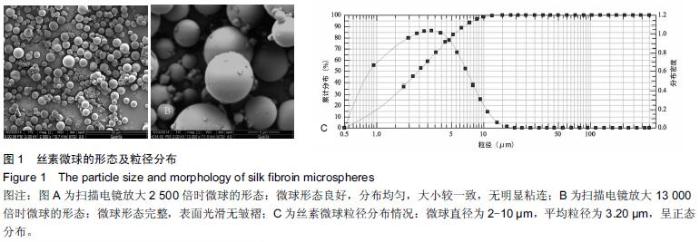
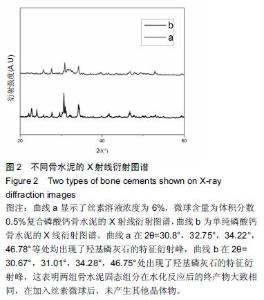
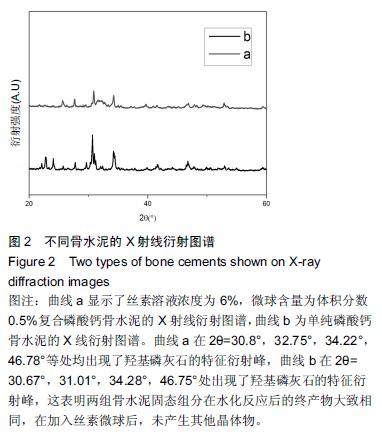
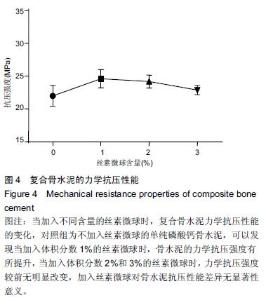
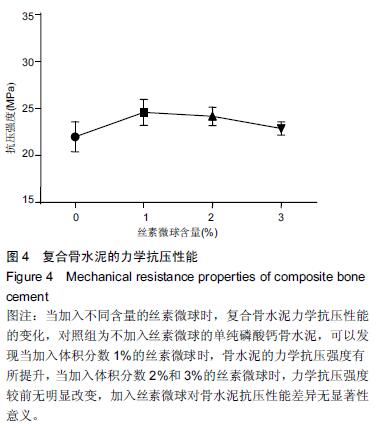
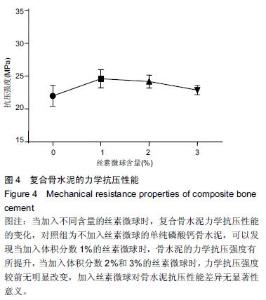
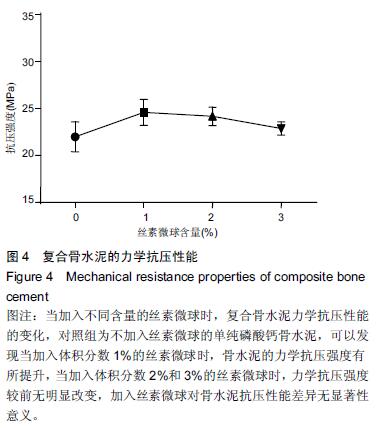
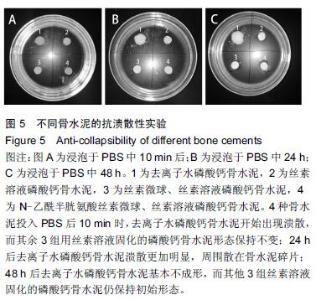
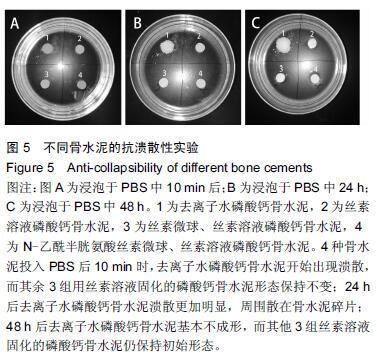
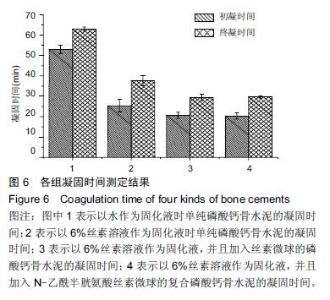
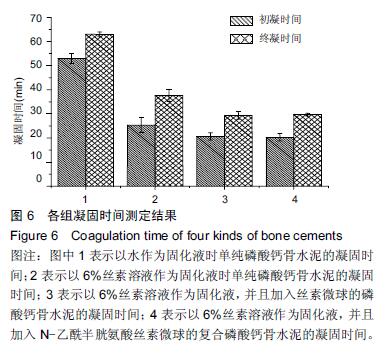
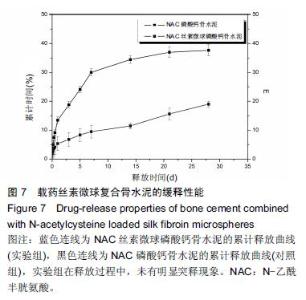
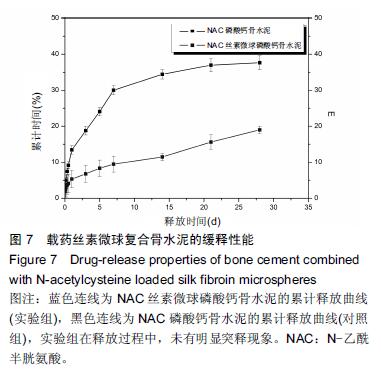
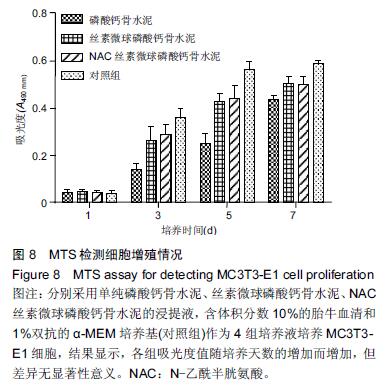
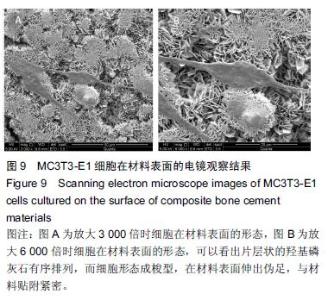
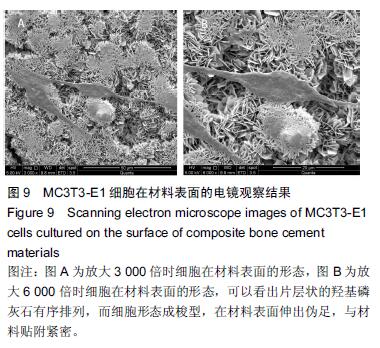
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (16): 2294-2302.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.16.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Calcium phosphate cement incorporated with N-acetylcysteine-loaded silk fibroin microspheres: preparation and characterization
Jiang Lei, Pi Bin, Feng Tao, Li Bin, Lu Ying-jie, Yang Hui-lin, Zhu Xue-song
- Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Orthopedic Institute of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2016-03-07Online:2016-04-15Published:2016-04-15 -
Contact:hu Xue-song, Master, Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Orthopedic Institute of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China Yang Hui-lin, M.D., Professor, Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Orthopedic Institute of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Jiang Lei, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Orthopedic Institute of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China Pi Bin, M.D., Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Orthopedic Institute of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China Jiang Lei and Pi Bin contributed equally to this work. -
Supported by:the National High-Technology Development and Research Project of China (863 Project), No. 2015AA020316; the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81171689, 81301559; the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, No. SBK201341421; the Graduate Scientific Innovation Plan of Universities in Jiangsu Province, No. CXZZ11-0123
Cite this article
Jiang Lei, Pi Bin, Feng Tao, Li Bin, Lu Ying-jie, Yang Hui-lin, Zhu Xue-song. Calcium phosphate cement incorporated with N-acetylcysteine-loaded silk fibroin microspheres: preparation and characterization[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(16): 2294-2302.
share this article
| [1] Nakamura T, Matsumine A, Asanuma K,et al. Treatment of bone defect with calcium phosphate cement subsequent to tumor curettage in pediatric patients. Oncol Lett. 2016;11(1):247-252. [2] Yuan H, Li Y, de Bruijn JD, et al. Tissue responses of calcium phosphate cement: a study in dogs. Biomaterials. 2000;21:1283-1290. [3] Ito T, Otsuka M. Application of calcium phosphate as a controlled-release device. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013; 36(11): 1676-1682. [4] Pastorino D, Canal C, Ginebra MP. Drug delivery from injectable calcium phosphate foams by tailoring the macroporosity-drug interaction. Acta Biomater. 2015: 250-259. [5] Kerckhofs G, Chai YC, Luyten FP. Combining microCT-based characterization with empirical modelling as a robust screening approach for the design of optimized CaP-containing scaffolds for progenitor cell-mediated bone formation. Acta Biomater. 2016. [6] Gu Y, Chen L, Yang HL, et al. Evaluation of an injectable silk fibroin enhanced calcium phosphate cement loaded with human recombinant bone morphogenetic protein-2 in ovine lumbar interbody fusion. J Biomed Mater ResA. 2011;97(2):177-185. [7] Chen L, Gu Y, Feng Y, et al. Bioactivity of porous biphasic calcium phosphate enhanced by recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 2/silk fibroin microsphere. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2014;25(7): 1709-1719. [8] Feng T, Pi B, Li B, et al. N-Acetyl cysteine (NAC)-mediated reinforcement of alpha-tricalcium phosphate/silk fibroin (α-TCP/SF) cement. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2015;136:892-899. [9] Nayak S, Dey S, Kundu SC. Silk sericin-alginate- chitosan microcapsules: hepatocytes encapsulation for enhanced cellular functions. Int J Biol Macromol. 2014; 65:258-266. [10] Wenk E, Merkle HP, Meinel L. Silk fibroin as a vehicle for drug delivery applications. J Control Release. 2011; 150: 128-141. [11] Tsukimura N, Yamada M, Aita H, et al. N-acetyl cysteine (NAC)-mediated detoxification and functionalization of poly (methyl methacrylate) bone cement. Biomaterials. 2009;30:3378-3389. [12] Yamada M, Tsukimura N, Ikeda T, et al. N-acetyl cysteine as an osteogenesis-enhanc ing molecule for bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2013;34: 6147-6156. [13] Hofmann S, Wong CT, Rossetti F, et al. Silk fibroin as an organic polymer for controlled drug delivery. J Control Release. 2006;111:219-227. [14] Lu S, Wang P, Zhang F, et al. A novel silk fibroin nanofibrous membrane for guided bone regeneration: a study in rat calvarial defects. Am J Transl Res. 2015; 7(11):2244-2253. [15] Qiao C, Zhang K, Sun B, et al. Sustained release poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres of bone morphogenetic protein 2 plasmid/calcium phosphate to promote in vitro bone formation and in vivo ectopic osteogenesis. Am J Transl Res. 2015;7(12):2561-2572. [16] Floren ML, Spilimbergo S, Motta A, et al. Carbon dioxide induced silk protein gelation for biomedical applications. Biomacromolecules. 2012;13(7):2060-2072. [17] Elia R, Guo J, Budijono S, et al. Encapsulation of Volatile Compounds in Silk Microparticles. J Coat Technol Res. 2015;12(4):793-799. [18] Ye M, Zeng S, Gao W, et al. Preparation and characterization of genipin-crosslinked silk fibroin/chitosan controlled-release microspheres. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2014;34(6):875-879. [19] Liu LS, Thompson AY, Heidaran MA, et al. An osteoconductive collagen/hyaluronate matrix for bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 1999;20(12): 1097-1108. [20] Budiraharjo R, Neoh KG, Kang ET. Hydroxyapatite-coated carboxymethyl chitosan scaffolds for promoting osteoblast and stem cell differentiation. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2012;366(1): 224-232. [21] 鲁红,田宇,吴织芬.珊瑚转化羟基磷灰石应用于牙周组织工程的细胞相容性和细胞毒性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(16):2955-2958. [22] Matsuoka H, Akiyama H, Okada Y, et al. In vitro analysis of the stimulation of bone formation by highly bioactive apatite- and wollastonite-containing glass-ceramic: released calcium ions promote osteogenic differentiation in osteoblastic ROS17/2.8 cells. J Biomed Mater Res. 1999;47(2):176-188. [23] Yang HL, Zhu XS, Chen L, et al. Bone healing response to a synthetic calcium sulfate/beta-tricalcium phosphate graft material in a sheep vertebral body defect model, J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2012;(100):1911-1921. [24] Zhang J, Liu W, Gauthier O, et al. A simple and effective approach to prepare injectable macroporous calcium phosphate cement for bone repair: syringe-foaming using a viscous hydrophilic polymeric solution. Acta Biomater. 2016;31:326-338. [25] Ratanavaraporn J, Kanokpanont S, Damrongsakkul S. The development of injectable gelatin/silk fibroin microspheres for the dual delivery of curcumin and piperine. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2014;25(2):401-410. [26] Preda R, Leisk G, Omenetto F, et al. Bioengineered silk proteins to control cell and tissue functions. Methods Mol Biol. 2013;996:19-41. [27] Habraken WJ, Wolke JG, Mikos AG, et al. Porcine gelatin microsphere/calcium phosphate cement composites: an in vitro degradation study. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2009;91(2):555-561. [28] 武莉,朱振锋,杨菁,等.影响微球药物释放因素的研究[J].生物医学工程与临床,2003,7(3):135-137. [29] 曹阳,王伯初,迟少萍,等.基于丝素蛋白的药物缓释材料[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(8):1533-1536. [30] Link DP, van den Dolder J, Wolke JG, et al. The cytocompatibility and early osteogenic characteristics of an injectable calcium phosphate cement. Tissue Eng. 2007;13(3):493-500. [31] Feng T, Pi B, Li B, et al. N-Acetyl cysteine (NAC)-mediated reinforcement of alpha-tricalcium phosphate/silk fibroin (α-TCP/SF) cement. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2015;136:892-899. [32] Yu T, Jiang T, Wei QM, et al. Wound healing effects of silk fibroin-bone morphogenetic protein-2 scaffolds on inflammatory pulp in rats. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao. 2015;47(5):814-819. [33] Buga MR, Zaharia C, B?lan M, et al. Surface modification of silk fibroin fibers with poly (methyl methacrylate) and poly (tributylsilyl methacrylate) via RAFT polymerization for marine antifouling applications. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015; 51:233-241. [34] Gu Y, Chen L, Yang HL, et al. Evaluation of an injectable silk fibroin enhanced calcium phosphate cement loaded with human recombinant bone morphogenetic protein-2 in ovine lumbar interbody fusion. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2011;97(2):177-185. [35] Wang CH, Hsieh CY, Hwang JC. Flexible organic thin-film transistors with silk fibroin as the gate dielectric. Adv Mater. 2011;23(14):1630-1634. [36] Ding T, Yang H, Maltenfort M, et al. Silk fibroin added to calcium phosphate cement to prevent severe cardiovascular complications. Med Sci Monit. 2010; 16(9):HY23-HY26. [37] Qu Y, Yang Y, Li J, et al. Preliminary evaluation of a novel strong/osteoinductive calcium phosphate cement. J Biomater Appl. 2011;26(3):311-325. [38] Kim DH, Viventi J, Amsden JJ, et al. Dissolvable films of silk fibroin for ultrathin conformal bio-integrated electronics. Nat Mater. 2010;9(6):511-517. [39] Takeuchi A, Ohtsuki C, Miyazaki T, et al. Deposition of bone-like apatite on silk fiber in a solution that mimics extracellular fluid. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2003;65(2): 283-289. [40] Li YH, Wang ZD, Wang W, et al. The biocompatibility of calcium phosphate cements containing alendronate-loaded PLGA microparticles in vitro. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2015;240(11):1465-1471. [41] Simon CG Jr, Khatri CA, Wight SA, et al. Preliminary report on the biocompatibility of a moldable, resorbable, composite bone graft consisting of calcium phosphate cement and poly (lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres. J Orthop Res. 2002;20(3):473-482. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||