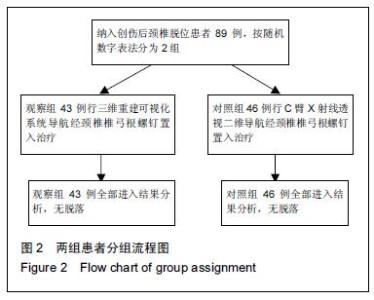
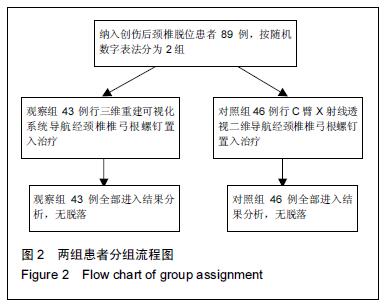
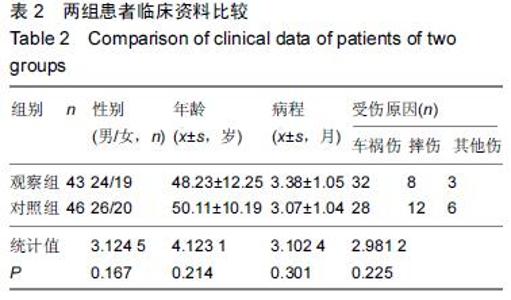
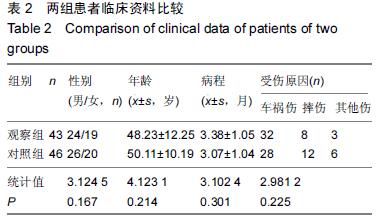
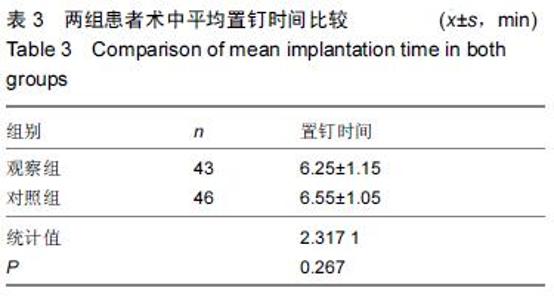
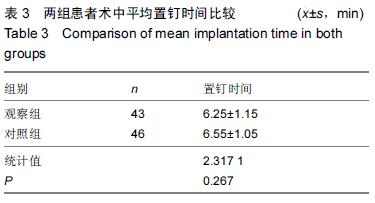
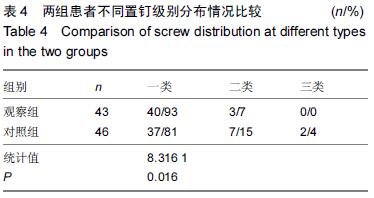
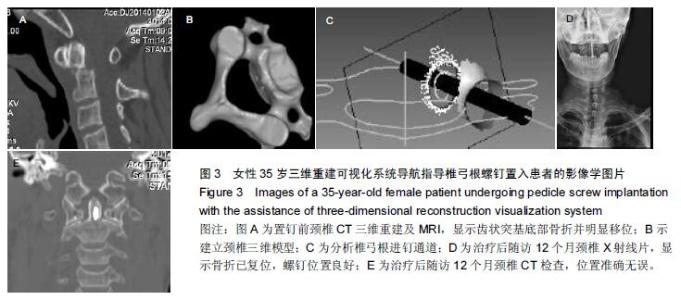
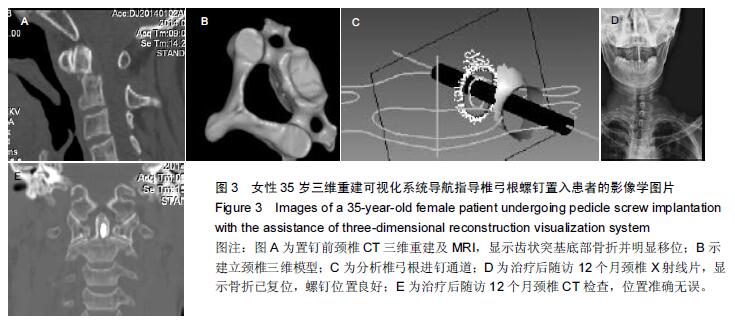
| [1] 谢伟,张倩倩,王德峰,等.颈椎椎弓根钉内固定治疗急性颈椎损伤的临床观察[J].中国实用医药,2012,7(25): 57-58. [2] 刘雅,王宗亮,蔡明,等.颈椎弓根钉技术在下颈椎骨折中的临床应用[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志,2009,5(1): 38-40. [3] 陈晓明,肖增明,宗少晖,等.计算机导航引导下脊柱后路椎弓根螺钉置入内固定:准确性及安全性[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(13):2119-2124. [4] 王亚明,程岗,张剑宁,等.颈髓战创伤早期三维可视图像技术引导颈椎内固定[C].//第二届中国医师协会神经损伤年会暨第二届天坛全国神经创伤学术研讨会论文集,2013: 196-199. [5] Lehman RA Jr,Kuklo TR,Belmont PJ Jr, et al. Advantage of pedicle screw fixation directed into the apex of the sacral promontory over bicortical fixation: a biomechanical analysis.Spine. 2002;27(8): 806-811. [6] Lehman-RA Jr,Polly-DW Jr,Kuklo TR, et al. Straight-forward versus anatomic trajectory technique of thoracic pedicle screw fixation: a biomechanical analysis. Spine. 2003;28(18):2058-2065. [7] 陈晓明,陈前芬,肖增明,等.腰骶骨椎弓根螺钉置入内固定:CT三维重建虚拟导航的辅助[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(9):1447-1451 [8] 王玮琦,覃涛,王婷,等.计算机3D建模在个体化寰枢椎椎弓根钉最佳进钉方式的研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志, 2015,33(3):295-300. [9] 刘恩志,郭东明,蔡维山,等.改良二维X线导航模拟椎体三维影像引导胸腰段椎弓根钉内固定的临床应用[J].中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志,2010,2(2):102-106. [10] 王亚明.与颅颈交界区、颈椎椎弓根内固定相关应用解剖和三维可视化图像引导椎弓根螺钉个体化植入研究[D].第二军医大学,2007. [11] 王小平,齐伟力,黄志澎,等.上颈椎运动节段数字模型建立及三维可视化研究[J].汕头大学医学院学报,2008,21(2): 87-89,封4. [12] 吕浩然,杨进顺,黄彦,等.三维导航引导下骨水泥椎体强化椎弓根钉在骨质疏松患者中的应用研究[J].微创医学, 2014,9(4):398-401. [13] 王长昇,史艳光,许卫红,等.寰枢椎椎弓根钉棒系统内固定治疗牵引复位不稳定型寰枢椎脱位[J].中华创伤杂志, 2011,27(2):128-132. [14] Chan CY,Kwan MK,Saw LB,et al.Thoracic pedicle screw insertion in Asian cadaveric specimen: does radiological pedicle profile affect outcome? Surg Radiol Anat. 2011;33(1):19-25. [15] 宋西正,王文军,薛静波,等.经皮椎弓根螺钉内固定联合骶前间隙轴向椎间融合治疗L5椎体滑脱症[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2014,24(5):407-411. [16] 魏建新.半椎体脊柱侧弯后路矫形中横向连接装置作用的有限元分析[D].河北医科大学,2013. [17] 靳冬,张果忠.椎弓根螺钉内固定及计算机导航技术的发展与应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(30): 5644-5647. [18] 移平,谭明生,杨峰,等.颈椎弓根钉固定治疗颈椎失稳症的临床应用[C].//中国老年学学会老年脊柱关节疾病专业委员会成立大会暨第一届学术大会论文汇编,2008: 117. [19] Yang BP, Wahl MM, Idler CS, et al. Percutaneous lumbar pedicle screw placement aided by computer-assisted fluoroscopy-based navigation: Perioperative results of a prospective, comparative, multicenter study. Spine. 2012;37(24):2055-2060. [20] 周栋,徐南伟,农鲁明,等.CT三维导航系统辅助胸椎椎弓根钉治疗胸椎骨折[J].中华医学杂志,2010,90(23): 1612-1614. [21] 谢瑞刚,葛英辉,史大鹏,等.椎弓根钉道参数CT三维测量方法的准确性分析[J].放射学实践,2010,25(12): 1392-1395. [22] 李晔,王以朋,仉建国,等.脊柱后路截骨并三维矫形及3代椎弓根钉系统置入治疗休门氏病脊柱后凸畸形:同一机构7年9例资料回顾[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(43):8167-8170. [23] Kramer DL, Ludwig SC, Balderston RA, et al. placement of pedicle screws in the cervical spine: comparative accuracy of cervical pedicle screw placement using three techniques(abstract). Orthop Trans. 1997;21(2): 484. [24] Ludwig SC, Kramer DL, Balderston RA, et al. Placement of pedicle screws in the human cadaveric cervical spine: comparative accuracy of three techniques. Spine. 2000;25(13):1655-1667. [25] Kotani Y, Abumi K, Ito M, et al. Improved accuracy of computer-assisted cervical pedicle screw insertion. Neurosurg. 2003;99(Suppl 3): 257-263. [26] Steven C, Ludwig MD, Joseph M, et al. Cervical pedical screws:comparative accuracy of two insertion techniques. Spine. 2000;25(20): 2675-268. [27] 未东兴,张震,王九辉,等.计算机重建技术辅助胸椎椎弓根钉置入的准确性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011, 15(4):593-596. [28] Stauff MP, Freedman BA, Kim JH, et al. The effect of pedicle screw redirection after lateral wall breach - A biomechanical study using human lumbar vertebrae. Spine J. 2014;14(1):98-103. [29] Augustine KE, Stans AA, Morris JM, et al. Plan to procedure: combining 3D templating with rapid prototyping toenhance pedicle screw placement[C].//Medical imaging 2010. Part one of two parts, Visualization, image-guided procedures, and modeling.2010:76250S:1-76250S:10. [30] Knox JB, Dai JM 3rd, Orchowski JR. Superior segment facet joint violation and cortical violation after minimally invasive pedicle screw placement. Spine J. 2011;11(3): 213-217. [31] Rao PJ, Mobbs RJ. The “TFP” Fusion Technique for Posterior 360° Lumbar Fusion: a Combination of Open Decompression, Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion, and Facet Fusion with Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Fixation. Orthop Surg. 2014;6(1):54-59. [32] 王亚明,田增民,郑奎宏,等.三维可视化图像引导枢椎椎弓根螺钉个体化置入[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2007,17(10): 769-772. [33] 陈雍君,赵慧毅,谢柏臻,等.寰椎椎弓根钉内固定通道的三维CT影像学研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2012,27(1): 1-3. [34] Lee CS,Kim MJ,Ahn YJ,et al.Thoracic pedicle screw insertion in scoliosis using posteroanterior C-arm rotation method. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2007;20(1): 66-71. [35] 葛志强,苗洁,李冠军,等.术前三维CT 测量个体化颈椎椎弓根置钉的应用研究[J].河北医药,2013,35(9): 1312-1314. [36] 樊继宏,焦培峰,刘畅,等.颈椎间盘髓核的计算机三维可视化与多参数测量[C].//中国解剖学会2010年年会论文集. 2010:22-22. [37] Chan CY,Kwan MK,Saw LB,et al.Safety of thoracic pedicle screw application using the funnel technique in Asians: a cadaveric evaluation. Eur Spine J. 2010; 19(1): 78-84. [38] 蔡维山,徐中和,郭东明,等.CT三维重建椎弓根钉导航系统在胸椎手术中的应用[J].中华骨科杂志, 2005,25(8): 458-461. [39] 陈为坚,段扬,林周胜,等.基于三维有限元法的腰椎动态稳定系统建立及生物力学行为初步分析[J].广东医学, 2015, 36(10):1497-1499,1500. [40] 范子文,谢楚海,黄彦,等.三维CT重建辅助胸椎椎弓根钉置入的实验研究[J].现代医院,2012,12(1):16-19. |