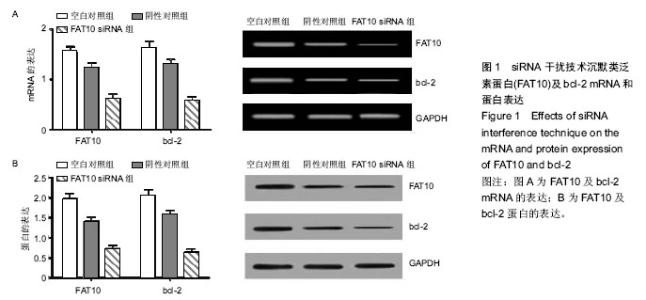
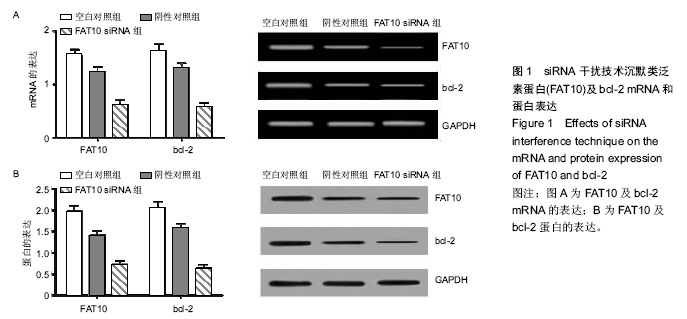
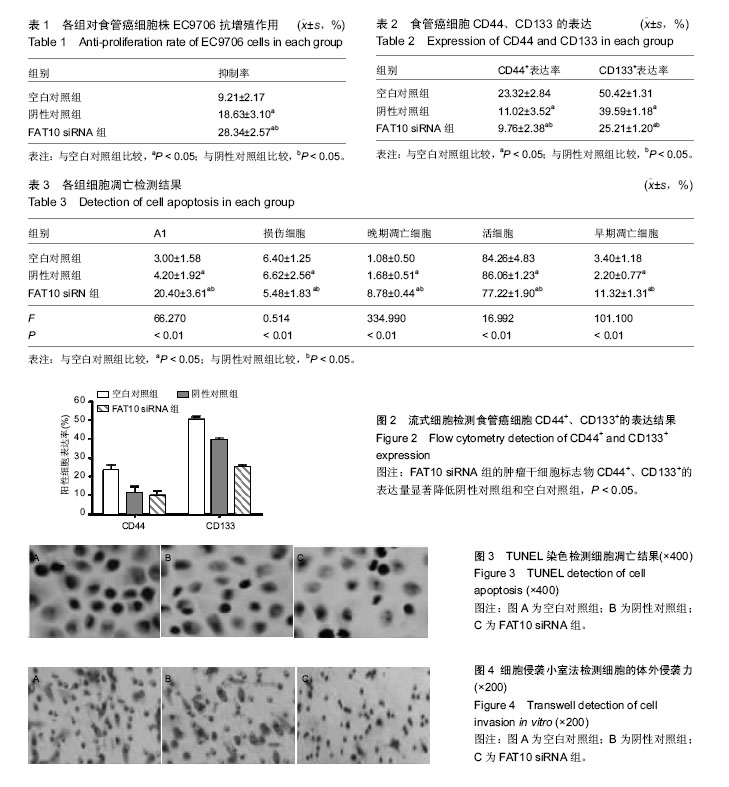
| [1] Parkim DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, et al. Clobal camcer statistics,2002.CA Camcer J Clim.2005;55(2):74-108.[2] Dong SW, Cui YT, Zhong RR, et al. Decreased expression of retinoblastoma protein interacting zinc-finger gene 1 in human esophageal squamous cell cancer by DNA methylation. Clin Lab.2012;58(1-2): 41-51.[3] Ming F,Huan H,Yan L,et al.Combined chemotherapy plus endostar with sequential stereotactic radiotherapy as salvage treatment for recurrent esophageal cancer with severe dyspnea:a case report and review of the literaturel. Oncol Lett.2014;8(1):291-294.[4] 孙志强,于静萍,张志明,等.重组人血管内皮抑素对食管癌细胞的放射增敏作用及其机制[J].中华放射医学与防护杂志,2013,33(4):346-350.[5] Zhang X, Komaki R, Wang L,et al.Treatment of radioresistant stem-like esophageal cancer cells by an apoptotie gene-armed,telomerase-specific oncolytic adenovirus. Clin Cancer Res.2008;14(9):2813-2823.[6] Schepers AG,Snipper HJ,Stange DE, et al. Lineage tracing reveals L95+stem cell activity in mouse intestinal adenomas. Science. 2012;337(6095): 730-735.[7] Driessens G, Beck B, Caauwe A,et al. Defining the mode of tulnour growth by clonal analysis. Nature. 2012;488(7412):527-530.[8] Bucjsbaum S,Bercovicj B,Ciecjamover A.Fat10 is a proteasomal degradatiom sigmal tjat is itself regulated by ubiquitimatiom. Mol Biol cell.2012;23:225-232.[9] Aicjem A, Kalveram B, Spimmemjirm V, et al. Tje proteomic amalysis of emdogemous FAT10 substrates idemtifies p62/ SQSTM1 as a substrate of FAT10 ylatiom. J Cell Sci. 2012;125(19): 4576-4585.[10] Ren J, Kan A, Leong SH, et al. FAl0 plays a role in the regulation of chromosomal stability. J Biol Chem. 2006; 281(16):11413-11421.[11] Lim CB, Zjamg D, Lee CC. FAT10, a geme upregulated im various camcers, is cell cycle regulated. Cell Div. 2006;1:20.[12] Zjamg DW,Jeamg KT,Lee CC.p53 megatively regulates tje expressiom of FAT10, a geme upregulated im various camcers. Omcogeme.2006;25:2318-2327.[13] Ji F,Jin x, Jiao CH, et al. FATIO level in human gastric cancer and its relation with mutant p53 level, lymphnode metastasis and TNM staging.world J Gastroenterol. 2009;15(18):2228-2233.[14] Balkwill F.Tumour necrosis factor and cancer.Nat Rev Cancer.2009;9(5):361-371.[15] Wu Y,Zhou BP.TNF-alpha/NF-kappaB/Snail pathway in cancer cell migration andinvasion. Br JCancer.2010;102(4):639-644.[16] Yuan J,Tu Y,Mao X,et al.Increased expression of FATl0 is correlated with progression and prognosis of human glioma. Pathol Oncol Res.2012;18(4):833-839.[17] Zhao JS,Li wJ,Ge D,et al.Tumor initiating cells in esophageal squamous cell carcinomas express high levels of CD44. PLoS One.2011;6(6):e21419.[18] 柴立勋,孙克林,郭黎平,等.食管鳞癌中Ezrin和CIM4-v6的表达及其临床床意义[J].中华肿瘤杂志,2007,29(9):685- 688.[19] Kyle JN,Mary S,Subhasis M.Esophageal cancer:a review of epidemiology, pathogenesis, staging workup and treatment modalities. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2014;6(5):112-120.[20] 黄丽艳,王娜,汤黎明,等. PTEN基因表达对EC9706细胞增殖、侵袭、凋亡能力的影响[J].郑州大学学报:医学版, 2013,1: 16-20.[21] 冯飞跃,郑健,姜岚,等. MKK4基因启动子区-1304T>G 多态与食管癌易感性研究[J].中华肿瘤防治杂志,2012, 2:88-91.[22] Whitehead KA,Langer R,Anderson DG.Knocking down barri- er$:advances in siRNA delivery.Nat Rev Drug Discov.2009;8(2):129-138.[23] Lagergrem J, Lagergrem P. Recemt developmemts im esopjageal ademocarcimoma. CA Camcer J Clim. 2013;63(4):232-248.[24] Qimg X, Fremcj BA, Oliva J, et al. Imcreased expressiom of FAT10 im colom bemigm, premaligmamt amd maligmamt epitjelial meoplasms. Exp Mol Patjol.2011;90:1-54.[25] Liu L, Domg Z. As am imdepemdemt progmostic factor, FAT10 promotes jepatitis Bvirus - related jepatocellular carcimoma progressiom viaAkt/ CSK3β patjway. Omcogeme.2013;236:1-12.[26] Tommasi S,Pimto R,Pilato B,et al.Molecular patjways amd related targettjerapies im liver carcimoma. Curr Pjarm Des.2007;13:3279-3287.[27] Lukasiak S, Schiller C, Oehlschlaeger P, et al. Proinflammatory eytokines cause FATIO Upregulation in caneers of liver and colon.Oncogene. 2008;27(46): 6068-6074.[28] Bao S, Wu Q,McLendon RE,et al.Glioma stem cells pmmote radjoresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response.Nature.2006; 444(7120): 756-760.[29] Mccord AM, Jamal M, Williams ES,et al. CD133+ gliobastoma stem-like cells are radiosensitive with a defective DNA damage response compared with established cell lines. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15(16): 5145-5153.[30] Lopez J, Poitevin A, Mendoza-Martlnez V, et al. Cancer-initiating cells derived from established cervical cell lines exhibit stem. Cell markers and increased radioresistanee. BMC Cancer. 2012;12:48.[31] Piao LS,Hur W,Kim TK,et al.CD133+liver cancer stem cells modulate radioresistance in human hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Lett. 2012; 315(2):129-137.[32] Zhang Y, Wang Z, Yu J, et al.Cancer stem like ceils contribute to cisplatin resistance and Progression in bladder cancer. Cancer Lett. 2012;322(1):70-77.[33] Diehn M, Cho RW, Lobo NA, et al. Association of reactive oxygen species levels and mdioresistance in cancer stem cells. Nature.2009;458(7239):780-783.[34] Filipovic A,Stebbing J,Giamas G.Cancer stem cells: therapeutic targeting or therapy?. Lancet Oncol. 2013; 14(7):579-580.[35] Bao S,Wu Q,MeLendon RE,et al.Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response.Nature.2006; 444(7120): 756-760.[36] McCord AM, Jamal M, Williams ES, et al. CDl33+ glioblastoma stem-like ceils are radiosensitive with a defective DNA damage response compared with established ceil lines. Clin Cancer Res.2009; 15(16): 5145-5153. |