Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (30): 4456-4462.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.30.007
Previous Articles Next Articles
Biodegradable AZ31 magnesium alloy stent in rabbit aorta: degradation time and effect
Zhang Xiao-qing1, Li Xin2
- 1Tianjin Fourth Hospital, Tianjin 300222, China; 2Tianjin Third Central Hospital, Tianjin 300170, China
-
Received:2016-06-03Online:2016-07-15Published:2016-07-15 -
Contact:Zhang Xiao-qing, Tianjin Fourth Hospital, Tianjin 300222, China -
About author:Zhang Xiao-qing, Attending physician, Tianjin Fourth Hospital, Tianjin 300222, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Xiao-qing, Li Xin. Biodegradable AZ31 magnesium alloy stent in rabbit aorta: degradation time and effect[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(30): 4456-4462.
share this article
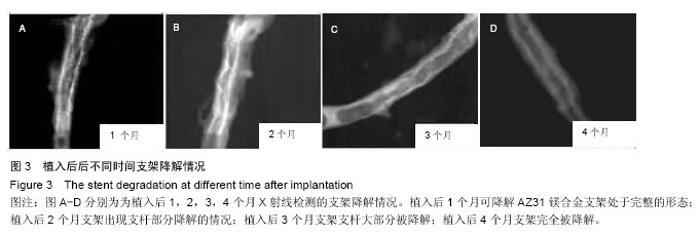
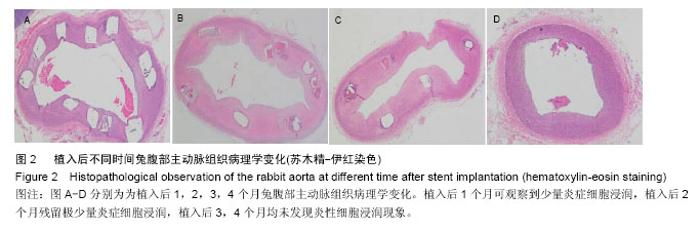
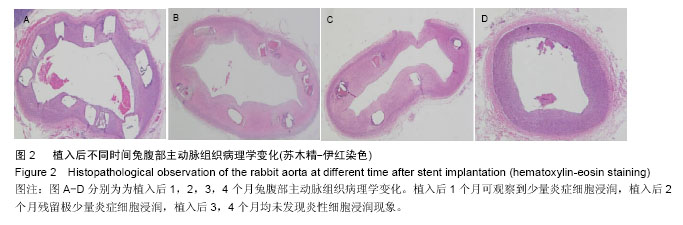
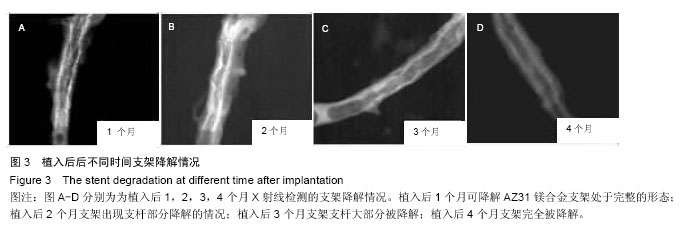
2.4 植入后不同时间支架降解情况分析 X射线观察结果显示,植入后1个月可降解AZ31镁合金支架处于完整的形态,且完全扩张;植入后2个月镁合金支架出现支杆部分降解的情况,失去支撑作用;植入后3个月镁合金支架支杆大部分被降解;植入后4个月镁合金支架完全被降解,见图3。 植入后1,2,3,4个月降解率分别为(2.35±0.05)%,(43.35±10.25)%,(79.29±20.18)%和100%,整体呈现出不断上升的趋势。 2.5 支架降解趋势回归分析 植入后1个月随访,支架支杆剩余数分别为15.12,10.23,9.15;2个月支架支杆剩余数分别为9.25,7.23,8.80;3个月支架支杆剩余数分别为3.25,2.12,2.05;4个月无剩余支杆。 对植入后1,2,3个月的支架支杆剩余数与时间进行相关性分析发现植入后不同时间的支架支杆剩余数与时间之间呈负相关关系(r=-0.943,P < 0.05)。经计算数据直线回归方程斜率为-0.12,表明支架植入之后,每日平均降解支架支杆0.12个。随后进行回归直线计算,可得支架完全降解需要耗费的时间为105 d。"
| [1] 王汝朋.可吸收镁合金支架植入后犬冠状动脉C-反应蛋白、基质金属蛋白酶9和血管性血友病因子的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(8):1216-1222.
[2] 谭志刚,周倩,蒋宇钢.生物可降解镁合金血管支架:缺点及未来研究趋势[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(8):1284-1288.
[3] 吴卫,Petrini L,Altomare L,等.可降解镁合金支架聚合物涂层剥离的有限元模型及实验研究[J].稀有金属材料与工程,2014,43(12):2877-2882.
[4] 闫现政,韩东明,杨瑞民,等.可降解镁合金覆膜支架治疗兔颈总动脉侧壁型动脉瘤的可行性[J].中华放射学杂志, 2015,49(2):138-142.
[5] 郭美卿,黄棣,戴震,等.镁合金支架材料AZ81表面PLGA (PTX)/PLLA/MAO涂层的研究[J].稀有金属材料与工程, 2015,44(2):412-418.
[6] Hansi C, Arab A, Rzany A, et al. Differences of platelet adhesion and thrombus activation on amorphous silicon carbide, magnesium alloy, stainless steel, and cobalt chromium stent surfaces. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2009;73(4):488-496.
[7] Drynda A, Hassel T, Hoehn R, et al. Development and biocompatibility of a novel corrodible fluoride-coated magnesium-calcium alloy with improved degradation kinetics and adequate mechanical properties for cardiovascular applications. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;93A(2):763-775.
[8] 王金瑞,于良,师建华.新型可降解镁合金胆道支架的体外降解规律及力学性能[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(25): 3980-3986.
[9] 邓希光.AZ31镁合金在模拟人体环境中的腐蚀行为研究[D].大连:大连理工大学,2009.
[10] 夏永辉,任玲,徐克,等.镁合金血管支架置入后内膜增生特点[J].介入放射学杂志,2014,23(2):132-135.
[11] khan Demir AG, Previtali B, Colombo D, et al. Fiber laser micromachining of magnesium alloy tubes for biocompatible and biodegradable cardiovascular stents. Fiber lasers IX: technology, systems, and applications. 2012:1-10.
[12] Hassel T, Bach FW, Krause C, et al. Corrosion protection and repassivation after the deformation of magnesium alloys coated with a protective magnesium fluoride layer. 2005 TMS Annual Meeting: magnesium Technology. 2005:485-490.
[13] 毛志刚.AZ31镁合金冠脉支架力学行为的有限元模拟[D].南京:南京理工大学,2012.
[14] 章晓波.可降解生物镁合金性能及心血管支架制备技术研究[D].上海:上海交通大学,2011.
[15] 朱兆金.新型医用可吸收镁合金JDBM的生物毒性、髓内降解及细菌学相关研究[D].苏州:苏州大学,2013.
[16] Wang J, He Y, Maitz MF, et al. A surface-eroding poly(1,3-trimethylene carbonate) coating for fully biodegradable magnesium-based stent applications: toward better biofunction, biodegradation and biocompatibility. Acta Biomaterialia. 2013;9(10): 8678-8689.
[17] Wittchow E, Adden N, Riedmüller J, et al. Bioresorbable drug-eluting magnesium-alloy scaffold: design and feasibility in a porcine coronary model. Euro Int. 2013;8(12):1441-1450.
[18] 章晓波,毛琳,张佳,等.Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr可降解镁合金心血管支架的制备及性能研究[C].第二届生物材料与组织工程产品质量控制国际研讨会论文集,2011.
[19] 徐新华,吴忠仕,尹邦良,等.彩色多普勒超声心动图检测牛颈静脉带瓣管道重建犬右室流出道后结构及血流动力学研究[J].中南大学学报(医学版),2007,32(4):599-603.
[20] Pinto Slottow TL, Pakala R, Waksman R. et al. Serial imaging and histology illustrating the degradation of a bioabsorbable magnesium stent in a porcine coronary artery. Eur Heart J. 2008;29(3):314-314.
[21] Lu P, Cao L, Liu Y, et al. Evaluation of magnesium ions release, biocorrosion, and hemocompatibility of MAO/PLLA-modified magnesium alloy WE42. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2011;96B(1): 101-109.
[22] 杨水祥,雷力成,王丽丽,等.新型血管内可吸收镁合金支架的实验研究[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志, 2012,14(7): 743-747.
[23] Pinto Slottow TL, Pakala R, Waksman R, et al. Serial imaging and histology illustrating the degradation of a bioabsorbable magnesium stent in a porcine coronary artery. Eur Heart J. 2008;29(3):314-314.
[24] 王萍,雷力成,王丽丽,等.冠状动脉内可吸收的镁合金支架[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(43):8071-8077.
[25] 张朝勇.生物可吸收镁合金药物支架研究进展[J].广西医科大学学报,2012,29(3):483-485.
[26] 马晓静,张兴华,陈博,等.支架置入植入后再狭窄患者病变近端参考血管重塑的研究-附63例报告[J].新医学, 2008, 39(9):585-587.
[27] 李海伟,徐克,杨柯,等.可降解AZ31镁合金支架在兔腹主动脉内的降解性能研究[J].介入放射学杂志, 2010,19(4): 315-317.
[28] 朱玉峰,黄新苗,秦永文.生物可降解材料在心血管介入治疗领域的应用进展[J].国际心血管病杂志, 2010,37(4): 235-238.
[29] 冯高科,任珊,郑晓新,等.生物全降解冠状动脉支架的研究进展[J].医学综述,2012,18(24):4130-4134.
[30] Gastaldi D, Sassi V, Petrini L, et al. Continuum damage model for bioresorbable magnesium alloy devices: application to coronary stents. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2011;4(3):352-365.
[31] Erbel R, Di Mario C, Bartunek J, et al. Temporary scaffolding of coronary arteries with bioabsorbable magnesium stents: a prospective, non-randomised multicentre trial. Lancet. 2007;369:1869-1875.
[32] Hou S, Mi L,Wang L, et al. Corrosion protection of Mg-Zn-Y-Nd alloy by flower-like nanostructured TiO2 film for vascular stent application. J Chem Tech Camp Biotechnol. 2013;88(11):2062-2066.
[33] Zhang Q, Yang H, Wei YG, et al. Selection of Destination Ports of Inland-Port-Transferring RHCTS Based on Sea-Rail Combined Container Transportation[C]. Innovation and sustainability of modern railway: third international symposium on Innovation and sustainability of modern railway (ISMR 2012), 2012, Nanchang, China. 2012:675-680.
[34] 丁健,刘利珍,王征宇.生物可降解镁合金支架的发展[J].医学综述,2015,21(4):646-647.
[35] 易雷,周倩.镁合金可降解血管支架发展历史与研究现状[J].医学与哲学:临床决策论坛版,2015,36(3):60-62.
[36] Bowen PK, Shearier ER, Zhao S, et al. Biodegradable Metals for Cardiovascular Stents: from Clinical Concerns to Recent Zn-Alloys. Adv Healthc Mater. 2016;5(10):1121-1140.
[37] Gu X, Mao Z, Ye SH, et al. Biodegradable, elastomeric coatings with controlled anti-proliferative agent release for magnesium-based cardiovascular stents. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2016;144:170-179.
[38] Mostaed E, Sikora-Jasinska M, Mostaed A, et al. Novel Zn-based alloys for biodegradable stent applications: Design, development and in vitro degradation. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2016;60:581-602.
[39] Ding W. Opportunities and challenges for the biodegradable magnesium alloys as next-generation biomaterials. Regen Biomater. 2016;3(2):79-86.
[40] Rahim MI, Rohde M, Rais B, et al. Susceptibility of metallic magnesium implants to bacterial biofilm infections. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016;104(6): 1489-1499.
[41] Tian P, Liu X. Surface modification of biodegradable magnesium and its alloys for biomedical applications. Regen Biomater. 2015;2(2):135-151.
[42] 李树新.生物可降解镁合金支架在冠状动脉血管中应用进展[J].医学综述,2015,21(2):193-195.
[43] 闫世新.可降解镁合金AZ31支架犬髂动脉置入植入后生物学反应[D].沈阳:中国医科大学,2011.
[44] Zartner P, Buettner M, Singer H, et al. First biodegradable metal stent in a child with congenital hean disease: evaluation of macro and histopathology histopathology. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2007;69(3): 443-446.
[45] Slottow TL, Pakala R, Okabe T, et al. Optical coherence tomography and intravascular ultrasound imaging of bioabsorbable magnesium stent degradation in porcine coronary ayeeries. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2008;9(4):248-254.
[46] 李海伟,徐克,杨柯,等.可降解AZ31镁合金支架在兔腹主动脉内的降解性能研究[J].介入放射学杂志,2010,19(4): 315-317. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||