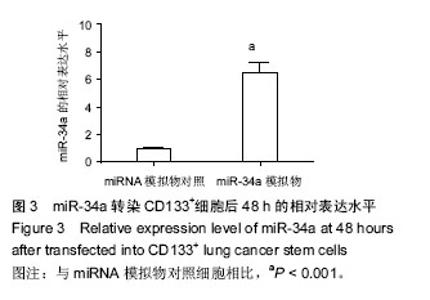
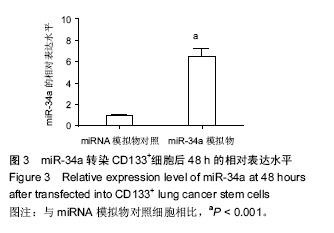
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (23): 3349-3356.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.23.001
Inhibitory effect of miR-34a on lung cancer stem cells via Notch1 signaling pathway
Han Ji-chang, Zhang Yi-jie, Li Hong-bing, Yang Cun-bao, Ma Chao-nan, Qi Guan-bin
- Department of Respiratory Medicine, Huaihe Hospital of Henan University, Kaifeng 475000, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2016-04-19Online:2016-06-03Published:2016-06-03 -
Contact:Zhang Yi-jie, Master’s supervisor, Chief physician, Department of Respiratory Medicine, Huaihe Hospital of Henan University, Kaifeng 475000, Henan Province, China -
About author:Han Ji-chang, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Respiratory Medicine, Huaihe Hospital of Henan University, Kaifeng 475000, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:the Science and Technology Innovation Project of Henan Provincial Health Department for Young Talents, No. 4189
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Han Ji-chang, Zhang Yi-jie, Li Hong-bing, Yang Cun-bao, Ma Chao-nan, Qi Guan-bin. Inhibitory effect of miR-34a on lung cancer stem cells via Notch1 signaling pathway[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(23): 3349-3356.
share this article
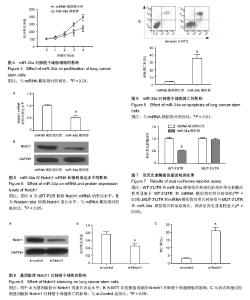
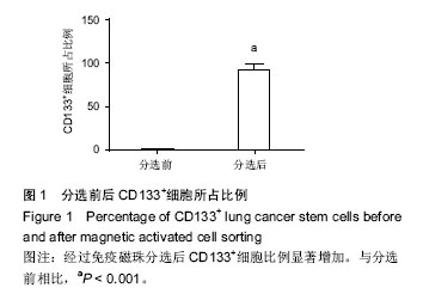
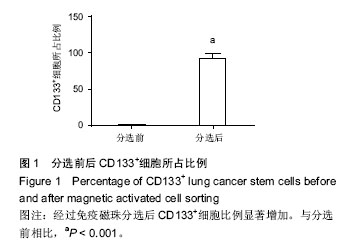
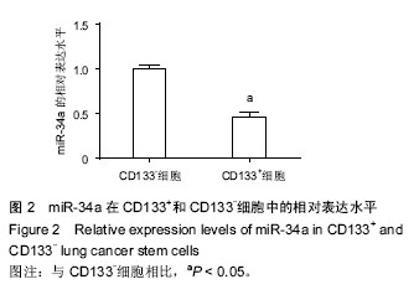
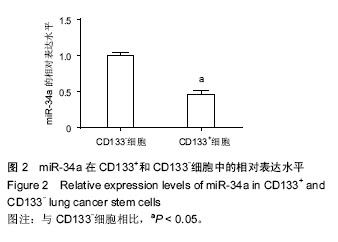
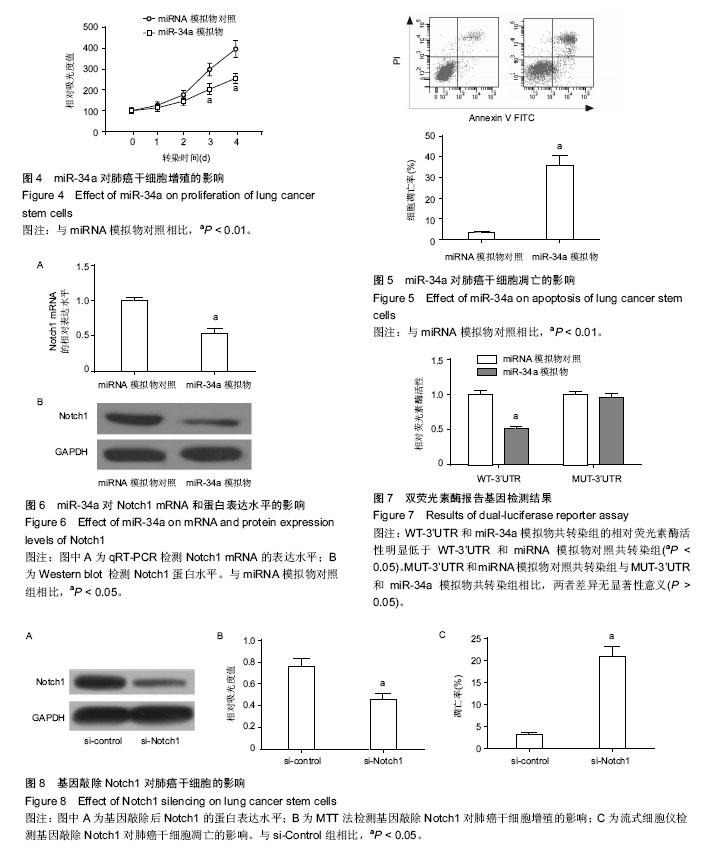
2.4 miR-34a对细胞增殖的影响 为了验证miR-34a对肺癌干细胞增殖的作用,采用MTT法检测了过表达miR-34a对细胞增殖的影响。结果发现,转染了miR-34a模拟物的细胞增殖速度明显低于miRNA模拟物对照组细胞(P < 0.01),说明miR-34a对肺癌干细胞具有明显的抑制作用(图4)。 2.5 miR-34a对细胞凋亡的影响 运用流式细胞术检测了过表达miR-34a对肺癌干细胞凋亡的影响。如图5所示,miR-34a模拟物组的凋亡率明显高于miRNA模拟物对照组(P < 0.01)。 2.6 miR-34a抑制Notch1表达 miR-34a模拟物及miRNA模拟物对照转染肺癌干细胞48 h后,用qRT-PCR方法检测各组细胞中Notch1 mRNA的表达水平(图6A)。结果显示,与对照组相比,miR-34a模拟物转染的细胞中Notch1 mRNA的表达水平明显降低(P < 0.01)。又用Western blot检测Notch1蛋白水平的表达(图6B)。结果显示,与对照组相比,miR-34a模拟物转染的细胞中Notch1的表达水平明显降低(P < 0.05)。 2.7 双荧光素酶报告基因检测结果 WT-3’UTR和miR-34a模拟物共转染组的相对荧光素酶活性明显低于miRNA模拟物对照共转染组(P < 0.05)。MUT-3’UTR和miRNA模拟物对照共转染组与MUT-3’UTR和miR-34a模拟物共转染组相比,两者差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见图7。结果说明miR-34a可以与Notch1 mRNA 3'UTR的特定位点结合,Notch1可能是miR-34a的靶向基因。 2.8 基因敲除Notch1对肺癌干细胞的影响 为了进一步检测Notch1与肺癌干细胞的增殖、凋亡的关系,首先利用基因敲除技术将肺癌干细胞中Notch1的基因进行敲除,图8A显示,基因敲除后干细胞中Notch1的表达显著降低。MTT法检测结果显示(图8B),基因敲除后干细胞的增殖明显受到抑制(P < 0.05)。流式细胞仪检测结果显示(图8C),si-Notch1显著增加了肺癌干细胞的凋亡(P < 0.05)。这些结果说明,基因敲除Notch1能够抑制肺癌干细胞的增殖,诱导细胞凋亡。"
| [1] Lortet-Tieulent J, Soerjomataram I, Ferlay J, et al. International trends in lung cancer incidence by histological subtype: adenocarcinoma stabilizing in men but still increasing in women. Lung Cancer. 2014; 84(1):13-22. [2] Shaw AT, Kim DW, Mehra R, et al. Ceritinib in ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(13):1189-1197. [3] Reya T, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF, et al. Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells.Nature. 2001;414(6859): 105-111. [4] Eramo A, Lotti F, Sette G, et al. Identification and expansion of the tumorigenic lung cancer stem cell population. Cell Death Differ. 2008;15(3):504-514. [5] Kim HS, Lee KS, Bae HJ, et al. MicroRNA-31 functions as a tumor suppressor by regulating cell cycle and epithelial-mesenchymal transition regulatory proteins in liver cancer. Oncotarget. 2015;6(10):8089-8102. [6] Christensen LL, Holm A, Rantala J, et al. Functional screening identifies miRNAs influencing apoptosis and proliferation in colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 2014; 9(6):e96767. [7] Lei SL, Zhao H, Yao HL, et al. Regulatory roles of microRNA-708 and microRNA-31 in proliferation, apoptosis and invasion of colorectal cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 2014;8(4):1768-1774. [8] Lin S, Gregory RI. MicroRNA biogenesis pathways in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2015;15(6):321-333. [9] Hermeking H. The miR-34 family in cancer and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2010;17(2):193-199. [10] Rokavec M, Öner MG, Li H, et al. IL-6R/STAT3/ miR-34a feedback loop promotes EMT-mediated colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis. J Clin Invest. 2014;124(4):1853-1867. [11] Liu C, Kelnar K, Liu B, et al. The microRNA miR-34a inhibits prostate cancer stem cells and metastasis by directly repressing CD44. Nat Med. 2011;17(2): 211-215. [12] Bu P, Chen KY, Chen JH, et al. A microRNA miR-34a-regulated bimodal switch targets Notch in colon cancer stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2013;12(5):602-615. [13] Ji Q, Hao X, Zhang M, et al. MicroRNA miR-34 inhibits human pancreatic cancer tumor-initiating cells. PLoS One. 2009;4(8):e6816. [14] Kang L, Mao J, Tao Y, et al. MicroRNA-34a suppresses the breast cancer stem cell-like characteristics by downregulating Notch1 pathway. Cancer Sci. 2015; 106(6): 700-708. [15] Chen C, Bai LP, Cao FQ, et al. Lin28B mediated IKK-β sustains the stemness of breast cancer stem cell via regulating Wnt/TCF4 and miR-34a/LEF1 signaling pathway. Cancer Res. 2014;74: 3046. [16] 赵欣.载microRNA-34a脂质体靶向治疗肺癌干细胞靶的研究[J].中国生化药物杂志,2014,35(1):68-71. [17] Bjornson CR, Cheung TH, Liu L, et al. Notch signaling is necessary to maintain quiescence in adult muscle stem cells. Stem Cells. 2012;30(2):232-242. [18] Tatarek J, Cullion K, Ashworth T, et al. Notch1 inhibition targets the leukemia-initiating cells in a Tal1/Lmo2 mouse model of T-ALL Blood. 2011;118(6): 1579-1590. [19] Suman S, Das TP, Damodaran C. Silencing NOTCH signaling causes growth arrest in both breast cancer stem cells and breast cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 2013; 109(10):2587-2596. [20] Liu C, Li Z, Bi L, et al. NOTCH1 signaling promotes chemoresistance via regulating ABCC1 expression in prostate cancer stem cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014; 393(1-2):265-270. [21] Sullivan JP, Spinola M, Dodge M, et al. Aldehyde dehydrogenase activity selects for lung adenocarcinoma stem cells dependent on notch signaling. Cancer Res. 2010;70(23):9937-9948. [22] Hassan KA, Wang L, Korkaya H, et al. Notch pathway activity identifies cells with cancer stem cell-like properties and correlates with worse survival in lung adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(8): 1972-1980. [23] Kashat M, Azzouz L, Sarkar SH, et al. Inactivation of AR and Notch-1 signaling by miR-34a attenuates prostate cancer aggressiveness. Am J Transl Res. 2012;4(4):432-442. [24] Schwitalla S, Fingerle AA, Cammareri P, et al. Intestinal tumorigenesis initiated by dedifferentiation and acquisition of stem-cell-like properties. Cell. 2013;152(1-2):25-38. [25] Wang P, Gao Q, Suo Z, et al. Identification and characterization of cells with cancer stem cell properties in human primary lung cancer cell lines. PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e57020. [26] Ponti D, Zaffaroni N, Capelli C, et al. Breast cancer stem cells: an overview. Eur J Cancer. 2006;42(9):1219-1224. [27] Tirino V, Camerlingo R, Franco R, et al. The role of CD133 in the identification and characterisation of tumour-initiating cells in non-small-cell lung cancer. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2009;36(3):446-453. [28] Mizugaki H, Sakakibara-Konishi J, Kikuchi J, et al. CD133 expression: a potential prognostic marker for non-small cell lung cancers. Int J Clin Oncol. 2014; 19(2):254-259. [29] Ha M, Kim VN. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15(8):509-524. [30] Spies N, Burge CB, Bartel DP. 3' UTR-isoform choice has limited influence on the stability and translational efficiency of most mRNAs in mouse fibroblasts. Genome Res. 2013;23(12):2078-2090. [31] Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, et al. Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro- RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(24): 15524-15529. [32] Cuk K, Zucknick M, Heil J, et al. Circulating microRNAs in plasma as early detection markers for breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 2013;132(7):1602-1612. [33] Rane JK, Scaravilli M, Ylipää A, et al. MicroRNA expression profile of primary prostate cancer stem cells as a source of biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Eur Urol. 2015;67(1):7-10. [34] Xua D, Lia S, Zhanga M, et al. microRNAs act as potential regulators in apoptosis and senescence against carcinogenicity induced by environmental pollutants. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology. 2015; 45(4): 319-335. [35] Li N, Fu H, Tie Y, et al. miR-34a inhibits migration and invasion by down-regulation of c-Met expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 2009;275(1):44-53. [36] Yamakuchi M, Ferlito M, Lowenstein CJ. miR-34a repression of SIRT1 regulates apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(36):13421-13426. [37] Nalls D, Tang SN, Rodova M, et al. Targeting epigenetic regulation of miR-34a for treatment of pancreatic cancer by inhibition of pancreatic cancer stem cells. PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e24099. [38] Guessous F, Zhang Y, Kofman A, et al. microRNA-34a is tumor suppressive in brain tumors and glioma stem cells. Cell Cycle. 2010;9(6):1031-1036. [39] Sriuranpong V, Borges MW, Ravi RK, et al. Notch signaling induces cell cycle arrest in small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2001;61(7):3200-3205. [40] Kang J, Kim E, Kim W, et al. Rhamnetin and cirsiliol induce radiosensitization and inhibition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) by miR-34a-mediated suppression of Notch-1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(38):27343-27357. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||