-17 induces osteoclastogenesis from human monocytes alone in the absence of osteoblasts, which is potently inhibited by anti-TNF-alpha antibody: a novel mechanism of osteoclastogenesis by IL-17. J Cell Biochem. 2009;108(4): 947-955.[33] Kamiya S, Nakamura C, Fukawa T, et al. Effects of IL-23 and IL-27 on osteoblasts and osteoclasts: inhibitory effects on osteoclast differentiation. J Bone Miner Metab. 2007;25(5): 277-285.[34] Korn T, Bettelli E, Oukka M, et al. IL-17 and Th17 Cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2009;27:485-517.[35] Schwandner R, Yamaguchi K, Cao Z. Requirement of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF)6 in interleukin 17 signal transduction. J Exp Med. 2000;191(7): 1233-1240. |