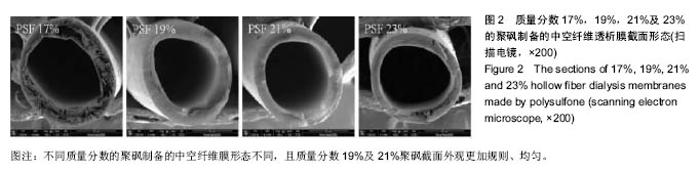
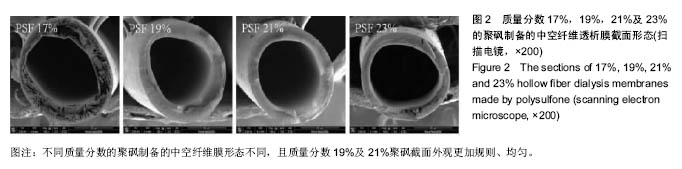
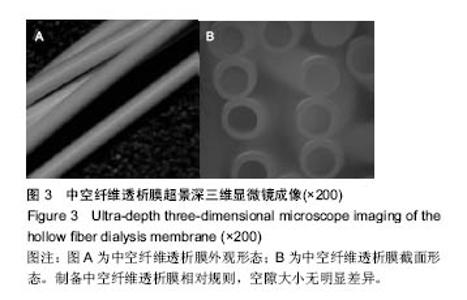
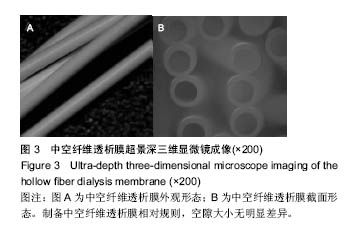
| [1]Manga F, Lim CS, Mangena L, et al. Acute pancreatitis in peritoneal dialysis: a case report with literature review. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;24(1):95-101.[2]郭增革,程博闻,宋俊,等.聚醚砜含量对纤维素/聚醚砜中空纤维血液透析膜结构和性能的影响[J].材料科学与工程学报, 2012, 30(4):567-570.[3]林晓,肖兆群,蒋挺,等.对重症急性胰腺炎患者合并胰腺感染的危险因素分析[J].当代医药论丛,2014,12(13):212-212.[4]曹斌,吕德超,王家宝,等.重症急性胰腺炎早期肠功能障碍与继发胰腺感染的关系[J].中国临床保健杂志,2014,17(5):478-479.[5]张卓,王清华,严华姿.终末期肾脏病维持性血液透析患者并发消化道出血危险因素分析[J].中国医刊,2011,46(5):54-56.[6]吴兴茂,吉凯强,汪海源,等.全肠内营养对急性重症胰腺炎的胰腺坏死性感染的预防作用的研究[J].中国现代医学杂志,2013, 23(4):101-104.[7]肖月,隋宾艳,赵琨.“治未病”理论在慢性肾脏病防治中的应用[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2013,15(9):164-165.[8]肖月,隋宾艳,赵琨.我国终末期肾病现状及透析技术的应用、费用及支付情况分析[J].中国卫生政策研究,2011,4(5):29-33.[9]于金刚,蒋新宇,焦飞鹏,等.血液透析膜的应用及其改性研究进展[J].科技导报,2013,31(5-6):98-105.[10]崔振宇,丁晓莉,李先锋.简易中空纤维超滤膜组件的制备与性能测定[J].大学化学,2013,8(4):48-52.[11]Zhao Longbao,Xu Zhengliang,Liu Min,et al. Preparation and characterization of PSf hollow fiber membrane from PSf-HBPEPEG400- NMP dope solution. J Membr Sci. 2014; 454:184-192.[12]Zhao LB, Liu M, Xu ZL, et al. PSF hollow fiber membrane fabricated from PSF-HBPE-PEG400-DMAc dope solutions via reverse thermally induced phase separation (RTIPS) process. Chem Eng Sci. 2015;137:131-139.[13]雷晓慧,丁雪佳,何金迎.添加剂对聚砜膜结构和性能的影响[J].化工进展,2013,32(8):1866-1886[14]郭增革,程博闻,宋俊.聚醚砜含量对纤维素/聚醚砜中空纤维血液透析膜结构和性能的影响[J].材料科学与工程学报, 2012,30(4): 567-585.[15]魏宇辰,翟庆洲.MCM-41固载牛血清白蛋白复合材料的制备、表征及发光[J].人工晶体学报,2012,41(6):1614-1618.[16]潘献辉,王晓楠,张艳萍.超滤膜截留性能检测用基准物质研究与应用进展[J].膜科学与技术.2013,33(2):104-108,124.[17]Zhang LZ. Heat and mass transfer in a randomly packed hollow fiber membrane module: a fractal model approach. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2011;54(13-14): 2921-2931.[18]兰薇,周结学,许风英.高通量血液透析与常规血液透析的临床疗效比较研究[J].中国医药指南,2013,15(2):262-263. [19]沙广琴.高通量血液透析与常规血液透析、血液透析滤过的透析效果比较[J].中国保健营养,2013(4):1617-1618.Liu M, Wei YM, Xu ZL, et al. Preparation and characterization of polyethersulfone microporous membrane via thermally induced phase separation with low critical solution temperature system. J Membr Sci. 2013;437:16 |