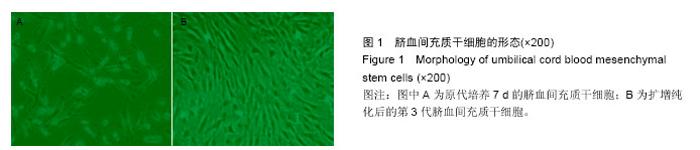
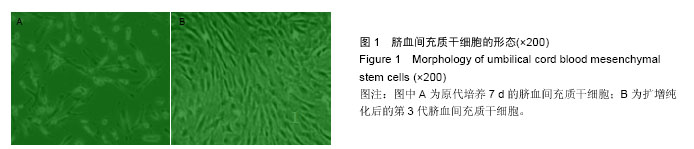
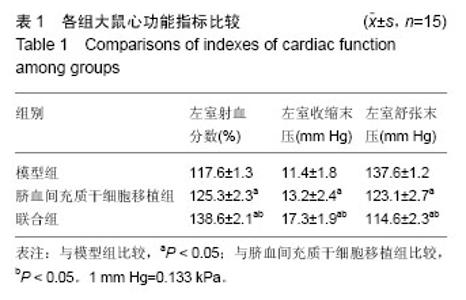
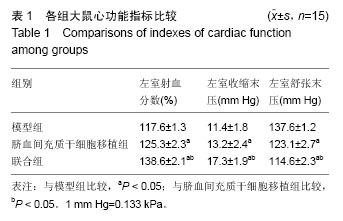
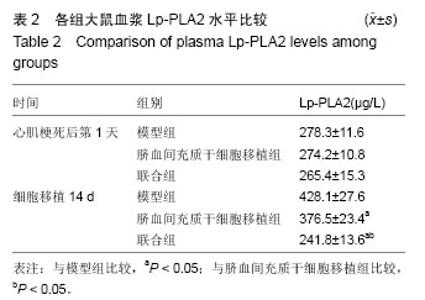
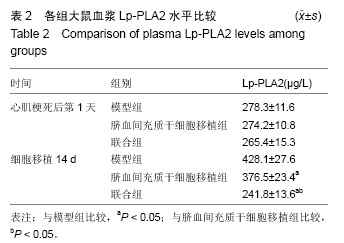
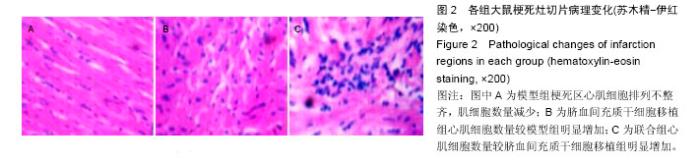
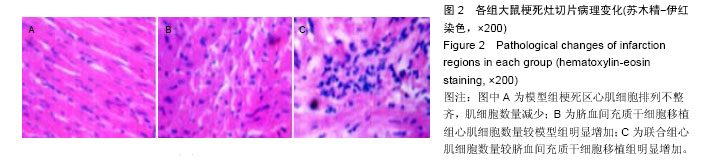
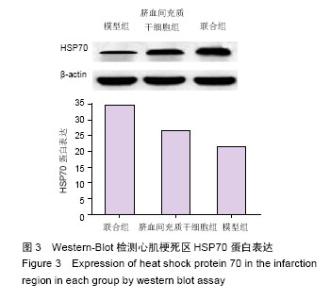
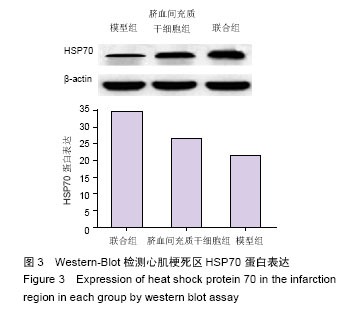
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (19): 2796-2802.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.19.009
Previous Articles Next Articles
Rosuvastatin combined with umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cell transplantation improves cardiac function after acute myocardial infarction
Wang Yan-li1, Li Jin-feng1, Wang Yan-ping2, Gao Ming1
- 1Department of Cardiology, Kailuan General Hospital of Tangshan, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China
2Zunhua People’s Hospital of Tangshan, Tangshan 064200, Hebei Province, China
-
Received:2016-03-18Online:2016-05-06Published:2016-05-06 -
About author:Wang Yan-li, Master, Attending physician, Department of Cardiology, Kailuan General Hospital of Tangshan, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Yan-li, Li Jin-feng, Wang Yan-ping, Gao Ming. Rosuvastatin combined with umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cell transplantation improves cardiac function after acute myocardial infarction[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(19): 2796-2802.
share this article
| [1] Pavo N, Charwat S, Nyolczas N, et al. Cell therapy for human ischemic heart diseases: critical review and summary of the clinical experiences. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014;75:12-24.[2] Hassink RJ, Dowell JD, Brutel de la Rivière A, et al. Stem cell therapy for ischemic heart disease. Trends Mol Med. 2003;9(10):436-441.[3] Molkentin JD. The zinc finger-containing transcription factors GATA-4, -5, and -6. Ubiquitously expressed regulators of tissue-specific gene expression. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(50):38949-38952.[4] 王永,吴继雄.骨髓间充质干细胞分化为心肌细胞的研究进展[J].心脏杂志,2008,20(2):229-231.[5] Ishida K, Geshi T, Nakano A, et al. Beneficial effects of statin treatment on coronary microvascular dysfunction and left ventricular remodeling in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol. 2012;155(3): 442-447.[6] Tang XL, Sanganalmath SK, Sato H, et al. Atorvastatin therapy during the peri-infarct period attenuates left ventricular dysfunction and remodeling after myocardial infarction. PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e25320.[7] Mathur N, Ramasubbu K, Mann DL. Spectrum of pleiotropic effects of statins in heart failure. Heart Fail Clin. 2008 Apr;4(2):153-161.[8] Cai A, Zheng D, Dong Y, et al. Efficacy of Atorvastatin combined with adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on cardiac function in rats with acute myocardial infarction. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2011;43(11):857-866.[9] 胡承恒,伍贵富,王小庆,等.人脐血单个核细移植治疗大鼠急性心肌梗死的实验研究[J].中华心血管病杂志, 2006, 34(7):587-590.[10] 何志裕, 陆东风.人脐带血间充质干细胞移植对急性心肌梗死大鼠心功能的影响[J].血栓与止血学,2010, 16(6): 244-249.[11] Brilakis ES, Khera A, Saeed B, et al. Association of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 mass and activity with coronary and aortic atherosclerosis: findings from the Dallas Heart Study. Clin Chem. 2008;54(12):1975-1981.[12] Przybyt E, Harmsen MC. Mesenchymal stem cells: promising for myocardial regeneration. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013;8(4):270-277.[13] Mohanty IR, Arya DS, Gupta SK. Withania somnifera provides cardioprotection and attenuates ischemia- reperfusion induced apoptosis. Clin Nutr. 2008;27(4): 635-642.[14] Pfeffer MA, Braunwald E. Ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction. Experimental observations and clinical implications. Circulation. 1990;81(4):1161- 1172.[15] Ballard VL. Stem cells for heart failure in the aging heart. Heart Fail Rev. 2010;15(5):447-456.[16] Bjugstad KB, Teng YD, Redmond DE Jr, et al. Human neural stem cells migrate along the nigrostriatal pathway in a primate model of Parkinson's disease. Exp Neurol. 2008;211(2):362-369.[17] Hodgkinson CP, Gomez JA, Mirotsou M, et al. Genetic engineering of mesenchymal stem cells and its application in human disease therapy. Hum Gene Ther. 2010;21(11):1513-1526.[18] Tang J, Xie Q, Pan G, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells participate in angiogenesis and improve heart function in rat model of myocardial ischemia with reperfusion. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2006;30(2):353-361.[19] Li F, Miao ZN, Xu YY, et al. Transplantation of human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of focal cerebral ischemia. Mol Med Rep. 2012; 6(3): 625-630.[20] Xu X, Xu Z, Xu Y, et al. Selective down-regulation of extracellular matrix gene expression by bone marrow derived stem cell transplantation into infarcted myocardium. Circ J. 2005;69(10):1275-1283.[21] Wei JP, Zhang TS, Kawa S, et al. Human amnion-isolated cells normalize blood glucose in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Cell Transplant. 2003;12(5):545-552.[22] Tropel P, Noël D, Platet N, et al. Isolation and characterisation of mesenchymal stem cells from adult mouse bone marrow. Exp Cell Res. 2004;295(2): 395-406.[23] Fukuhara S, Tomita S, Yamashiro S, et al. Direct cell-cell interaction of cardiomyocytes is key for bone marrow stromal cells to go into cardiac lineage in vitro. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2003;125(6):1470-1480.[24] Davidson MH, Corson MA, Alberts MJ, et al. Consensus panel recommendation for incorporating lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 testing into cardiovascular disease risk assessment guidelines. Am J Cardiol. 2008;101(12A):51F-57F.[25] Brilakis ES, Khera A, McGuire DK, et al. Influence of race and sex on lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 levels: observations from the Dallas Heart Study. Atherosclerosis. 2008;199(1):110-115.[26] Koenig W, Twardella D, Brenner H, et al. Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 predicts future cardiovascular events in patients with coronary heart disease independently of traditional risk factors, markers of inflammation, renal function, and hemodynamic stress. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26(7):1586-1593. [27] 陈志扬,薛张纲,蒋豪.静脉复合胸段硬膜外阻滞对兔心肌梗死后c-fos和HSP70基因表达的影响[J].中华麻醉学杂志,2002, 22(5):294-296.[28] Knowlton AA, Brecher P, Apstein CS. Rapid expression of heat shock protein in the rabbit after brief cardiac ischemia. J Clin Invest. 1991;87(1):139-147.[29] 吕彩萍,陈爱华.他汀类药物的临床应用进展[J].中国心血管病研究,2014,12(8) :748-752.[30] Sheng FQ, Xu R, Cheng LX, et al. In rats with myocardial infarction, interference by simvastatin with the TLR4 signal pathway attenuates ventricular remodelling. Acta Cardiol. 2009;64(6):779-785.[31] Ishida K, Geshi T, Nakano A, et al. Beneficial effects of statin treatment on coronary microvascular dysfunction and left ventricular remodeling in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol. 2012;155(3): 442-447.[32] 刘振吉,赵树芬,张玉榕.瑞舒伐他汀强化治疗对心肌梗死患者PCI术后APN?BNP的影响[J].国际医药卫生导报, 2014,20(9):1229-1232.[33] 彭兰兰.瑞舒伐他汀对慢性心力衰竭患者血清细胞因子及心功能的影响[J]. 河南医学研究, 2015,24(7):17-18.[34] Ridker PM, Danielson E, Fonseca FA, et al. Rosuvastatin to prevent vascular events in men and women with elevated C-reactive protein.N Engl J Med. 2008;359(21):2195-2207. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [3] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [4] | Nie Huijuan, Huang Zhichun. The role of Hedgehog signaling pathway in transforming growth factor beta1-induced myofibroblast transdifferentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 754-760. |
| [5] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [6] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [7] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [8] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [9] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [10] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [11] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [12] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [13] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [14] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [15] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||