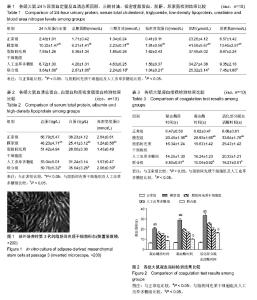
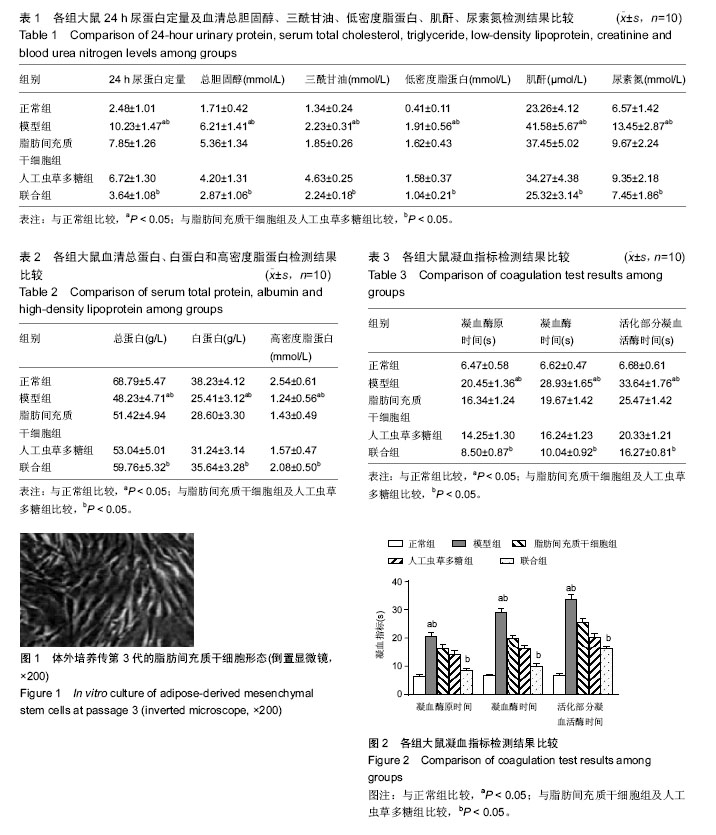
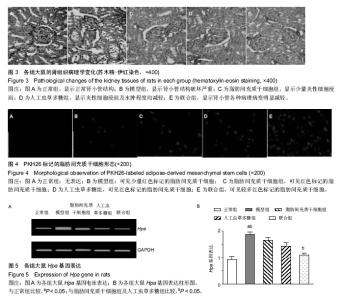
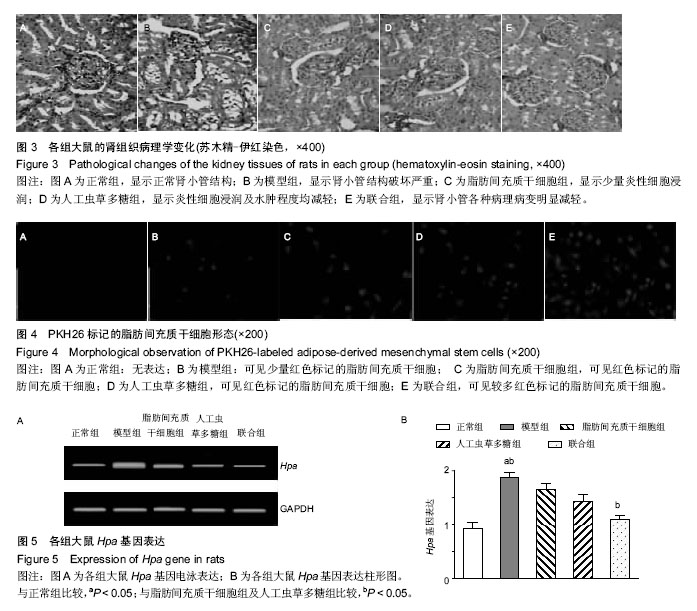
| [1] 刘娇娇,徐虹,戴如凤,等.血管生成素样蛋白3参与肾病综合征高脂血症发生的初步探索[J].中华肾脏病杂志, 2015, 31(9): 669-673.[2] 魏立新,邹和群,詹林达.HMG-CoA还原酶抑制剂对肾病综合征大鼠肝脏低密度脂蛋白受体表达的影响[J].华中科技大学学报(医学版),2007,36(2):265-268.[3] 陈子安,隋昕,聂志勇,等.汞中毒致大鼠肾病综合征模型的建立[J].中国急救医学,2015,35(5): 449-454.[4] 王静,吕洪财.补肾健脾方对肾病综合征模型大鼠性腺保护的研究[J].泰山医学院学报,2015,36(8):859-862.[5] 田云,卢向阳,何小解,等.儿茶素微胶囊对肾病综合征大鼠肾功能的影响[J].中国临床康复,2004,8(33):7592-7594.[6] 胡剑卓,邱细敏,江建锋.人工虫草多糖对阿霉素致肾病综合征大鼠的作用研究[J].中医临床研究,2015,7(20):6-8.[7] 刘柳,高红宇,何晓峰,等.阿托伐他汀抑制Rac1减轻嘌呤毒素氨基核苷诱导的大鼠肾病综合征[J].医学分子生物学杂志,2015,12(5):249-253.[8] Cohen C, El-Karoui K, Alyanakian MA,et al.Light and heavy chain deposition disease associated with CH1 deletion.Clin Kidney J. 2015;8(2):237-239. [9] 王静,王娟.补肾健脾方对肾病综合征模型大鼠性腺功能及病理结构的影响[J].泰山医学院学报,2015,36(4): 384-387.[10] 李丽,王长山,康晓明,等.肾病综合征大鼠血清IL-4和IL-12的动态变化及其意义[J].黑龙江医药科学,2015,38(2): 12-14.[11] 宣伟东,唐大海,范正平.百瑞口服液对阿霉素肾病大鼠综合征的治疗作用[J].中国药业, 2014,23(9):8-10.[12] Bautista J, Bella A, Chaudhari A, et al. Advanced chronic kidney disease in non-valvular atrial fibrillation: extending the utility of R2CHADS2 to patients with advanced renal failure. Clin Kidney J. 2015;8(2):226- 231. [13] Wang Y, Yin HP, Lv XB, et al. Protection of chronic renal failure by a polysaccharide from Cordyceps sinensis. Fitoterapia. 2010;81(5):397-402.[14] 葛斌,谢梅林,顾振纶,等.肾炎灵对阿霉素肾病大鼠肾脏的保护作用[J].苏州大学学报(医学版),2009,29(2):252-255.[15] 郑京,陈雪兰,黄璐,等.骨髓间充质干细胞对阿霉素肾病大鼠的治疗作用及黏着斑激酶的影响[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2013,7(22):10148-10153.[16] 周芳,张梅,李龙珠,等.冬虫夏草提取液对大鼠实验性肾脏缺血/再灌注后VEGF及肾功能影响[J].浙江临床医学, 2015, 17(10):1678-1680.[17] 江雪莲,李敏,李莉,等.冬虫夏草提取液对肾移植大鼠肾缺血再灌注损伤免疫调节作用的影响[J].国际中医中药杂志,2015,37(10):904-908.[18] Lin CY, Ku FM, Kuo YC, et al. Inhibition of activated human mesangial cell proliferation by the natural product of Cordyceps sinensis (H1-A): an implication for treatment of IgA mesangial nephropathy. J Lab Clin Med. 1999;133(1):55-63. [19] 李蓉,孙书娟,江晓路.虫草多糖的分离纯化及结构鉴定[J].中国药师,2015,18(3): 407-409,419.[20] 刘雪芹,于湄,张燕,等.人工虫草多糖对2型糖尿病小鼠胰岛素抵抗的影响[J].医药导报, 2011,30(1):5-8.[21] 王蕾,于荣敏,张辉,等.人工培养蛹虫草多糖的分离纯化及其结构的初步研究[J].中国生化药物杂志,2003,24(1): 23-25.[22] Kim HS, Kim JY, Kang JS, et al. Cordlan polysaccharide isolated from mushroom Cordyceps militaris induces dendritic cell maturation through toll-like receptor 4 signalings. Food Chem Toxicol. 2010;48(7):1926-1933.[23] 龚晓健,李绍平.人工虫草多糖对小鼠免疫功能的影响[J].中国药科大学学报,2000,31(1):53-55.[24] Chang Y, Hsu WH, Lu WJ, et al. Inhibitory Mechanisms of CME-1, a Novel Polysaccharide from the Mycelia of Cordyceps sinensis, in Platelet Activation. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2015;16(5):451-461.[25] 唐惠玲,陈涛,王莹,等.虫草多糖荧光标记的方法学研究[J].药学与临床研究,2010,18(3):279-281.[26] 宾文,宋丽艳,于荣敏,等.人工培养蛹虫草多糖的抗炎及免疫作用研究[J].时珍国医国药,2003,14(1): 1-2.[27] Wang Y, Liu D, Zhao H, et al. Cordyceps sinensis polysaccharide CPS-2 protects human mesangial cells from PDGF-BB-induced proliferation through the PDGF/ERK and TGF-β1/Smad pathways. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2014;382(2): 979-988.[28] Chen W,Zhang W,Shen W,et al.Effects of the acid polysaccharide fraction isolated from a cultivated Cordyceps sinensis on macrophages in vitro. Cell Immunol. 2010;262(1): 69-74.[29] 王琴,侯晓强,崔向军,等.黄芪白花蛇舌草汤对阿霉素肾病大鼠的治疗作用[J].长春中医药大学学报,2015,31(1): 6-9.[30] 杨智,向爱国,金红,等.中药复方对肾病综合征大鼠肾功能影响的实验研究[J].湖南中医杂志,2007,23(2):82-83.[31] 任健,张倩落,郑莉.人工虫草多糖对免疫低下小鼠免疫功能的影响[J].第四军医大学学报,2007,28(21):1967- 1969.[32] 张芬芳,王喜栋,范焕芳,等.柴苓归芪汤加蚓激酶对实验性肾病综合征大鼠肾功能的保护作用[J].中西医结合学报, 2005,3(4):294-298.[33] 姜燕.黄芪甲苷孵育的人脂肪源性干细胞对急性肾损伤模型小鼠的影响及机制研究[D].上海中医药大学,2014.[34] 高加胜.温敏性氯化壳聚糖水凝胶增强脂肪间充质干细胞治疗急性肾损伤的疗效[J].福建医科大学,2012.[35] 胡丹.人脂肪源间充质干细胞对顺铂致小鼠急性肾损伤的影响[J].新乡医学院,2012.[36] 孙雅娟,李华,刘娜,等.Apical bud上皮诱导脂肪间充质干细胞向成牙本质样细胞分化的研究[J].中华老年口腔医学杂志,2015,13(1):7-11.[37] Guo J, Zou Y, Wu Z, et al. Protective effects of mesenchymal stromal cells on adriamycin-induced minimal change nephrotic syndrome in rats and possible mechanisms. Cytotherapy. 2014;16(4): 471-484. [38] Dellepiane S, Ribaldone DG. Pathogenesis of nephrotic syndrome after hematopoietic stem cell transplantations. Minerva Med. 2016;107(3):183-184. [39] Wong E, Lasica M, He SZ, et al. Nephrotic syndrome as a complication of chronic graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic haemopoietic stem cell transplantation. Intern Med J. 2016;46(6):737-341. [40] Fuyama M, Ikeda H, Isoyama K. [A case of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis with nephrotic syndrome after hematopoietic stem cell transplantatation for aplastic anemia]. Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi. 2013;55(1): 83-89. [41] Beyar Katz O, Kruzel Davila E, Zuckerman T, et al. Nephrotic syndrome after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a single center experience. Minerva Med. 2015;106(6):355-357. [42] Beyar-Katz O, Davila EK, Zuckerman T, et al. Adult Nephrotic Syndrome after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: Renal Pathology is the Best Predictor of Response to Therapy. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016;22(6):975-981. [43] Dhakal B, Singavi A, Cohen EP, et al. Chronic GVHD and concurrent new-onset nephrotic syndrome in allogeneic transplant recipients. Incidence, pattern and therapeutic outcomes. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2015; 50(3):449-451. |