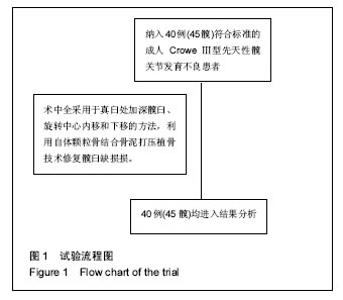
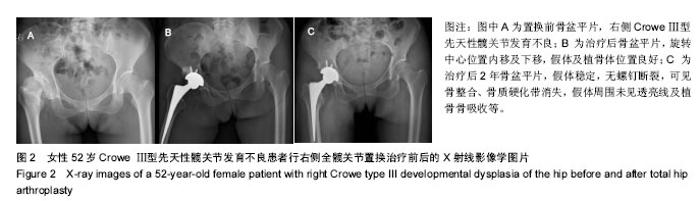
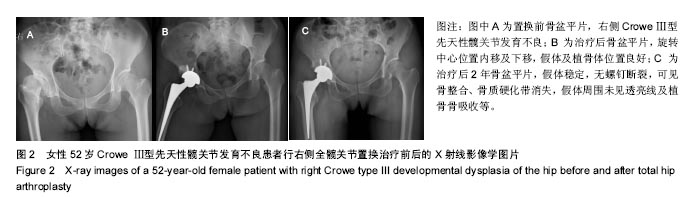
| [1]Crowe JF,Mani VJ,Ranawat CS.Total hip replacement in congenital dislocation and dysplasia of the hip.J Bone Joint Surg Am.1979;61:15.[2]Russotti GM,Harris WH.Proximal placement of the acetabular component in total hip arthroplasty: A long-term follow-up study.J Bone Joint Surg Am.1991;73:587.[3]Dorr LD,Tawakkol S,Moorthy M,et al.Medial protrusio technique for placement of a porous-coated hemispherical acetabular component without cement in a total hip arthroplasty in patients who have acetabular dysplasia.Bone Joint Surg Am.1999;81(1): 83-92.[4]Harris WH.Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures: treatment by mold arthroplasty.An end-result study using a new method of result evaluation.J Bone Joint Surg Am.1969;51:737-755.[5]Westacott D,Pattison G,Cooke S.Developmental dysplasia of the hip. Community Pract.2012;85(11):42-44.[6]Fujii M,Nakashima Y,Sato T,et al.Pelvic deformity influences acetabular version and coverage in hip dysplasia.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2011;469:1735-1742.[7]周建生,王志岩,官健中,等.成人髋关节发育不良髋臼解剖学特征及临床意义[J].中华解剖与临床杂志,2014,19(1):2-6.[8]程亮亮,赵德伟.成人发育性髋关节发育不良的诊治现状[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2016,15(7): 516-520.[9]Rosenstein AD,Diaz RJ.Challenges and solutions for total hip arthroplasty in treatment of patients with symptomatic sequelae of developmental dysplasia of the hip. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ).2011;40(2):87-91.[10]丁良甲,刘晓民,刘莹丽.全髋关节置换修复CroweⅢ和Ⅳ型髋关节脱位:假体位置及其稳定性[J].中国组织工程研究,2015, 19(31):4921-4926.[11]Stans AA,Pagnano MW,Shaughnessy WJ,et al.Results of total hip arthroplasty for Crowe Type III developmental hip dysplasia.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1998;348:149-157.[12]Antoniades J,Pellegrini VD Jr.Cross-sectional anatomy of the ilium: implications for acetabular component placement in total hip arthroplasty.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2012; 470: 3537-3541.[13]Rogers BA,Garbedian S,Kuchinad RA,et al.Total Hip Arthroplasty for Adult Hip Dysplasia.J Bone Joint Surg(Am). 2012;94:1809.[14]Li H,Wang L,Dai K,et al.Autogenous impaction grafting in total hip arthroplasty with developmental dysplasia of the hip.J Arthroplasty.2013;28:637-643.[15]杨帆,杨磊,覃开蓉,等.成人Crowe III-IV型发育性髋关节发育不良的全髋关节置换29例中远期随访报告[J].中国骨与关节杂志, 2016,5(7):499-502.[16]张勇,朱振安,朱明生,等.Crowe Ⅱ/Ⅲ 型髋关节发育不良继发重度骨关节炎髋臼解剖旋转中心重建方法及效果[J].中华关节外科杂志,2016,10(4):393-398.[17]Liu RY,Wang KZ,Wang CS,et al.Evaluation of Medial Acetabular Wall Bone Stock in Patients with Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip Using a Helical Computed Tomography Multiplanar Reconstruction Technique.Acta Radiologica. 2009;50:791-797.[18]肖瑜,张福江,马信龙,等.成人髋关节发育不良不同Crowe分型的三维CT影像学特征[J].中华骨科杂志,2014,34(3):311-316.[19]杨育晖,左建林,高忠礼,等.成人髋关节发育不良髋臼侧影像学评估的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24(15):1390-1394.[20]Bicanic G,Delimar D,Delimar M,et al.Influence of the acetabular cup position on hip load during arthroplasty in hip dysplasia.Int Orthop.2009;33:397-402.[21]Garvin KL,Bowen MK,Salvati EA,et al.long-term results of total hip arthroplasty in congenitial dislocation and dysplasia of the hip.A follow-up note.J Bone Joint Surg (Am).1991;73(9): 1348-1354.[22]Linde F,Jensen J.Socket loosening in arthroplasty for congenital dislocation of the hip.Acta Orthop Scand.1988; 59(3):254-257.[23]刘王卫,杨静,裴福兴,等.颗粒骨打压植骨结合多孔非骨水泥臼杯在AAOS III型髋臼大面积骨缺损翻修中的应用[J].中国骨与关节外科,2012,5(1):22-26.[24]Somford MP,Bolder SB,Gardeniers JW,et al.Favorable survival of acetabular reconstruction with bone impaction grafting in dysplastic hips.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466: 359-365.[25]Spangehl MJ,Berry DJ,Trousdale RT,et al.Uncemented acetabular components with bulk femoral head autograft for acetabular reconstruction in developmental dysplasia of the hip:results at five to twelve years.Bone Joint Surg Am.2001; 83:1484-1489.[26]Kobayashi S,Saito N,Nawata M,et al.Total hip arthroplasty with bulk femoral head autograft for acetabular reconstruction in DDH.Surgical technique.Bone Joint Surg Am.2004;86(1): 11-17.[27]Hartofilakidis G,Karachalios T.Total hip arthroplasty for congenital hip disease. Bone Joint Surg Am.2004;86: 242-250.[28]Hendrich C,Mehling I,Sauer U,et al.Cementless acetabular reconstruction and structural bone-grafting in dysplastic hips.Bone Joint Surg Am.2006;88:387-394.[29]Shinar AA,Harris WH.Bulk structural autogenous grafts and allografts for reconstruction of the acetabulum in total hip arthroplasty. Sixteen-year-average follow-up.Bone Joint Surg Am.1997;79:159-168.[30]Pulido L,Rachala SR,Cabanela ME.Cementless acetabular revision: past, present, and future.Int Orthop.2011;35: 289-298. [31]Deakin DE,Bannister GC.Graft Incorporation After Acetabular and Femoral Impaction Grafting With Washed Irradiated Allograft and Autologous Marrow.J Arthroplasty.2007;22: 89-94.[32]Van der Donk S,Weernink T,Buma P,et al.Rinsing morselized allograft improves bone and tissue ingrowth.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2003;408:302-310. [33]Hannink G,Piek E,Hendriks JM,et al.Biological effects of rinsing morsellised bone graft before and after impaction.Int Orthop.2009;33(3):861-866.[34]Colo E,Rijnen WH,Schreurs BW.The biological approach in acetabular revision surgery: impaction bone grafting and a cemented cup.Hip Int.2015;25(4):361-367.[35]McNamara IR.Impaction bone grafting in revision hip surgery: past, present and future.Cell Tissue Bank.2010;11:57-73. [36]Van der Donk S,Buma P,Sloof TJ,et al.Incorporation of morselized bone graft: a study of 24 acetabular biopsy specimens.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2002;396:131-141. [37]Bavadekar A,Cornu O,Godts B,et al.Stiffness and compactness of morselized graft during impaction: an in vitro study with human femoral heads. Acta Orthop Scand.2001; 72(5):470-476. [38]Dunlop DG,Brewster NT,Madabhushi SP,et al.Techniques to improve the shear strength of impacted bone graft the effect of particle size and washing of the graft.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2003;85(4):639-646. |