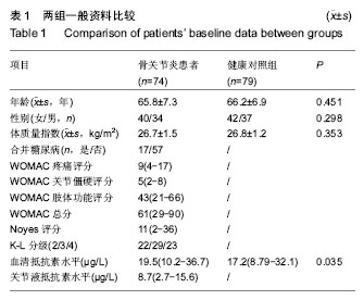
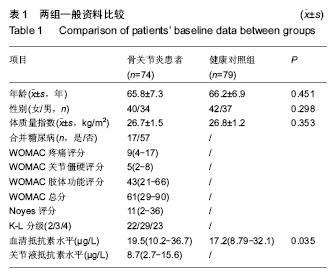
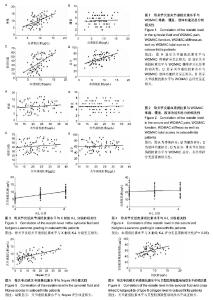
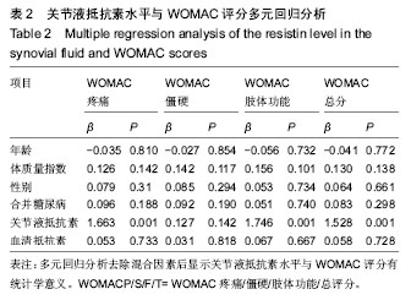
| [1] Goldring MB. The role of the chondrocyte in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum.2000;43(9):1916-1926.[2] Kraus VB,Nevitt M,Sandell LJ.Summary of the OA Biomarkers Workshop 2009-biochemical biomarkers: biology, validation, and clinical studies. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010; 18(6): 742-745.[3] Kraus VB, Burnett B, Coindreau J, et al.Application of biomarkers in the development of drugs intended for the treatment of osteoarthritis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2011;19(5): 515-542.[4] Kang EH, Lee YJ, Kim TK,et al.Adiponectin is a potential catabolic mediator in osteoarthritis cartilage.Arthritis Res Ther.2010;12(6):R231[5] McNulty AL, Miller MR, O'Connor SK,et al.The effects of adipokines On cartilage and meniscus catabolism. Connect Tissue Res.2011;52(6):523-533.[6] Steppan CM, Brown EJ,Wright CM,et al.A family of tissue-specific resistin-like molecules. Proc Natl Acad Scit USA.2001;98(2):502-506.[7] Nogueiras R, Gallego R, Gualillo O,et al. Resistin is expressed in different rat tissues and is regulated in a tissue-and gender-specific manner. FEBS Lett 2003;548 (1-3):21-27.[8] Savage DB, Sewter CP, Klenk ES,et al.Resistin/Fizz3 expression in relation to obesity and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma action in humans. Diabetes.2001;50(10):2199-2202.[9] Bokarewa M,Nagaev I,Dahlberg L,et al.Resistin, an adipokine with potent prointlammtory properties.J Immunol.2005; 174(9): 5789-5795.[10] Zhang Z,Xing X,Hensley G,et al.Resistin induces expression of prointlammatory cytokines and chemokines in human articular chondrocytes via transcription and messenger RNA stabilization. Arthritis Rheum.2010;62(7): 1993-2003.[11] Lee JH, Ort T, Ma K,et al. Resistin is elevated following traumatic joint injury and causes matrix degradation and release of inflammatory cytokines from articular cartilage in vitro.Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2009;17(5):613-620.[12] Filkova M, Liskova M, Hulejova H,et al.Increased serum adiponectin levels in female patients with erosive compared with non-erosive osteoarthritis.Ann Rheum Dis.2009;68(2): 295-296.[13] Perruccio AV,Mahomed NN, ChandranV,et al.Plasma adipokine levels and their association with overall burden of painful joints among individuals with hip and knee osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol.2014;41(2): 334-337.[14] Bellamy N,Buchanan WW,Goldsmith CH,et al. Validation study of WOMAC: a health status instrument for measuring clinically important patient relevant outcomes to antirheumatic drug therapy in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip or knee. J Rheumatol.1988;15(12):1833-1840.[15] Leach RE, Gregg T, Siber FJ. Weight-bearing radiography in osteoarthritis of the knee.Radiology.1970;97(2):265-268.[16] Kellgren JH,Lawrence JS.Radiological assessment of osteoarthrosis.Ann Rheum Dis.1957;16(4):494-502.[17] Engstrom G,Gerhardsson de Verdier M,Rollof J,et al. C-reactive protein, metabolic syndrome and incidence of severe hip and knee osteoarthritis. A population-based cohort study.Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2009;17(2):168-173.[18] Juge-Aubry CE, Somm E, Pernin A, et al. Adipose tissue is a regulated source of interleukin-10.Cytokine.2005;29(6): 270-274.[19] Poonpet T, Honsawek S. Adipokines: Biomarkers for osteoarthritis?.World J Orthop.2014;5(3):319-327.[20] Harvey S, Weisman M, O’Dell J, et al. Chondrex: new marker of joint disease. Clin Chem.1998;44(3):509-516.[21] Blanco FJ.Osteoarthritis year in review 2014:We need more biochemical biomarkers in qualification phase.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014;22(12):2025-2032.[22] Tilg H,Moschen AR.Adipocytokines: Mediators linking adipose tissue, inflammation and immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6(10):772-783.[23] Thommesen L, Stunes AK, Monjo M, et al. Expression and regulation of resistin in osteoblasts and osteoclasts indicate a role in bone metabolism.J Cell Biochem.2006;99(3):824-834.[24] Steppan CM, Bailey ST, Bhat S, et al. The hormone resistin links obesity to diabetes. Nature.2001;409(6818):307-312.[25] Degawa-Yamauchi M,Bovenkerk JE,Juliar BE,et al.Serum resistin (FIZZ3) protein is increased in obese humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.2003;88(11):5452-5455.[26] Choe JY,Bae J,Jung HY,et al.Serum resistin level is associated with radiographic changes in hand osteoarthritis: Cross-sectional study.Joint Bone Spine.2012;79(2):160-165.[27] Massengale M, Lu B, Pan JJ, et al. Adipokine hormones and hand osteoarthritis: Radiographic severity and pain. PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e47860.[28] Schaffler A, Ehling A, Neumann E, et al. Adipocytokines in synovial fluid[J]. JAMA.2003;290(13):1709-1710.[29] Koskinen A,Vuolteenaho K,Moilanen T,et al.Resistin as a factor in osteoarthritis: Synovial fluid resistin concentrations correlate positively with interleukin 6 and matrix metalloproteinasesMMP-1 and MMP-3.Scand J Rheumatol. 2014;43(3):249-253. |