Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (38): 5770-5776.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.38.022
Screening and application of drug-eluting stents in patients with cardiovascular diseases
- Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430060, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2016-08-12Online:2016-09-16Published:2016-09-16 -
About author:Wu Jin, Associate chief physician, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430060, Hubei Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wu Jin.
share this article

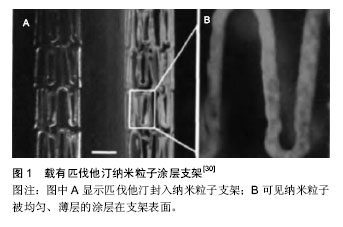
2.1 雷帕霉素及其衍生物的涂层支架 2.1.1 雷帕霉素相关支架 雷帕霉素洗脱支架是第一个应用于临床的药物洗脱支架。因为雷帕霉素抑制再狭窄效果良好,雷帕霉素洗脱支架可有效降低支架置入后再狭窄的风险,获得了广泛的临床应用。与雷帕霉素洗脱支架相关的临床试验(RAVEL试验,SIRIUS试验)证实,雷帕霉素洗脱支架置入后1年的造影结果显示未出现支架内再狭窄,而且雷帕霉素洗脱支架的再狭窄率仅为3.2%,显著低于裸支架的35.4%[3]。窦克非等[4]收集了2004年4月至2006年10月在阜外心血管病医院择期置入FIREBIRD雷帕霉素洗脱支架的2 274例患者的2年临床随访资料,2年累计血栓发生率为1.19%,靶血管血运重建累计发生率为4.2%,主要不良心血管事件累计发生率为6.6%。王哲颖等[5]则观察了雷帕霉素洗脱支架治疗43例无保护冠状动脉左主干严重狭窄性病变的安全性和远期效果,43例中急性冠脉综合征41例,急性ST段抬高型心肌梗死2例,成功置入83枚雷帕霉素洗脱支架,随访(37.2±17.2)个月,主要不良心血管事件累计发生率为7.0%(3/43),平均管腔丢失(18.5±10.3)%。以上结果均说明雷帕霉素洗脱支架治疗成功率高且安全,主要不良心血管事件发生率较低,远期效果好。 随着雷帕霉素洗脱支架临床应用时间的延长,晚期支架内血栓发生率不断增加,而发生支架内血栓的机制可能为:①雷帕霉素引起的再内皮化延迟:由于雷帕霉素的抗增殖作用缺乏选择性,在抑制平滑肌细胞增生的同时也抑制血管内皮细胞的内皮化,使损伤部位难以愈合[6];②支架本身以及介入因素引起的局部炎症:支架本身材料或设计因素导致炎症反应和免疫反应,以及长期存在的载药聚合物涂层引起过敏反应和炎症反应都会增加血栓形成的风险[7];③患者本身因素。近年来,针对以上因素研究者对支架进行改良,出现了许多新型雷帕霉素相关载药支架[8],这些支架或多或少地改善了内皮化,增加了远期效果,但对雷帕霉素及相关支架的长期安全问题仍需引起重视。 雷帕霉素与CD34抗体联合支架系统结合了干细胞和生物工程技术,支架上的CD34+抗体可吸附血液循环中的内皮祖细胞,并使其分化为成熟的内皮细胞而加速局部的内皮化,进而降低支架内再狭窄和晚期血栓的发生。胡江乔等[9]的临床试验观察了雷帕霉素与CD34抗体联合支架系统的安全性,并与雷帕霉素洗脱支架比较,观察30天主要心脏不良事件和9个月晚期管腔丢失,结果发现雷帕霉素与CD34抗体联合支架是安全的、有效的、血运重建率和支架内血栓形成比例均不高,并有血管内皮化更良好的特征。 可降解雷帕霉素药物涂层支架中携带药物的聚合物涂层是可降解的,从而避免了聚合物永久存留对血管壁的不良影响。韩雅玲等[8]评估了EXCEL可降解涂层雷帕霉素洗脱支架置入3年后的安全性和有效性,入选了100例单一置入EXCEL支架的冠心病患者,3年共发生主要不良心血管事件6例,可能的支架内血栓事件仅1例,晚期支架贴壁不良发生率6.3%,但随访期间无任何临床事件发生,提示其早期临床获益可持续至术后3年。 针对雷帕霉素本身会影响血管内皮的再内皮化,国内研发了FIREHAWK冠脉雷帕霉素靶向洗脱支架,该支架载药量仅为同类传统药物洗脱支架的1/3。刘慧竹[10]报告了雷帕霉素靶向洗脱支架治疗冠心病的1年随访结果,纳入了78例患者,共置入151枚FIREHAWK支架,靶病变失败1例(1.28%),无ARC定义的支架血栓事件发生;冠脉造影、血管内超声及光学相干断层扫描分析显示FIREHAWK支架具有低晚期管腔丢失、P&M体积减小、支架偏心性增大、高支架贴壁率及支架覆盖率、低新生内膜体积,两支架重叠部分较非重叠节段有更好的支架贴壁性。 2.1.2 依维莫司洗脱支架 依维莫司是一种雷帕霉素衍生物,作用机制类似。Raber等[11]临床试验中,随访4年的结果显示,依维莫司洗脱支架的支架内血栓发生率明显低于雷帕霉素洗脱支架,其中极晚期支架血栓发生率降低得尤为明显。刘强等[12]收治了60例接受依维莫司洗脱支架置入治疗的冠心病冠状动脉长病变患者,共置入86个依维莫司洗脱支架(Xience V),支架释放后靶病变局部残余狭窄<5%,无并发症发生;随访9-12个月,冠状动脉造影复查在靶病变处均未出现显著新生内膜增殖现象,仅1例患者出现再狭窄迹象,支架内平均晚期管腔丢失(0.12±0.03) mm,初步证实依维莫司洗脱支架治疗冠心病冠状动脉长病变安全有效。庞明杰等[13]应用依维莫司洗脱支架(Xience V)治疗急性冠脉综合征66例,术后病变残余狭窄(4.1±3.2)%,住院期间无急性、亚急性血栓形成,无心肌梗死,无死亡;随访6-9个月,1例心绞痛复发,1例再狭窄,提示依维莫司洗脱支架置入治疗急性冠脉综合征安全可行,成功率高。依维莫司支架应用于糖尿病[14]、小血管及分叉病变等特殊条件中,也显示了优于雷帕霉素支架及紫杉醇支架的安全性及有效性。 2.1.3 佐他莫司洗脱支架 佐他莫司是一种雷帕霉素衍生物,具有极高的安全性,除了与雷帕霉素有相似的免疫抑制性能外还具有更强的亲脂性,使之易定位于血管壁中,抑制新生内膜过度增生,并且减少了药物向循环系统的弥散,降低了全身不良反应,但其防止再狭窄的能力略弱于雷帕霉素[15]。佐他莫司洗脱支架置入后的再狭窄率及靶病变血运重建率较裸金属支架显著降低,支架内血栓发生率较紫杉醇支架降低[16]。魏敬飞等[17]对比了国产西罗莫司洗脱支架(Firebird 支架)和进口佐他莫司洗脱支架(Resolute 支架)治疗冠心病无保护左主干病变患者的疗效和安全性,共纳入了76例患者,随访(23.3±10.7)个月,两种支架远期预后相似。2012年一项前瞻性、多中心临床研究比较了TIVOLI生物可降解涂层西罗莫司洗脱支架与ENDEAVOR佐他莫司洗脱支架治疗冠心病的有效性和安全性,纳入了中国12家医院的324例患者(TIVOLI组168例,ENDEAVOR组156例),主要终点为术后240 d冠状动脉造影确定的支架内晚期管腔丢失,次级终点为术后1-3年的临床预后,结果显示TIVOLI支架晚期管腔丢失优于ENDEAVOR支架,两种支架的再狭窄和3年靶病变血运重建的发生率均较低,3年主要心脏不良事件发生率方面差异不显著[18]。 2.2 紫杉醇涂层支架 紫杉醇洗脱支架与雷帕霉素洗脱支架一样属于第一代药物洗脱支架,具有代表性,广泛应用于临床。紫杉醇是由短叶红豆杉树皮提取的衍生二萜类化合物,是一种抗肿瘤药物,紫杉醇可使细胞分裂受阻于M期,从而可有效抑制血管平滑肌细胞的增殖,预防再狭窄,同时其具有高度的亲脂性,能与细胞组织牢固结合。很多临床试验验证了紫杉醇洗脱支架的安全性和有效性[19]。窦克非等[4]报道了在阜外心血管病医院择期置入TAXUS紫杉醇洗脱支架836例患者的临床资料,2年累计血栓发生率为2.65%,靶血管血运重建累计发生率为9.5%,主要不良心血管事件累计发生率为12.2%,其效果比雷帕霉素洗脱支架差。陈少伯等[20]比较了国产雷帕霉素洗脱支架(EXCEL)和进口紫杉醇洗脱支架(TAXUS)的长期有效性和安全性,106例冠心病患者,55例置入国产雷帕霉素洗脱支架,51例置入进口紫杉醇洗脱支架,随访3年,两组死亡、心肌梗死、支架内血栓和靶血管血运重建及总不良事件发生率差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),两种支架在临床长期随访中均显示了较高的安全性和较好的有效性,效果相似。与雷帕霉素洗脱支架一样,紫杉醇在抑制了平滑肌细胞的迁移、增生及细胞外基质合成及分泌的同时,对内皮细胞的再生也会产生一定的抑制,造成内皮细胞对支架植入部位的覆盖延迟,导致了血小板激活,以致出现晚期支架内血栓发生率增加;同样,长期存在的未完全吸收的聚合物涂层带来的动脉壁局部炎症反应也是导致远期再狭窄形成的原因之一。基于以上原因,近年来研究者致力于发展新型的紫杉醇涂层支架。 由于聚合物涂层可产生一系列不良反应,因此研究无聚合物涂层的紫杉醇支架,通过对支架表面的特殊处理,将药物包埋于支架表面,使其缓慢释放,直接消除聚合物的不利影响成为研究热点。国内开发了无聚合物微盲孔紫杉醇药物支架,并进行了一系列试验。一项关于永久聚合物涂层雷帕霉素洗脱支架(FIREBIRD2)与无聚合物涂层紫杉醇洗脱支架(YINYI)术后应用双联抗血小板治疗的停药时间的安全性比较研究中,纳入了282例冠心病患者,其中168例置入雷帕霉素洗脱支架,114例置入无聚合物涂层紫杉醇洗脱支架,术后均口服阿司匹林100 mg/d作为长期的基础治疗,同时加用氯吡格雷75 mg/d进行双联抗血小板治疗,之后随访1年,结果无聚合物涂层支架(YINYI)3个月停用氯吡格雷与永久聚合物涂层支架(FIREBIRD2)9个月停用氯吡格雷在临床疗效上无差异,无聚合物涂层支架(YINYI)在临床应用上能减少双联抗血小板的疗程,并能减少出血风险[21]。张兰等[22]的临床试验比较了国产无聚合物紫杉醇涂层支架(YINYI)和可降解聚合物雷帕霉素涂层支架(EXCEL)治疗冠心病,预防心血管事件的有效性和安全性,12个月临床随访观察中,两组均无晚期肯定支架血栓形成事件发生,全因死亡率、主要不良心血管事件、再次住院率差异均无统计学意义(P > 0.05),提示国产YINYI治疗冠心病,预防心血管事件与EXCEL相当,二者均用有良好的有效性和安全性。彭育红等[23]的研究则发现国产无聚合物紫杉醇微孔载药支架(垠艺支架)与雷帕霉素涂层支架(乐普支架)在治疗急性心肌梗死时具有相同的近、中期临床疗效和安全性。 2.3 肝素涂层支架 肝素是天然的凝血抑制剂,早期的肝素涂层支架是一种多聚物涂层支架,在金属支架表面涂以数层多聚物,最外层共价结合肝素分子片段,而肝素分子片段的另一端保持抗凝活性,伸入血流,可以减少支架置入后的急性血栓形成和血管痉挛。但是临床应用以来发现,肝素涂层支架的短期保护效应良好,长时间体内植入的效果并不理想,这是因为肝素容易脱离支架表面,所以肝素预防平滑肌细胞的增殖作用是有限的。 近年来,研究者致力于寻找合适的缓释体固化肝素,延长其体内缓释时间。沈雳等[24]将壳聚糖/肝素层层自组装涂层支架置入猪冠状动脉,1个月后行血管内超声随访,未发生晚期支架贴壁不良,也未见支架内血栓形成,未引起血管异常重构,管腔面积虽小于聚乳酸涂层雷帕霉素洗脱支架组,但显著大于裸金属支架组。作者认为这种壳聚糖/肝素层层自组装涂层具有促进血管内皮快速修复、抗凝血特性;不过该实验仅是动物实验,而且观察时间过短,远期效果还需进一步观察。丁付燕等[25]制备了一种以植物源性玉米醇溶蛋白zein为基质包载的地塞米松-肝素双微球涂层支架,并观察其在小型猪血管损伤模型中近期抑制支架内再狭窄的有效性和安全性,结果显示地塞米松-肝素双微球涂层可以有效抑制支架置入后4,12周时的内膜增生,预防支架内再狭窄。虽然以上研究均为动物实验,但新型的肝素涂层支架毋庸置疑具有良好的生物相容性,也有着良好的临床应用前景。 2.4 载中药涂层支架 理想的药物涂层支架,其涂层中负载的药物应该选择性地抑制血管平滑肌,但是对血管内皮细胞没有作用或者有促进其增殖作用,同时期望具有抗凝血作用,许多中药中含有的活性组分可通过作用于多个靶点而共同发挥治疗作用,而且不良反应更少,因此也成为很多学者的研究方向。大黄素可以呈时间依赖性和浓度依赖性抑制平滑肌细胞的增殖,赵燕超等[26]应用可降解共聚物材料为药物载体,大黄素作为药物,制备了大黄素药物洗脱支架,该药物支架扩张后表面无撕裂、挂膜;此外,高含量比的药物支架(大黄素含量50%)中的药物10 d内的释放达到90%;动物实验证明,涂层材料3个月后在体内大部分发生降解,从血管切片和内膜厚度可以看出,大黄素对内膜增生有着明显的作用,可以抑制血管内的再狭窄。 中药莪术的提取物有抑制血管平滑肌细胞迁移、增殖以及抑制二磷酸腺苷诱导的血小板聚集作用。赵福海等[27]的实验首先制备中华实验用小型猪冠状动脉再狭窄模型,分别在左前降支、左回旋支及右冠状动脉置入莪术组分涂层支架、雷帕霉素涂层支架及金属裸支架,实验终点为支架置入后30 d,莪术组分涂层支架组合帕霉素涂层支架租平均管腔直径和平均管腔面积大于金属裸支架组,而且莪术组分涂层支架组支架置入处内皮化及炎性细胞浸润程度优于雷帕霉素涂层支架,说明莪术组分涂层支架可有效地抑制血管内膜增殖,具有良好的生物相容性。 张海燕[28]则发现栀子苷(12.5 mg/L)与黄芩苷 (50 mg/L)配伍比例为1∶2的药物涂层1个月内的药物累积释放量达到90%,具有促进内皮细胞、抑制平滑肌细胞的双相调节作用,同时可降低血小板数量且显著延长血浆凝血酶时间和活化部分凝血活酶时间,可以作为药物洗脱血管支架的药物涂层。 2.5 其他涂层支架 雌激素的心血管保护作用已被人们认识,雌激素能有效抑制球囊拉伤所致的血管内膜增生,并能加速损伤部位的内皮化,基于此,开发了雌二醇洗脱支架。梁明等将雌二醇洗脱支架置入高脂喂饲兔的腹主动脉,观察12周,发现雌二醇洗脱支架安全、有效,可明显减少支架置入后的血管内膜增生;与普通裸金属支架对比,雌二醇洗脱支架能够加速支架段血管的再内皮化[29]。 新型降血脂、防治动脉粥样硬化的他汀类药物,特别是对人冠状动脉平滑肌细胞增殖有更强抑制作用的匹伐他汀,近年已被用于可吸收性高分子聚合物聚乳酸-羧基乙酸共聚体(PLGA)纳米涂层的载入药物,动物实验结果显示,载有匹伐他汀纳米粒子涂层支架既可抑制支架内再狭窄,也可减少支架内血栓形成(图1)[30]。"
| [1]Kereiakes DJ, Cannon LA, Feldman RL, et al.Clinical and angiographic outcomes after treatment of de novo coronary stenoses with a novel platinum chromium thin-strut stent: primary results of the PERSEUS (Prospective Evaluation in a Randomized Trial of the Safety and Efficacy of the Use of the TAXUS Element Paclitaxel-Eluting Coronary Stent System) trial.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;56(4):264-271. [2]Kimura T, Morimoto T, Nakagawa Y,et al.Very late stent thrombosis and late target lesion revascularization after sirolimus-eluting stent implantation: five-year outcome of the j-Cypher Registry.Circulation. 2012; 125(4):584-591. [3]Spaulding C, Teiger E, Commeau P,et al.Four-year follow-up of TYPHOON (trial to assess the use of the CYPHer sirolimus-eluting coronary stent in acute myocardial infarction treated with BallOON angioplasty). JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2011;4(1):14-23. [4]窦克非,尹栋,吴元,等.FIREBIRD雷帕霉素洗脱支架与TAXUS紫杉醇洗脱支架成功置入后长期临床结果观察:单中心、大规模注册研究[J].中国循环杂志,2012, 27(4): 254-257. [5]王哲颖,刘同库.雷帕霉素洗脱支架治疗无保护冠状动脉左主干严重狭窄性病变的安全性和远期效果研究[J].中国全科医学,2013, 16(27):3192-3196. [6]Ma Q, Zhou Y, Nie X, et al.Rapamycin affects tissue plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor I expression: a potential prothrombotic mechanism of drug-eluting stents.Angiology. 2012; 63(5):330-335. [7]Nakazawa G, Finn AV, Vorpahl M, et al.Coronary responses and differential mechanisms of late stent thrombosis attributed to first-generation sirolimus- and paclitaxel-eluting stents.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;57(4): 390-398. [8]韩雅玲,鄢高亮,荆全民,等.EXCEL可降解涂层雷帕霉素洗脱支架长期临床应用的安全性和有效性[J].中国循环杂志,2010,25(2):88-91. [9]胡江乔,宋现涛,贾博.雷帕霉素与CD34抗体联合支架系统的安全有效性研究[J].心肺血管病杂志,2014, 33(6): 795-798. [10]刘慧竹.雷帕霉素靶向洗脱支架治疗冠心病临床及血管内影像研究[D].上海:上海交通大学.2015. [11]Räber L, Magro M, Stefanini GG,et al.Very late coronary stent thrombosis of a newer-generation everolimus-eluting stent compared with early-generation drug-eluting stents: a prospective cohort study.Circulation. 2012;125(9):1110-1121. [12]刘强,李忠红,王丽丽,等.依维莫司洗脱支架在冠状动脉长病变中应用的效果分析[J].广东医学, 2011,32(15): 2041-2042. [13]庞明杰,张宏,赵燕,等.依维莫司洗脱支架在急性冠脉综合征中应用的效果分析[J].医药前沿,2013, (10):60-61. [14]郑勇.药物洗脱支架在糖尿病冠状动脉长病变中的应用研究[J].医学综述,2012,18(21):3682-3683. [15]Townsend JC, Rideout P, Steinberg DH. Everolimus-eluting stents in interventional cardiology. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2012;8:393-404. [16]Leon MB, Mauri L, Popma JJ, et al.A randomized comparison of the Endeavor zotarolimus-eluting stent versus the TAXUS paclitaxel-eluting stent in de novo native coronary lesions 12-month outcomes from the ENDEAVOR IV trial.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;55(6):543-554. [17]魏敬飞,鄢华,宋丹,等.国产西罗莫司洗脱支架与进口佐他莫司洗脱支架治疗无保护左主干病变临床疗效的对比分析[J].中国介入心脏病学杂志,2015,23(11):617-622. [18]窦克非,徐波,杨跃进,等.TIVOLI完全可降解涂层西罗莫司洗脱支架与ENDEAVOR佐他莫司洗脱支架的临床随访结果[J].中国循环杂志,2012, 27(5):334-337. [19]Grube E, Silber S, Hauptmann KE,et al.Two-year-plus follow-up of a paclitaxel-eluting stent in de novo coronary narrowings (TAXUS I).Am J Cardiol. 2005;96(1):79-82. [20]陈少伯,岳继华,梁国庆,等.国产雷帕霉素洗脱支架和进口紫杉醇洗脱支架对照研究[J].山东医药,2010, 50(52):85-86. [21]刘丹丹.永久聚合物涂层支架与无聚合物涂层支架 双联抗血小板治疗术后停药时间的对比研究[D].大连:大连医科大学.2014. [22]张兰,刘干,钟金鹏,等.国产无聚合物紫杉醇涂层支架和可降解聚合物雷帕霉素涂层支架治疗冠心病疗效评价[J].临床心血管病杂志,2011,27(7):494-498. [23]彭育红,汝磊生,王冬梅,等.国产无聚合物紫杉醇微孔载药支架与雷帕霉素涂层支架对比治疗急性心肌梗死[J].介入放射学杂志,2013, 22(6):458-460. [24]沈雳,吴轶喆,张峰,等.血管内超声评价壳聚糖/肝素层层自组装涂层支架贴壁情况及对猪冠状动脉重构的影响[J].中华心血管病杂志,2012, 40(7):569-574. [25]丁付燕,吕志前,王瑾晔,等.新型地塞米松-肝素双涂层支架在小型猪动脉损伤模型中预防支架内再狭窄的实验研究[J].国际心血管病杂志,2011,38(1):52-55. [26]赵燕超,龚飞荣,葛均波,等.大黄素洗脱可降解涂层支架的制作及其体内外实验研究[J].华东理工大学学报(自然科学版),2008,34(2):242-246. [27]赵福海,刘剑刚,王欣,等.莪术组分涂层支架预防猪冠状动脉再狭窄的研究[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志, 2012, 14(8):859-862. [28]张海燕.栀子苷/黄芩苷心血管作用及应用于血管支架药物涂层研究[D].西南交通大学.2014. [29]梁明,韩雅玲,康建,等.雌二醇洗脱支架抑制血管内膜增生的实验研究[J].中华老年多器官疾病杂志,2010, 9(5):454-459. [30]赵钢,朱伟,陆志刚,等.载有匹伐他汀的纳米涂层支架的研究[J].介入放射学杂志,2012,21(6):486-491. [31]陆跃,沈雳,龚飞荣,等.新型肝素化聚氨酯涂层三氧化二砷洗脱支架的初步研究[J].上海医学,2012,35(3):185-189. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||