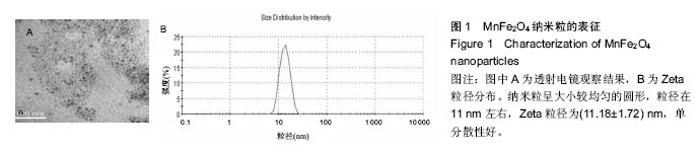
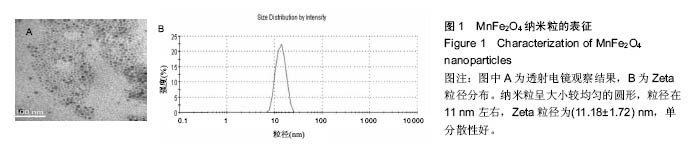
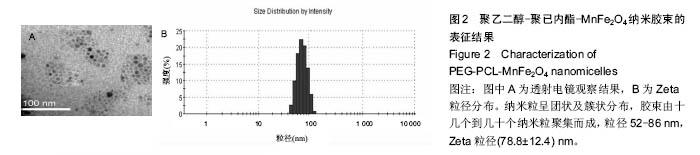
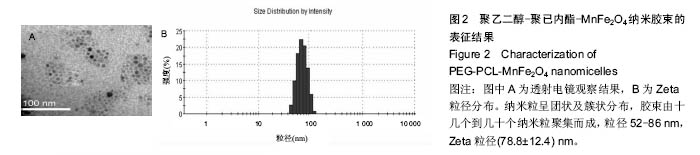
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (47): 7090-7096.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.47.014
Previous Articles Next Articles
Synthesis of MnFe2O4 nanomicelles and its application in magnetic resonance molecular imaging
- 1Department of Radiology, Chongqing Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Chongqing 400021, China; 2Department of Radiology, Xinqiao Hospital, Third Military Medical University of PLA, Chongqing 400037, China
-
Received:2016-08-21Online:2016-11-18Published:2016-11-18 -
Contact:Zhou Pei-hua, Chief physician, Department of Radiology, Chongqing Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Chongqing 400021, China -
About author:Yang Hua, M.D., Associate chief physician, Department of Radiology, Chongqing Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Chongqing 400021, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81071197, 81501521; Frontier and Applied Basic Research Projects in Chongqing, No. cstc2015jcyjA1338
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Hua, Gong Ming-fu, Zou Li-guang, Zhang Song, Shu Tong-sheng, Zhou Pei-hua. Synthesis of MnFe2O4 nanomicelles and its application in magnetic resonance molecular imaging[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(47): 7090-7096.
share this article
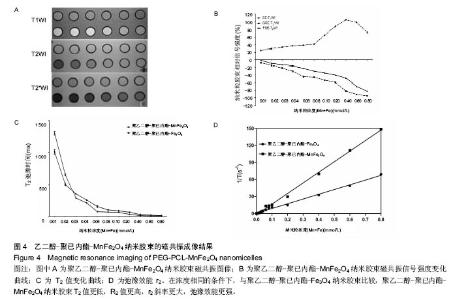
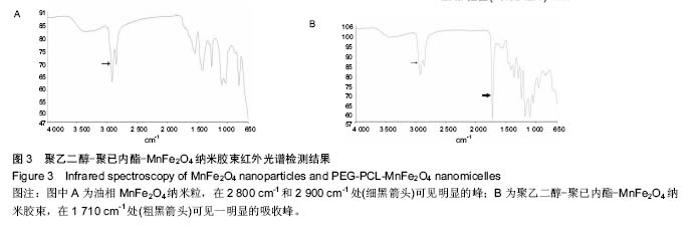
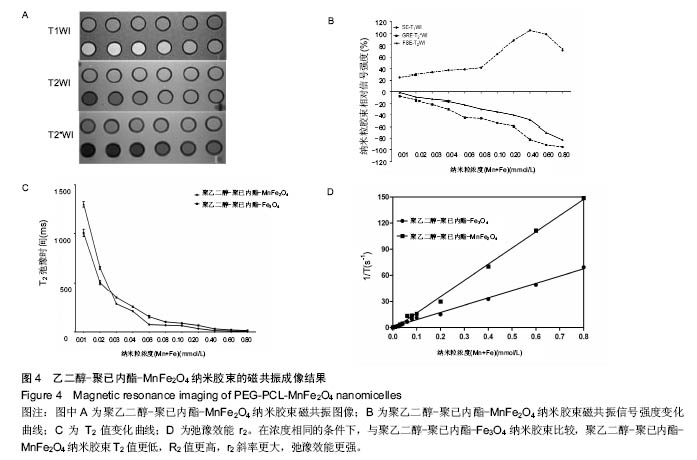
2.3 PEG-PCL-MnFe2O4纳米胶束的磁共振成像结果 PEG-PCL-MnFe2O4和PEG-PCL-Fe3O4两种纳米胶束溶液的磁共振信号改变,见图4所示。两种纳米胶束的信号变化趋势相似:①当铁浓度低于0.4 mmol/L时,T1WI信号强度逐渐升高;当铁浓度高于0.4 mmol/L后,T1WI信号强度开始降低;②T2WI信号强度随着铁浓度的增加逐渐下降,以T2*WI信号强度改变更明显(P < 0.05)。T2 mapping显示:随着铁浓度的增加T2值逐渐降低,且PEG-PCL-MnFe2O4的T2值降低较PEG-PCL- Fe3O4更明显,在浓度相同的条件下,与PEG-PCL- Fe3O4比较,PEG-PCL-MnFe2O4 T2值更低,R2值更高,r2斜率更大,弛豫效能更强。"
| [1]Sheng Y,Liao LD,Thakor NV,et al. Nanoparticles for molecular imaging.J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2014; 10(10):2641-2676. [2]Weissleder R.Molecular Imaging: Exploring the Next Frontier.Radiology.1999;212(3): 609-614. [3]Zhang Y,Zhang B,Liu F,et al.In vivo tomographic imaging with fluorescence and MRI using tumor-targeted dual-labeled nanoparticles.Int J Nanomedicine.2014;9:33-41. [4]Gao X,Cui Y,Levenson RM,et al.In vivo cancer targeting and imaging with semiconductor quantum dots.Nat Biotechnol.2004;22(8):969-976. [5]Jin R,Lin B,Li D,et al.Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for MR imaging and therapy: design considerations and clinical applications.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2014;18:18-27. [6]Rogers JL,Tarrant T,Kim JS.Nanoparticle-based diagnostic imaging of inflammation in rheumatic disease.Curr Rheumatol Rev.2014;10(1):3-10. [7]Liu S,Jia B,Qiao R,et al.A novel type of dual-modality molecular probe for MR and nuclear imaging of tumor: preparation, characterization and in vivo application. Mol Pharm.2009;6(4):1074-1082. [8]Lee JH,Huh YM,Jun YW,et al.Artificially engineered magnetic nanoparticles for ultra-sensitive molecular imaging.Nat Med.2006;13(1):95-99. [9]Kanagesan S,Aziz SB,Hashim M,et al.Synthesis, characterization and in Vitro evaluation of manganese ferrite(MnFe2O4) nanoparticles for their biocompatibility with murine breast cancer cells(4T1). Molecules.2016;21(3):312-321. [10]Safarik I,Horska K,Pospiskova K,et al.Magnetic techniques for the detection and determination of xenobiotics and cells in water.Anal Bioanal Chem.2012; 404(4):1257-1273. [11]Peng Y,Wang Z,Liu W,et al.Size- and shape-dependent peroxidase-like catalytic activity of MnFe2O4 nanoparticles and their applications in highly efficient colorimeteric detection of target cancer cells.Dalton Trans.2015;44(28):12871-12877. [12]龚明福,杨华,邹利光.锰对比剂磁共振成像研究进展[J].中国医学影像技术,2013, 29(1):142-145. [13]Choi D,Han A,Park JP,et al.Fabrication of MnxFe1-xO colloidal solid solution as a dual magnetic-resonance-contrast agent.Small. 2009;5(5): 571-573. [14]Im GH,Kim SM,Lee DG,et al.Fe(3)O(4)/MnO hybrid nanocrystals as a dual contrast agent for both T(1)- and T(2)-weighted liver MRI.Biomaterials. 2013;34(8): 2069-2076. [15]Felton C,Karmakar A,Gartia Y,et al.Magnetic nanoparticles as contrast agents in biomedical imaging: recent advances in iron- and manganese-based magnetic nanoparticles.Drug Metab Rev. 2014;46(2): 142-154. [16]Chen W,Lu F,Chen CC,et al.Manganese-enhanced MRI of rat brain based on slow cerebral delivery of manganese(II) with silica-encapsulated Mn x Fe(1-x)O nanoparticles.NMR Biomed.2013;26(9):1176-1185. [17]Li Z,Wang SX,Sun Q,et al.Ultrasmall manganese ferrite nanoparticles as positive contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging.Adv Healthc Mater. 2013; 2(7):958-964. [18]Li T,Shi T,Li X,et al.Effects of Nano-MnO2 on dopaminergic neurons and the spatial learning capability of rats.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2014; 11(8):7918-7930. [19]Praveen P,Viruthagiri G,Mugundan S,et al.Sol-gel synthesis and characterization of pure and manganese doped TiO2 nanoparticles—a new NLO active material. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2014;120: 548-557. [20]Ereath BA,Nazeer SS,Fernandez FB,et al.An aqueous method for the controlled manganese (Mn(2+)) substitution in superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for contrast enhancement in MRI.Phys Chem Chem Phys.2015; 17(6):4609-4619. [21]Taresco V,Francolini I,Padella F,et al.Design and characterization of antimicrobial usnic acid loaded-core/shell magnetic nanoparticles.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appel. 2015;52:72-81. [22]Douglas FJ,MacLaren DA,Tuna F,et al.Formation of octapod MnO nanoparticles with enhanced magnetic properties through kinetically-controlledthermal decomposition of polynuclear manganese complexes. Nanoscale.2014;6(1):172-176. [23]Joshi HM,Lin YP,Aslam M,et al.Effects of shape and size of cobalt ferrite nanostructures on their MRI contrast and thermal activation.J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces.2009;113(41):17761-17767. [24]Hu Y,Jiang X,Ding Y,et al.Preparation and drug release behaviors of nimodipine- loaded poly (caprolactone)-poly (ethylene oxide)-polylactide amphiphilic copolymer nanoparticles. Biomaterials. 2003;24(13):2395-2404. [25]Yang Hua,Zou Li-guang,Zhang Song, et al.Feasibility of MR imaging in evaluating breast cancer lymphangiogenesis using Polyethylene glycol-GoldMag nanoparticles.Clin Radiol. 2013; 68(12):1233-1240. [26]Lu J,Ma S,Sun J,et al.Manganese ferrite nanoparticle micellar nanocomposites as MRI contrast agent for liver imaging.Biomaterials.2009;30(15):2919-2928. [27]Yang H,Zhang C,Shi X,et al.Water-soluble superparamagnetic manganese ferrite nanoparticles for magnetic resonance imaging.Biomaterials. 2010; 31(13):3667-3673. [28]Naidek KP,Bianconi F,Da Rocha TC,et al.Structure and morphology of spinel MFe2O4(M= Fe, Co, Ni) nanoparticles chemically synthesized from heterometallic complexes.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2011;358(1):39-46. [29]Salatin S,Maleki DS,Yari KA.Effect of the surface modification, size, and shape on cellular uptake of nanoparticles.Cell Biol Int.2015;39(8):881-890 [30]Wan Y,Zhao H,Yu R,et al.Synthesis and Characterization of Multifunctional Iron Oxide Nanoparticles.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2012;12(3): 2456-2461. [31]Hu M,Stanzione F,Sum AK,et al.Design Principles for Nanoparticles Enveloped by a Polymer-Tethered Lipid Membrane.ACS Nano.2015;9(10):9942-9954. [32]Qiao R,Yang C,Gao M.Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: from preparations to in vivo MRI applications.J Mater Chem.2009;19(35):6274-6293. [33]Xin H,Sha X,Jiang X,et al.Anti-glioblastoma efficacy and safety of paclitaxel-loading Angiopep-conjugated dual targeting PEG-PCL nanoparticles. Biomaterials. 2012;33(32):8167-8176. [34]龚明福,杨华,邹利光,等.包被材料对磁性纳米粒胶束 MRI 信号和弛豫效能的影响[J].第三军医大学学报, 2013,35(1):5-9. [35]Long NV,Yang Y,Teranishi T,et al.Biomedical applications of advanced multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles.J Nanosci Nanotechnol.2015; 15(12): 10091-10107. [36]Zhu H,Zhang S,Huang YX,et al. Monodisperse M(x)Fe(3-x)O4 (M = Fe, Cu, Co, Mn) nanoparticles and their electrocatalysis for oxygen reduction reaction. Nano Lett. 2013;13(6):2947-2951. [37]Huh YM,Jun YW,Song HT,et al.In vivo magnetic resonance detection of cancer by using multifunctional magnetic nanocrystals.J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127(35): 12387-12391. |
| [1] | Min Youjiang, Yao Haihua, Sun Jie, Zhou Xuan, Yu Hang, Sun Qianpu, Hong Ensi. Effect of “three-tong acupuncture” on brain function of patients with spinal cord injury based on magnetic resonance technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-8. |
| [2] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [3] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [4] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [5] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [6] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [7] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [8] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [9] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [10] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [11] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [12] | Yi Meizhi, Luo Guanghua, Xiao Yawen, Hu Rong, Chen Xiaolong, Zhao Heng. MRI findings of anatomical variations of the talus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3888-3893. |
| [13] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [14] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [15] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||