Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (15): 2297-2302.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.15.001
Influencing factors for the prognosis of the patients undergoing reversion metal-on-metal hip arthroplasty for inflammatory pseudotumor
Wang Heng1, 2, Wang Yue1, 3
- 1Department of Orthopedics, the Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Shehong Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shehong 629200, Sichuan Province, China; 3Department of Orthopedics, Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, Chengdu 610000, Sichuan Province, China
-
Revised:2017-03-28Online:2017-05-28Published:2017-06-07 -
Contact:Wang Yue, M.D., Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, the Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; Department of Orthopedics, Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, Chengdu 610000, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Wang Heng, Studying for master’s degree, Physician, Department of Orthopedics, the Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; Department of Orthopedics, Shehong Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shehong 629200, Sichuan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Heng, Wang Yue. Influencing factors for the prognosis of the patients undergoing reversion metal-on-metal hip arthroplasty for inflammatory pseudotumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(15): 2297-2302.
share this article
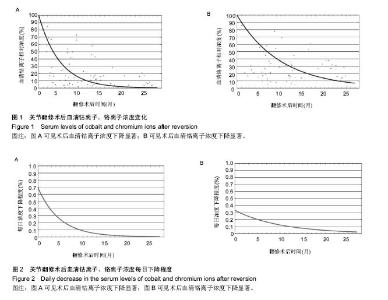
2.1 参与者数量分析 纳入患者81例,按意向性处理分析,全部进入结果分析。 2.2 髋关节置换翻修术中情况 髋关节置换翻修术中按照组织分级评估假体周围损伤情况,其中1级52例,2级23例,3级6例。股骨头表面置换组中有3例存在组织硬化,3例患者存在不同类型髋臼假体松动,全髋关节置换组中5例存在髋臼假体松动。 所有研究对象随访期股骨假体固定均良好。对于股骨头表面置换患者,使用生物型髋臼及股骨假体翻修。对于全髋置换患者,其中35例髋臼假体固定良好,保留髋臼假体,对于出现或者疑似出现骨溶解及假体移位的患者,予以翻修髋臼假体,该组所有患者予以生物性股骨假体翻修。在髋臼翻修病例中,使用钽金属髋臼及聚乙烯衬垫,钴铬合金股骨柄及陶瓷头。 翻修股骨假体参数:表面置换组28 mm 2例,30 mm 1例,36 mm 16例,40 mm 6例;全髋关节置换为28 mm 3例,32 mm 4例,36 mm 28例,40 mm 19例,44 mm 2例。 2.3 临床评分及影像学评估结果 翻修术后所有研究对象平均关节功能评分较术前显著上升,术前平均髋关节功能评分为(43.2±11.6)分,术后6周平均髋关节评分功能为(76.3±9.5)分,经t 检验,差异有显著性意义(t=18.007,P=0.000),提示术后HHS评分高于术前。术后6周13例患者平均髋关节功能评分高于90,40例患者HHS评分高于80,28例患者HHS评分小于79分。术后3个月平均髋关节评分为(82.7±10.4)分,术后12个月平均髋关节功能评分为(88.3±12.6)分。术后影像学评估提示3例患者在术后6周内出现假体脱位,2例出现不同程度无菌性松动,余研究对象假体位置良好。 2.4 血清金属离子浓度 实验室检查提示术前血清钴离子浓度为(8.2±3.4) mg/L,术后12个月下降至(1.2± 0.6) mg/L,经t 检验,差异有显著性意义(t=18.246,P=0.000),提示术后血清钴离子浓度下降显著。术前血清铬离子浓度为(5.3±2.4)mg/L,术后12个月下降至 (1.6±0.4)mg/L,经t 检验,差异有显著性意义(t=9.645,P=0.000),提示术后血清铬离子浓度下降显著。钴铬离子下降至术前水平的50%,半衰期分别为3.2个月和7个月,见图1。在术后1个月内,血清钴离子下降率为0.7%/d,在术后6个月内,为0.2%/d。在术后1个月内,血清铬离子下降率为0.32%/d,在术后6个月内,为1.8%/d,术后1年内下降为0.1%,见图2。术前血清钴离子浓度、铬离子浓度以及钴/铬离子浓度比例均与术后并发症的发生率无关(P1=0.561,P2=0.632,P3=0.448)。"
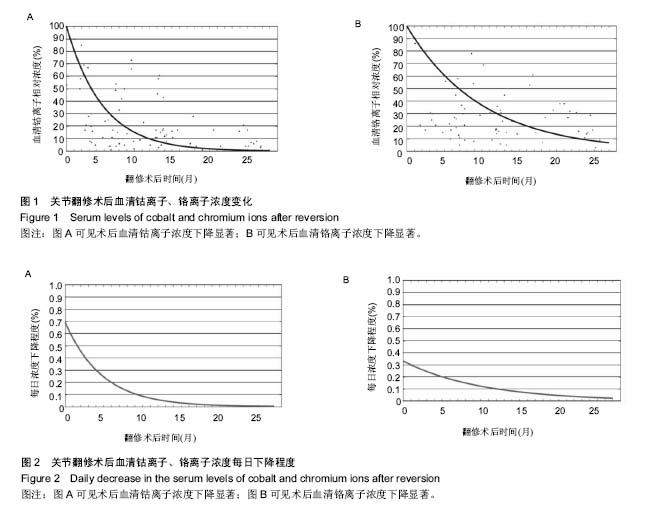
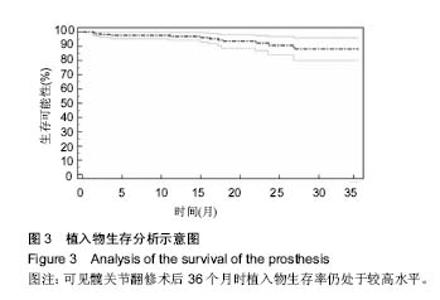
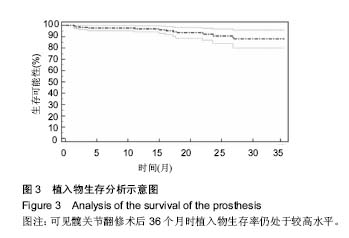
2.5 翻修后并发症发生率及植入物寿命 随访期间,术后并发症发生率为15%,再翻修发生率为6%。3例患者在术后6周内出现假体脱位,其中2例患者脱位程度较轻,在镇静麻醉下闭合复位。1例患者脱位严重复位困难,接受翻修手术。上述3例患者中股骨假体36 mm 1例,40 mm 2例。3例患者出现炎性假瘤复发,接受翻修手术治疗。上述患者术中组织损伤程度评级均为3级。2例患者出现无菌性松动,其中1例接受保守治疗,1例接受翻修手术。2例患者出现浅表伤口感染,接受抗生素治疗。1例患者出现下肢深静脉血栓,1例患者术中损伤动脉组织,接受血管手术治疗。KM生存曲线分析结果提示,术后36个月时植入物生存率为88%,见图3。 2.6 并发症危险因素 危险因素相关性分析结果提示术前假体松动(P=0.012)、MRI检查提示组织硬化(P=0.000)、术中组织损伤分级较高(P=0.049)等因素与翻修术后并发症相关。年龄(P=0.792)、性别(P=0.486)、术前金属离子浓度、初次置换关节类型(P=0.326)及股骨头大小(P=0.622)与术后并发症无关。"
| [1] Sabah SA, Henckel J, Koutsouris S, et al. Are all metal-on-metal hip revision operations contributing to the National Joint Registry implant survival curves? : a study comparing the London Implant Retrieval Centre and National Joint Registry datasets.Bone Joint J. 2016;98-B(1):33-39. [2] Browne JA, Bechtold CD, Berry DJ, et al. Failed Metal-on-Metal Hip Arthroplasties: A Spectrum of Clinical Presentations and Operative Findings. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468(9):2313-2320.[3] Du HR, Cho Y, Lee S, et al. Extent of vertical cementing as a predictive factor for radiolucency in revision total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016; 24(8):2710-2717.[4] Brodén C, Mukka S, Muren O, et al. High risk of early periprosthetic fractures after primary hip arthroplasty in elderly patients using a cemented, tapered, polished stem.Acta Orthop.2015;86(2):169-174.[5] Marks R. Impact of Obesity on Complications following Primary Hip Joint Arthroplasty Surgery for Osteoarthritis. J Arthritis. 2015; s1:3.[6] 金大地. SL非骨水泥假体柄在髋关节翻修术中的应用: 2007全国骨坏死及髋关节疾病学术会议[C].大连:2007.[7] Mahmoud SS, Pearse EO, Smith TO, et al. Outcomes of total hip arthroplasty, as a salvage procedure, following failed internal fixation of intracapsular fractures of the femoral neck: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Bone Joint J.2016;98-B(4):452-460.[8] Schrama JC, Fenstad AM, Dale H, et al. Increased risk of revision for infection in rheumatoid arthritis patients with total hip replacements.Acta Orthop. 2015;86(4):469-476.[9] Lee G W, Park KS, Kim DY, et al. Results of Total Hip Arthroplasty after Core Decompression with Tantalum Rod for Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. Clin Orthop Surg.2016;8(1):38-44.[10] Zhu Y, Chen W, Sun T, et al. Risk factors for the periprosthetic fracture after total hip arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Scand J Surg. 2015;104(3):139-145 [11] 廖威明,康焱,傅明,等.人工髋关节置换术后假体脱位原因分析与处理[J].中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志,2010,2(4):261-265.[12] Garland A, Rolfson O, Garellick G, et al. Early postoperative mortality after simultaneous or staged bilateral primary total hip arthroplasty: an observational register study from the swedish Hip arthroplasty register. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16:77.[13] 金佳,艾红珍. 高龄患者人工髋关节置换术后并发症的观察及护理[J]. 护士进修杂志,2011,26(3):256-258.[14] 孙强,鲁尧,王洪勋,等. 改良记忆合金环抱器治疗髋关节置换术后股骨假体周围骨折的生物力学研究[J].中华创伤杂志, 2015, 31(7):637-640.[15] Lainiala O, Elo P, Reito A, et al. Comparison of extracapsular pseudotumors seen in magnetic resonance imaging and in revision surgery of 167 failed metal-on-metal hip replacements. Acta Orthop.2014;85(5):474-479.[16] Rahman WA, Amenábar T, Hetaimish BM, et al. Outcome of Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty in Management of Failed Metal-on-Metal Hip Arthroplasty.J Arthrop. 2016;31(11): 2559-2563.[17] 曾羿,沈彬,杨静,等. 大直径股骨头金属对金属全髋关节置换术的中期随访结果[J]. 中华骨科杂志, 2016,36(7):385-391.[18] 王华溢,杨重飞,朱锦宇,等. 大直径金属对金属全髋置换假体松动原因分析一例报道[J]. 中华关节外科杂志电子版, 2015, (4): 98-100.[19] Liu W, Wahafu T, Cheng M, et al. Iconography : The influence of obesity on primary total hip arthroplasty outcomes: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2015;101(3):289-296. [20] 甄平,李旭升,田琦,等. 手术治疗双侧人工关节置换术后一侧假体周围感染[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2015, 30(10): 1079-1082.[21] 林谋明,姚小福,毛平,等. 人工关节置换假体周围感染的临床分析[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志,2015(7):1620-1622.[22] 曹建刚,刘军. 关节假体周围感染预防的研究进展[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2015(2):250-253.[23] 吕增亮,葛武. 髋膝关节置换术后假体周围感染的危险因素分析[J].中国临床研究, 2015, 28(11):1496-1497.[24] Menendez ME, Memtsoudis SG, Opperer M, et al. A nationwide analysis of risk factors for in-hospital myocardial infarction after total joint arthroplasty. Int Orthop.2015;39(4): 777-786.[25] Vendittoli PA, Ganapathi M, Roy AG, et al. A comparison of clinical results of hip resurfacing arthroplasty and 28 mm metal on metal total hip arthroplasty: a randomised trial with 3-6 years follow-up. Hip Int.2010;20(1):1-13.[26] Fernandez-Sampedro M, Salas-Venero C, Fariñas-Álvarez C, et al. 26Postoperative diagnosis and outcome in patients with revision arthroplasty for aseptic loosening. BMC Infect Dis. 2015;15:232.[27] Hu D, Yang X, Tan Y, et al. Ceramic-on-Ceramic Versus Ceramic-on-Polyethylene Bearing Surfaces in Total Hip Arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2015;38(4):e331-e338.[28] Nwachukwu BU, Gurary EB, Lerner V, et al. Effect of smoking and soft tissue release on risk of revision after total knee arthroplasty: a case- control study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16:245.[29] Cadossi M, Mazzotti A, Baldini N, et al. New couplings, old problems: Is there a role for ceramic-on-metal hip arthroplasty?. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2016; 104(1):204-209.[30] Goveia VR, Mendoza YQ, Ferreira JA, et al. Profile of hip arthroplasty patients in a teaching hospital. Rev Col Bras Cir. 2015;42(2):106-110.[31] 杨立宇,杨礼庆,付勤. 人工髋关节置换术后感染翻修治疗临床观察[J]. 海南医学,2016,27(14):2295-2299.[32] 郭文彤. 人工髋关节置换术后翻修原因及临床疗效[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2015,19(19):178-180.[33] Sebestyén A, Mester S, Vokó Z, et al. Wintertime surgery increases the risk of conversion to hip arthroplasty after internal fixation of femoral neck fracture. Osteoporos Int. 2015 ;26(3):1109-1117.[34] 曹群英,罗菊英,程娅南. 89例髋关节置换翻修术后患者的护理[J]. 湖北科技学报:医学版, 2015,29(2):147-148.[35] 张利勇. 人工髋关节置换术后翻修的原因分析及假体选择[J]. 中外医疗, 2015, 34 (34):96-98.[36] 郭国栋,樊根涛,郭亭,等. 人工髋关节置换后感染二期翻修中的彻底清创[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(48):7741-7746.[37] 甄平,李旭升,田琦,等. 圆锥形生物翻修柄髋关节置换治疗90岁以上高龄患者Dorr C型股骨髓腔的髋部骨折[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24(18):1633-1638. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Wu Liang, Wang Qiang, Wang Wenbo, Xin Tianwen, Xi Kun, Tang Jincheng, Xu Jingzhi, Chen Liang, Gu Yong. Risk factors for traumatic central cord syndrome underlying with cervical spondylotic myelopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1388-1394. |
| [3] | Xue Yadong, Zhou Xinshe, Pei Lijia, Meng Fanyu, Li Jian, Wang Jinzi . Reconstruction of Paprosky III type acetabular defect by autogenous iliac bone block combined with titanium plate: providing a strong initial fixation for the prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1424-1428. |
| [4] | Zhuang Zhikun, Wu Rongkai, Lin Hanghui, Gong Zhibing, Zhang Qianjin, Wei Qiushi, Zhang Qingwen, Wu Zhaoke. Application of stable and enhanced lined hip joint system in total hip arthroplasty in elderly patients with femoral neck fractures complicated with hemiplegia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1429-1433. |
| [5] | Zhang Lichuang, Xu Hao, Ma Yinghui, Xiong Mengting, Han Haihui, Bao Jiamin, Zhai Weitao, Liang Qianqian. Mechanism and prospects of regulating lymphatic reflux function in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1459-1466. |
| [6] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [7] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [8] | He Shiping, Jia Dazhou, Li Xiaolei, Wang Qiang. Establishment of prediction model of blood transfusion after proximal femoral nail anti-rotation fixation of femoral intertrochanteric fracture in elderly adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 929-933. |
| [9] | Xu Kuishuai, Zhang Liang, Chen Jinli, Ren Zhongkai, Zhao Xia, Li Tianyu, Yu Tengbo. Effect of force line changes on lower limb joints after medial open wedge high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 821-826. |
| [10] | Shao Yangyang, Zhang Junxia, Jiang Meijiao, Liu Zelong, Gao Kun, Yu Shuhan. Kinematics characteristics of lower limb joints of young men running wearing knee pads [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 832-837. |
| [11] | Huang Hao, Hong Song, Wa Qingde. Finite element analysis of the effect of femoral component rotation on patellofemoral joint contact pressure in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 848-852. |
| [12] | Yuan Jing, Sun Xiaohu, Chen Hui, Qiao Yongjie, Wang Lixin. Digital measurement and analysis of the distal femur in adults with secondary knee valgus deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 881-885. |
| [13] | Zhou Jianguo, Liu Shiwei, Yuan Changhong, Bi Shengrong, Yang Guoping, Hu Weiquan, Liu Hui, Qian Rui. Total knee arthroplasty with posterior cruciate ligament retaining prosthesis in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis with knee valgus deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 892-897. |
| [14] | Wang Shaoling, Wang Yanxue, Zheng Yaochao, Yu Shaojun, Ma Chao, Wu Shaoling. Feasibility of ultrasound-guided intra-articular injection in rabbit hip joint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 657-662. |
| [15] | Lu Qinxue, Xu Ning, Yang Yinglan, Han Qianqian, Duanmu Xianyu, Guo Yuwei, Han Qing. Femoroacetabular impingement: strength trainings for nerve-muscle, peripheral muscle and core muscle [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 786-791. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||