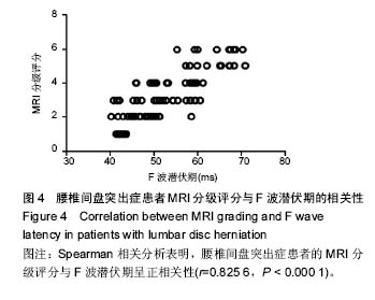
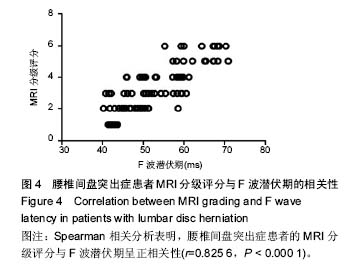
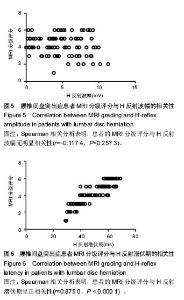
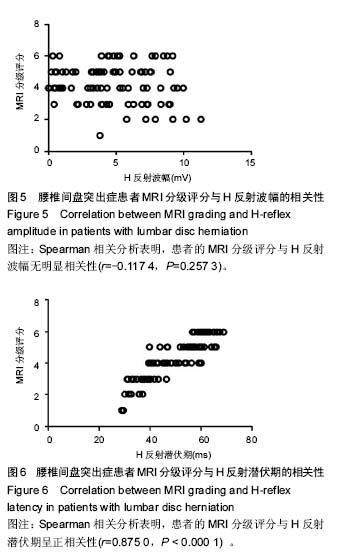
| [1] 徐安波.腰椎间盘突出症核磁共振影像分析152例[J]. 中国中医药现代远程教育,2013,11(6):45-46.
[2] 张凤山,陈仲强,党耕町,等.椎间孔与椎间孔外腰椎间盘突出症的影像学诊断[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,1999,9(5): 246-249.
[3] van Rijn JC, Klemetso N, Reitsma JB, et al. Observer variation in MRI evaluation of patients suspected of lumbar disk herniation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005; 184(1):299-303.
[4] 邹艺,刘英,李素荣,等.腰椎间盘突出症58例神经电生理检查分析[J].实用医院临床杂志,2012,9(5): 201-202.
[5] 柳三凤,王汉龙,翁文水,等.肌电图应用于辅助诊断腰椎间盘突出症的临床分析[J].中国医药科学,2016,6(3): 21-24, 32.
[6] Mondelli M, Aretini A, Arrigucci U, et al. Clinical findings and electrodiagnostic testing in 108 consecutive cases of lumbosacral radiculopathy due to herniated disc. Neurophys Clin. 2013;43(4): 205-215.
[7] 刘雅丽,高伟,黄晓琳,等.脊髓损伤患者与正常人F波的差异性研究[J].中国康复,2006,21(1):23-25.
[8] 梁镇宏,肖雪. F波检测在腰骶神经根压迫征的诊断和康复评定中的价值[J].中国康复医学杂志,1998,13(1):11-13.
[9] Toyokura M, Murakami K. F-wave study in patients with lumbosacral radiculopathies. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1997;37(1):19-26.
[10] 王涛,赵复来,邵克.不同影像学方法对腰椎间盘突出症评估的应用价值[J].中国临床康复,2005,9(14):52.
[11] 孙莉华,宋云龙,毕永民,等. 3.0T MR IDEAL序列成像应用于腰骶神经根受压的初步临床研究[J]. 临床军医杂志, 2015,43(3):285-289.
[12] Jackson RP, Glah JJ. Foraminal and extraforaminal lumbar disc herniation: diagnosis and treatment. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1987;12(6):577-585.
[13] 王晓明,王生伟,陈丽娟,等.极外侧型腰椎间盘突出症磁共振分级与下腰痛评分的相关性[J].中国临床研究,2014, 27(7):778-781.
[14] 杨维琦,李世和,曾才铭.腰椎间盘突出致腰腿疼的病因探讨[J].颈腰痛杂志,2000,21(3):247-249.
[15] 胡星新,刘立岷.临床症状体征与影像学检查分离的腰椎间盘突出症的发生机制研究进展[J].中国骨伤,2015, 28(10): 970-975.
[16] Zhang J, Han L, Han X, et al. [Observation of CT three-dimensional reconstruction in the treatment of standard manipulation for lumbar intervertebral disc herniation]. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2011;24(10):854-856.
[17] Liu X, Liu Y, Lian X, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging on disc degeneration changes after implantation of an interspinous spacer and fusion of the adjacent segment. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(4):6097-6102.
[18] Truumees E. A history of lumbar disc herniation from Hippocrates to the 1990s. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015; 473(6):1885-1895.
[19] 郜璐璐,张进,林斌,等. 腰椎间盘突出症的影像学诊断研究现状[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2015,9(9): 1724-1727.
[20] 唐嫄科,薛金山,张文,等.动态脊髓造影诊断腰椎间盘突出症[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2003,13(7):395-397.
[21] 韩巧林,赵卫东.能谱CT及其在腰椎间盘突出症中的临床应用价值[J].国际医学放射学杂志,2014,37(1):50-53.
[22] Ghosh S, Alomari RS, Chaudhary V, et al. Composite features for automatic diagnosis of intervertebral disc herniation from lumbar MRI. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2011;2011:5068-5071.
[23] 赵建,郭智萍,王林峰,等. 腰痛患者腰椎3.0T MR弥散加权成像腰椎间盘表观弥散系数与椎间盘退变分级的相关性[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2013,23(12):1074-1078.
[24] 杨海涛,王仁法,王娟,等.腰椎间盘纤维环MR扩散张量成像的临床应用[J].中华放射学杂志,2007,41(10): 1100-1103.
[25] 陈兴灿,刘淼,何东,等.仰卧位和俯卧过屈位CT、MRI对腰椎间盘突出症显示的比较研究[J].中华放射学杂志, 2011,45(1):65-68.
[26] Liu T, Zhou Y, Wang J, et al. Clinical efficacy of three different minimally invasive procedures for far lateral lumbar disc herniation. Chin Med J (Engl). 2012; 125(6):1082-1088.
[27] Epstein NE, Epstein JA, Carras R, et al. Far lateral lumbar disc herniations and associated structural abnormalities. An evaluation in 60 patients of the comparative value of CT, MRI, and myelo-CT in diagnosis and management. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1990;15(6):534-539.
[28] 吴学武,陈莹.腰椎间盘突出症的病因及护理[J]. 中国医药指南,2008,(24):401-402.
[29] Takahashi N, Yabuki S, Aoki Y, et al. Pathomechanisms of nerve root injury caused by disc herniation: an experimental study of mechanical compression and chemical irritation. Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2003;28(5):435-441.
[30] 李鹤平,庄文权,杨建勇,等.腰椎间盘突出症体感诱发电位改变及其机制[J].中国临床康复,2002,6(22): 3402-3403.
[31] 潘勇,周跃.髓核对背根节的损伤以及与痛觉过敏的关系[J].重庆医学,2003,32(2):142-144.
[32] Ozawa K, Atsuta Y, Kato T. Chronic effects of the nucleus pulposus applied to nerve roots on ectopic firing and conduction velocity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(24):2661-2665.
[33] 张献宇,李强,吴广智,等.F波在神经型胸廓出口综合征诊断中的作用[J].中华手外科杂志,2015,31(6): 433-435.
[34] 吴小丽,李朝健,吴宏胜,等.神经电生理检查早期诊断面神经炎的价值分析[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2010, 32(7):539-540.
[35] 史广,石权,张楠楠.神经电生理检测在腕管综合征诊断中的应用价值研究[J].中国医刊,2015,65(3):75-79.
[36] Adamova B, Vohanka S, Dusek L. Dynamic electrophysiological examination in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis: is it useful in clinical practice? Eur Spine J. 2005;14(3):269-276.
[37] Trujillo-Hernandez B, Huerta M, Trujillo X, et al. F-wave and H-reflex alterations in recently diagnosed diabetic patients. J Clin Neurosci. 2005;12(7):763-766.
[38] 梁镇宏.常规肌电图及F波传导速度量化判断手法治疗神经根型颈椎病疗效的探讨[J].现代康复,2001,5(20): 87.
[39] 张卉.肌电图F波检查对腰骶神经根病辅助诊断的临床使用[J]. 检验医学与临床,2013,10(17):2350-2351.
[40] 张翅,金宙,廖恩光. H反射及F波测定对腰骶神经根病诊断的临床意义[J].现代康复,2000,4(5):696-697.
[41] Toyokura M, Ishida A. Diagnostic sensitivity of predicted F-wave latency by age, height, and MCV. Acta Neurol Scand. 2000;102(2):106-113.
[42] 赵朝晖,吴华荣,张连锁,等.神经电生理检查在腰椎间盘突出症诊断中的临床价值[J]. 河北医药,2014(20): 3128-3129.
[43] 齐宗华,西永明,胡有谷.腰椎间盘突出症神经根损害的肌电图检查分析[J].中国骨与关节外科,2009,2(1): 9-11.
[44] 谢青,朱珊珊,毛韶丽,等.H反射在腰腿痛患者中的应用[J].中国康复医学杂志,2001,16(4):225-227.
[45] 陈斯雄,陈璇,刘恋.腰椎间盘突出患者与健康人H反射与运动神经传导速度比较分析[J]. 中国临床医生杂志, 2007,35(1):38-39.
[46] 张淑玲,刘志诚,张斌,等.腰椎间盘突出症肌电图检查的独特价值[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2007,10(2): 25-26.
[47] 金翔,姜建元.H反射在神经系统功能检查中的作用及局限性[J].国际骨科学杂志,2013,34(4):281-282, 286.
[48] 安梅. 神经肌电图对腰椎间盘脱出症的诊断意义[J]. 河南科技大学学报(医学版),2006,24(3):216-217.
[49] 赵伟,王子敬.腰椎间盘突出后神经传导速度改变的自然过程[J].中国临床康复,2005,9(14):72-73.
[50] Onda A, Yabuki S, Kikuchi S, et al. Effects of lidocaine on blood flow and endoneurial fluid pressure in a rat model of herniated nucleus pulposus. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(20): 2186-2191, 2191-2192.
[51] 蔡少康,尹晶,刘巧妹,等.经皮椎间盘旋切术联合臭氧治疗腰椎间盘突出症对下肢肌电图F波的影响[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2015,21(6):461-463, 467.
[52] Toyokura M, Ishida A, Murakami K. Follow-up study on F-wave in patients with lumbosacral radiculopathy. Comparison between before and after surgery. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1996;36(4): 207-214. |