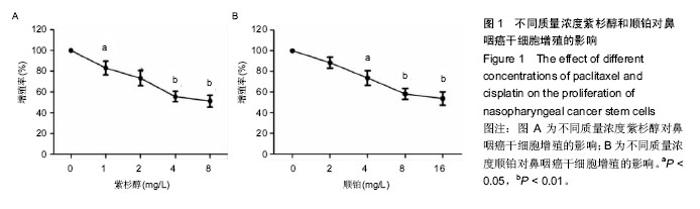
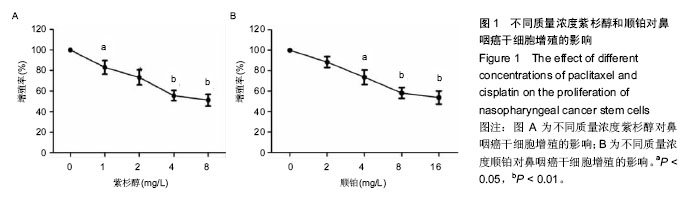
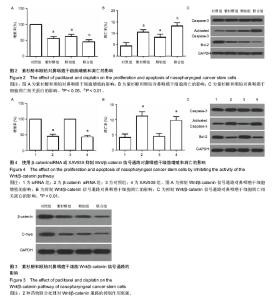
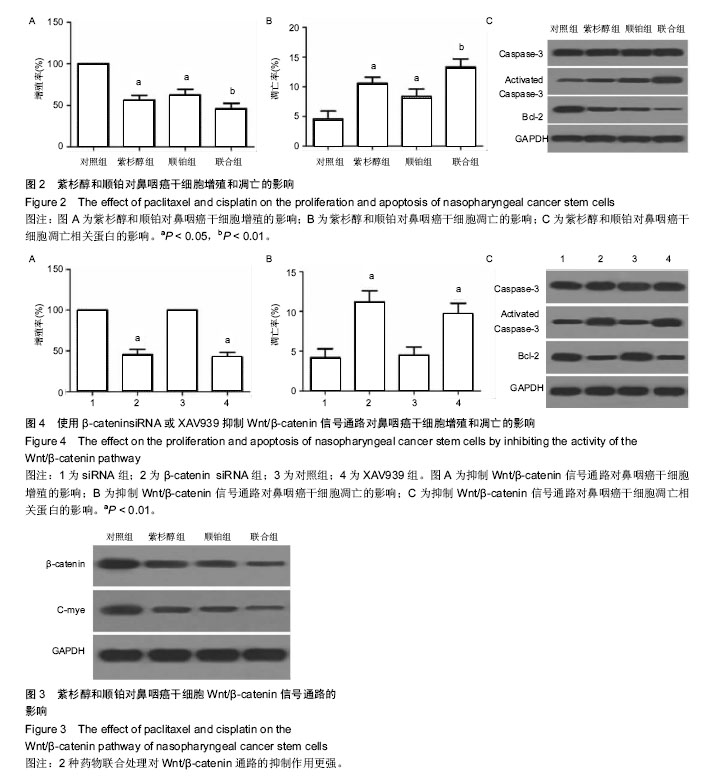
| [1] Eduardo B,Raquel C,Rui M.Nasopharyngeal carcinoma in a south European population: epidemiological data and clinical aspects in Portugal. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2010; 267(10): 1607-1612.
[2] Kamran SC, Riaz N, Lee N. Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2015;24(3): 547-561.
[3] Xie YJ, Long ZF, He XS. Involvement of EBV-encoded BART-miRNAs and dysregulated cellular miRNAs in nasopharyngeal carcinoma genesis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14: 5637-5644.
[4] Wang J, Guo LP, Chen LZ, et al.Identification of cancer stem cell–like side population cells in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line. Cancer Res.2007; 67(8): 3716-3724.
[5] Garvalov BK, Acker T. Cancer stem cells: a new framework for the design of tumor therapies. J Mol Med (Berl). 2011;89(2): 95-107.
[6] Ogawa K, Yoshioka Y, Isohashi F, et al. Radiotherapy targeting cancer stem cells: current views and future perspectives. Anticancer Res. 2013;33(3): 747-754.
[7] Tirino V, Desiderio V, Paino F, et al. Cancer stem cells in solid tumors: an overview and new approaches for their isolation and characterization. FASEB J. 2013; 27(1): 13-24.
[8] Morrison R, Schleicher S M, Sun Y, et al. Targeting the mechanisms of resistance to chemotherapy and radiotherapy with the cancer stem cell hypothesis. J Oncol. 2011;2011:941876.
[9] Howat S, Park B, Oh I S, et al. Paclitaxel: biosynthesis, production and future prospects. N Biotechnol. 2014; 31(3):242-245.
[10] Sarkar T.Microtubule Targeting Anti-mitotic Agents as Anti-Cancer Drugs: A Review. International Journal of Multidisciplinary Approach & Studies.2015;2(5).
[11] Qiu L, Di W, Jiang Q, et al. Targeted inhibition of transient activation of the EGFR-mediated cell survival pathway enhances paclitaxel-induced ovarian cancer cell death. Int J Oncol. 2005;27(5):1441-1448.
[12] Li XY, Zhao Y, Sun MG, et al. Multifunctional liposomes loaded with paclitaxel and artemether for treatment of invasive brain glioma. Biomaterials.2014; 35(21): 5591-5604.
[13] Volk-Draper L, Hall K, Griggs C, et al. Paclitaxel therapy promotes breast cancer metastasis in a TLR4-dependent manner.Cancer Res.2014;74(19): 5421-5434.
[14] Langer C, Hirsh V, Okamoto I, et al. Survival, quality-adjusted survival, and other clinical end points in older advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with albumin-bound paclitaxel. Br J Cancer. 2015;113(1): 20-29.
[15] Meng F, Wu G. Novel mechanism links p63 and cisplatin resistance. Cell Cycle. 2014;13(6): 881-881.
[16] Zhu S,Pabla N,Tang C,et al.DNA damage response in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Arch Toxico.2015; 89(12): 2197-2205.
[17] Wu X, Zhi X, Ji M, et al. Midkine as a potential diagnostic marker in epithelial ovarian cancer for cisplatin/paclitaxel combination clinical therapy. Am J Cancer Res. 2015;5(2): 629.
[18] Eberhardt WE, Gauler TC, Lepechoux C, et al. 10-year long-term survival (LTS) of induction chemotherapy with three cycles cisplatin/paclitaxel followed by concurrent chemoradiation cisplatin/etoposide/45Gy (1.5 Gy bid) plus surgery in locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC)-A multicenter phase-II trial (CISTAXOL). Lung Cancer.2013;82(1): 83-89.
[19] Petrasch S, Welt A, Reinacher A, et al. Chemotherapy with cisplatin and paclitaxel in patients with locally advanced, recurrent or metastatic oesophageal cancer. Br J Cancer. 1998; 78(4): 511.
[20] Chen K, Huang YH, Chen JL. Understanding and targeting cancer stem cells: therapeutic implications and challenges. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica. 2013; 34(6):732-740.
[21] Sassi N,Laadhar L,Allouche M, et al. WNT signaling and chondrocytes: from cell fate determination to osteoarthritis physiopathology. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2014; 34(2): 73-80.
[22] Macdonald BT, Tamai K, He X. Wnt/β-catenin signaling: components, mechanisms, and diseases. Developmental cell.2009;17(1): 9-26.
[23] Kühl SJ, Kühl M.On the role of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in stem cells. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subjects.2013;1830(2): 2297-2306.
[24] Arend RC, Londoño-Joshi AI, Straughn JM, et al. The Wnt/β-catenin pathway in ovarian cancer: a review. Gynecol Oncol. 2013;131(3): 772-779.
[25] 李冠雪,申聪香,文忠,等. Lenti-TK介导间充质干细胞对鼻咽癌CD133+干细胞的靶向迁移及杀伤作用[J].中国肿瘤生物治疗杂志,2013,20(2):145-152.
[26] Zhuang HW, Mo T-T, Hou W-J, et al. Biological characteristics of CD133+ cells in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2013;30(1):57-63.
[27] Magri L, Gacias M, Wu M, et al. c-Myc-dependent transcriptional regulation of cell cycle and nucleosomal histones during oligodendrocyte differentiation. Neuroscience.2014;276: 72-86.
[28] Eberhart CG, Kratz J, Wang Y, et al. Histopathological and Molecular Prognostic Markers in Medulloblastoma: c-myc, N-myc, TrkC, and Anaplasia.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2004;63(5): 441-449.
[29] Turashvili G, Bouchal J, Burkadze G, et al. Wnt signaling pathway in mammary gland development and carcinogenesis. Pathobiology.2006;73(5): 213-223.
[30] Malanchi I, Peinado H, Kassen D, et al. Cutaneous cancer stem cell maintenance is dependent on &bgr;-catenin signalling. Nature.2008;452(7187): 650-653.
[31] He XC, Zhang J, Tong WG, et al. BMP signaling inhibits intestinal stem cell self-renewal through suppression of Wnt-β-catenin signaling. Nature genetics. 2004;36(10):1117-1121.
[32] Polakis P.The oncogenic activation of β-catenin. Current opinion in genetics & development.1999;9(1): 15-21.
[33] Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive molecular characterization of human colon and rectal cancer. Nature, 2012, 487(7407): 330-337.
[34] Bodnar L, Stanczak A, Cierniak S, et al. Wnt/β-catenin pathway as a potential prognostic and predictive marker in patients with advanced ovarian cancer. J Ovarian Res.2014;7(1):16.
[35] Lin YC, You L, Xu Z, et al. Wnt signaling activation and WIF-1 silencing in nasopharyngeal cancer cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;341(2): 635-640.
[36] Fu Q,Chen Z,Gong X,et al.β-Catenin expression is regulated by an IRES-dependent mechanism and stimulated by paclitaxel in human ovarian cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;461(1): 21-27.
[37] Lou P J, Chen W P, Lin C T, et al. Taxol reduces cytosolic E-cadherin and β-catenin levels in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line TW-039: Cross-talk between the microtubule-and actin-based cytoskeletons. J Cell Biochem. 2000;79(4): 542-556.
[38] 黄彤辉. β-catenin 蛋白在紫杉醇治疗宫颈癌中表达的研究[J]. 医学理论与实践, 2015, 28(3): 305-306.
[39] 王永富,秦治明.紫杉醇对肺癌细胞株A549 Wnt/ β-catenin信号通路相关基因和蛋白表达的影响[J].中国药房, 2012,23(45):4233-4235.
[40] 腊蕾,班武,任青青. p53和顺铂对 Wnt通路抑制剂 Frp HE的表达作用[J].生命科学研究, 2011,15(5): 415-419. |