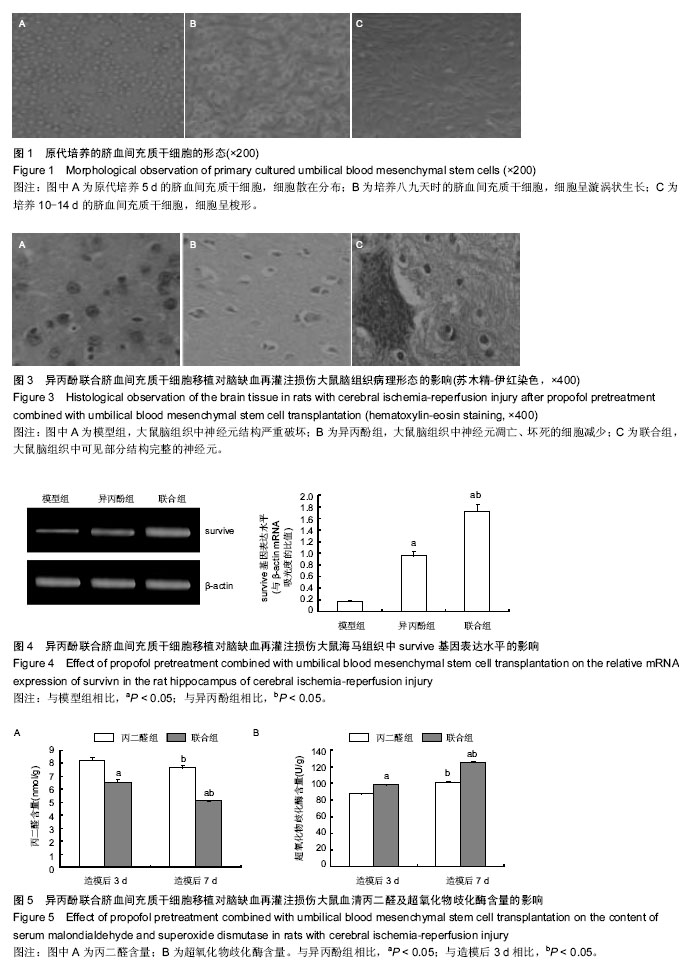
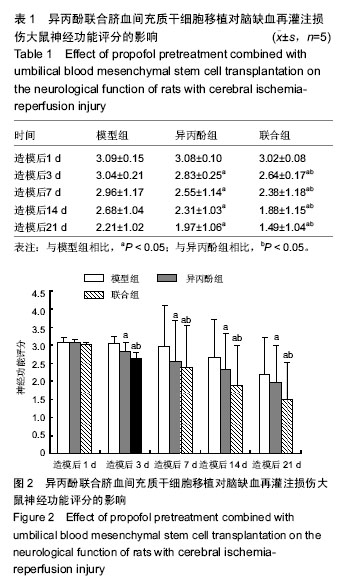
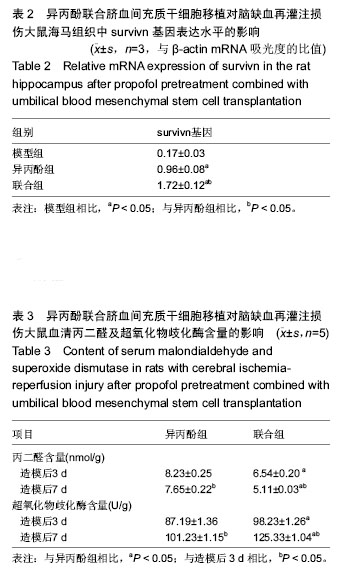
| [1] Koerner IP, Brambrink AM. Brain protection by anesthetic agents. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2006; 19(5):481-486.[2] 于志君,成彩莲.脑缺血再灌注损伤中凋亡调控基因表达的变化及意义[J].武汉科技大学学报:自然科学版,2006, 29(4):425-428.[3] 谭海波,于灵芝,边雯,等.脑缺血再灌注后大鼠氧化水平和神经功能损伤及异丙酚的影响[J].山东大学学报(医学版), 2010,48(1):41-44.[4] 刘显明,李国平,刘月芬.异丙酚对脑缺血-再灌注后大鼠体内氧化水平的影响[J].创伤外科杂志,2008,10(1):61-63.[5] 刘鹏斌,蔡英敏,宋金鑫.异丙酚对大鼠局灶性脑缺血再灌注损伤细胞凋亡的影响[J].第四军医大学学报,2007, 28(8):682- 684.[6] 郭建荣,岳云,崔健君,等.异丙酚对缺血再灌注损伤大鼠海马氨基酸递质水平变化及神经元凋亡的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志,2007,23(8):1547-1550.[7] 唐静,朱京慈.生态营养对重型颅脑损伤后大鼠超氧化物歧化酶及丙二醛的影响[J].中国实用护理杂志,2007, 23(9):1-3.[8] 吕平,林明涛.银杏内酯对活性氧自由基和过氧化氢清除作用的研究[J].华北农学报,2010,25(1):151-154.[9] Tuttolomondo A, Di Sciacca R, Di Raimondo D, et al. Neuron protection as a therapeutic target in acute ischemic stroke. Curr Top Med Chem. 2009; 9(14): 1317-1334.[10] Zhu SM, Xiong XX, Zheng YY, et al. Propofol inhibits aquaporin 4 expression through a protein kinase C-dependent pathway in an astrocyte model of cerebral ischemia/reoxygenation. Anesth Analg. 2009; 109(5):1493-1499. [11] 侯玲玲,曹华,魏国荣,等.人脐血间充质干细胞体外扩增和向神经元样细胞定向诱导分化的研究[J].中华血液学杂志,2002(8):415-419.[12] 王斌,洪小杨,杜江,等.人脐带血间充质干细胞体外诱导分化为神经元样细胞的可行性[J].中华实用儿科临床杂志, 2006,21(10):617-619.[13] Yang Z, Duan H, Mo L, et al. The effect of the dosage of NT-3/chitosan carriers on the proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells. Biomaterials. 2010; 31(18):4846-4854.[14] 何展文,刘木金,孟哲,等.异体骨髓间充质干细胞对 EAE 大鼠神经再生保护作用的研究[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2015,18(4):1-4.[15] 戴文达,方涛林,李熙雷,等.人骨髓间充质干细胞的分离培养、多向分化与鉴定[J].复旦学报(医学版),2008,35(3): 448-452.[16] Estécio MR, Gharibyan V, Shen L, et al. LINE-1 hypomethylation in cancer is highly variable and inversely correlated with microsatellite instability. PLoS One. 2007;2(5):e399.[17] 陈娜,周建平,黄安宁,等.异丙酚对缺血再灌注损伤神经细胞的保护作用[J].军医进修学报,2011,32(12): 1253-1256.[18] 钟守琳,陈会平,朱志良,等.异丙酚减轻大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤[J].基础医学与临床,2011,31(7):804-808.[19] 王士雷,王世瑞,李瑜,等.异丙酚和异氟醚对大鼠全脑缺血再灌注损伤的影响[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2006, 11(5):562-564.[20] 贾鹤龄,冷玉芳,张彬.靶控输注异丙酚对心脏瓣膜置换术患者炎性细胞因子浓度变化的影响[J].兰州大学学报(医学版),2010, 36(1):78-81.[21] 沈宁,甘小亮,黑子清,等.异丙酚对沙土鼠全脑缺血再灌注后脑保护作用研究[J].中山大学学报(医学科学版),2010, 31(3):354-358.[22] Zhou QB, Jia Q, Zhang Y, et al. "Effects of baicalin on protease-activated receptor-1 expression and brain injury in a rat model of intracerebral hemorrhage". Chin J Physiol. 2012;55(3):202-209.[23] Li Q, Lu J, Wang XY.Propofol and remifentanil at moderate and high concentrations affect proliferation and differentiation of neural stem/progenitor cells. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9 (22):2002-2007.[24] Sahin1 M, Gullu H, Peker K,et al.Does the intrathecal propofol have a neuroprotective effect on spinal cord ischemia? . Neural Regen Res. 2015; 10(11): 1825-1829.[25] Manaenko A, Sun X, Kim CH, et al. PAR-1 antagonist SCH79797 ameliorates apoptosis following surgical brain injury through inhibition of ASK1-JNK in rats. Neurobiol Dis. 2013;50:13-20.[26] Chen WF, Lee JJ, Chang CC, et al. Platelet protease-activated receptor (PAR)4, but not PAR1, associated with neutral sphingomyelinase responsible for thrombin-stimulated ceramide-NF-κB signaling in human platelets. Haematologica. 2013;98(5):793-801.[27] Babu R, Bagley JH, Di C, et al. Thrombin and hemin as central factors in the mechanisms of intracerebral hemorrhage-induced secondary brain injury and as potential targets for intervention. Neurosurg Focus. 2012;32(4):E8.[28] Mead B, Scheven BA.Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for retinal ganglion cell neuroprotection and axon regeneration. Neural Regen Res. 2015; 10(3): 371-373.[29] 王华,熊英,母得志.配对免疫球蛋白B抑制新生大鼠缺氧缺血损伤神经元细胞再生的研究[J].中国新生儿科杂志, 2012,27(4):269-273.[30] Bao X, Wei J, Feng M, et al. Transplantation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells promotes behavioral recovery and endogenous neurogenesis after cerebral ischemia in rats. Brain Res. 2011;1367:103-113.[31] Wang J, Jin H, Hua Y, et al. Role of protease-activated receptor-1 in brain injury after experimental global cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 2012;43(9):2476-2482.[32] Crigler L, Robey RC, Asawachaicharn A, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cell subpopulations express a variety of neuro-regulatory molecules and promote neuronal cell survival and neuritogenesis. Exp Neurol. 2006;198(1):54-64. |