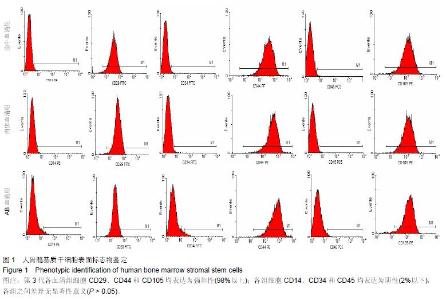
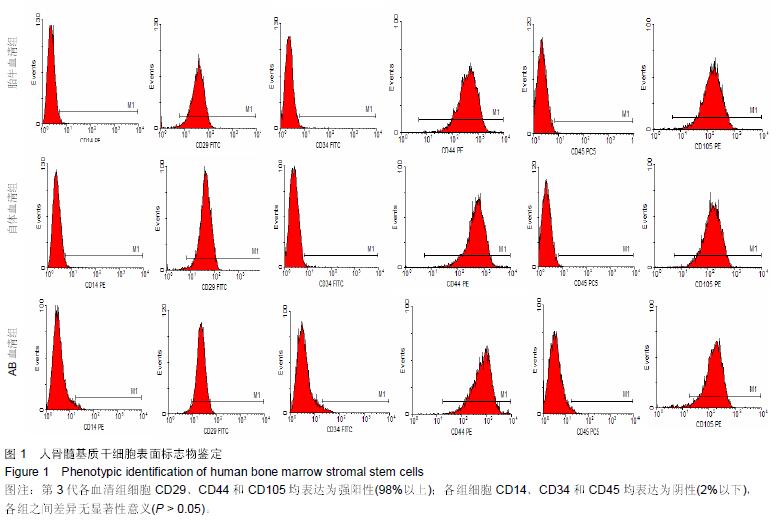
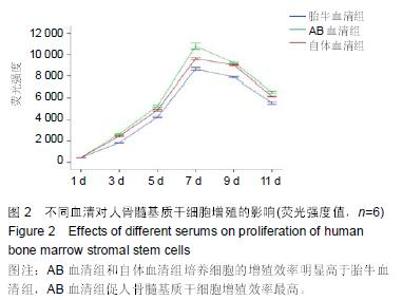
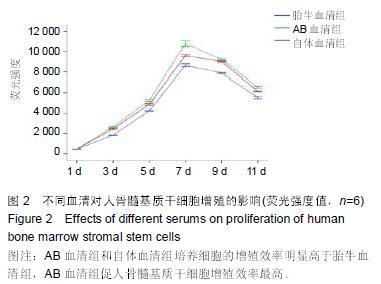
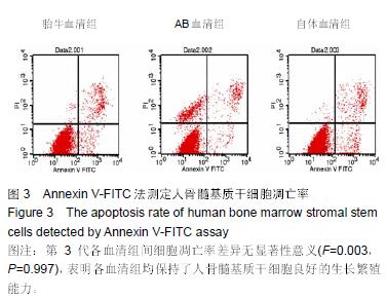
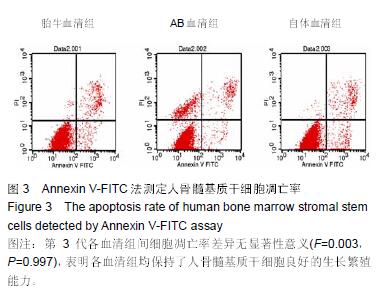
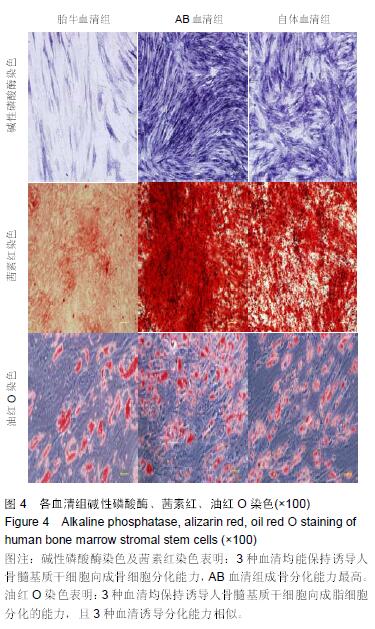
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (45): 7242-7248.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.45.005
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of allogeneic versus autologous serum on the proliferation of bone marrow stromal stem cells
Li Fang-guo1, Lu Yan-dong1, Cui Meng1, Zhao Jia-guo1, Yang Qiang1, Wang Lei2, Pei Guo-xian3, Sun Jie1
- 1Department of Orthopedic Traumatology, Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin 300211, China; 2Department of Orthopedic Traumatology, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China; 3International College of Orthopedics Education, Fourth Military Medical University of Chinese PLA, Xi’an 710032, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Received:2015-09-11Online:2015-11-05Published:2015-11-05 -
Contact:Sun Jie, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedic Traumatology, Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin 300211, China -
About author:Li Fang-guo, Master, Physician, Department of Orthopedic Traumatology, Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin 300211, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 31470937, 331300798; President Foundation of Nanfang Hospital, No. 2014CO14
Cite this article
Li Fang-guo, Lu Yan-dong, Cui Meng, Zhao Jia-guo, Yang Qiang, Wang Lei, Pei Guo-xian, Sun Jie. Effects of allogeneic versus autologous serum on the proliferation of bone marrow stromal stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(45): 7242-7248.
share this article
|
[1] Service RF. Tissue engineers build new bone. Science. 2000;289(5484):1498-1500.
[2] Chou ML, Bailey A, Avory T, et al. Removal of transmissible spongiform encephalopathy prion from large volumes of cell culture media supplemented with fetal bovine serum by using hollow fiber anion-exchange membrane chromatography. PLoS One. 2015;10(4):e0122300.
[3] Vacanti CA, Bonassar LJ, Vacanti MP, et al. Replacement of an avulsed phalanx with tissue-engineered bone. N Engl J Med. 2001;344(20):1511-1514.
[4] Plomer A, Taymor KS, Scott CT. Challenges to human embryonic stem cell patents. Cell Stem Cell. 2008;2(1):13-17.
[5] 但洋,刘鹏,刘琦斌,等. 骨形态发生蛋白-2、-4和-6在脂肪间充质干细胞向软骨细胞诱导中的调节作用[J].中华实验外科杂志, 2014,31(4):808-811.
[6] Feldman GJ, Billings PC, Patel RV, et al. Over-expression of BMP4 and BMP5 in a child with axial skeletal malformations and heterotopic ossification: a new syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2007;143A(7):699-706.
[7] 王庆,陈光兴,郭林,等.腺病毒介导的骨形态发生蛋白-2和骨形态发生蛋白-7基因联合转染大鼠脂肪来源干细胞对成骨分化的影响[J].中华实验外科杂志,2013,30(3):599-601.
[8] 王清富,陈庄洪,蔡贤华,等.聚乙烯亚胺介导骨形态发生蛋白2基因转染兔脂肪干细胞的研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2014, 31(7): 1472-1474.
[9] Feng W, McCabe NP, Mahabeleshwar GH, et al. The angiogenic response is dictated by beta3 integrin on bone marrow-derived cells. J Cell Biol. 2008;183(6):1145-1157.
[10] Bieback K, Hecker A, Kocaömer A, et al. Human alternatives to fetal bovine serum for the expansion of mesenchymal stromal cells from bone marrow. Stem Cells. 2009;27(9): 2331-2341.
[11] Shih DT, Burnouf T. Preparation, quality criteria, and properties of human blood platelet lysate supplements for ex vivo stem cell expansion. N Biotechnol. 2015;32(1):199-211.
[12] Bahn JJ, Chung JY, Im W, et al. Suitability of autologous serum for expanding rabbit adipose-derived stem cell populations. J Vet Sci. 2012;13(4):413-417.
[13] Muschler GF, Midura RJ. Connective tissue progenitors: practical concepts for clinical applications. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;(395):66-80.
[14] Turnovcova K, Ruzickova K, Vanecek V, et al. Properties and growth of human bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells cultivated in different media. Cytotherapy. 2009;11(7):874-885.
[15] Poloni A, Maurizi G, Rosini V, et al. Selection of CD271(+) cells and human AB serum allows a large expansion of mesenchymal stromal cells from human bone marrow. Cytotherapy. 2009;11(2):153-162.
[16] 郑东,杨述华,冯勇,等. 骨髓基质干细胞的单克隆化培养和多向分化的实验研究[J].实用骨科杂志,2007,13(5):277-282.
[17] Adamzyk C, Emonds T, Falkenstein J, et al. Different Culture Media Affect Proliferation, Surface Epitope Expression, and Differentiation of Ovine MSC. Stem Cells Int. 2013;2013: 387324.
[18] 韩祥祯,何惠宇,胡杨,等.重组慢病毒载体转染羊骨髓间充质干细胞及成骨基因表达量的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(6): 821-828.
[19] Pittenger MF, Martin BJ. Mesenchymal stem cells and their potential as cardiac therapeutics. Circ Res. 2004;95(1):9-20.
[20] McCarty RC, Gronthos S, Zannettino AC, et al. Characterisation and developmental potential of ovine bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Physiol. 2009;219(2):324-333.
[21] Spees JL, Gregory CA, Singh H, et al. Internalized antigens must be removed to prepare hypoimmunogenic mesenchymal stem cells for cell and gene therapy. Mol Ther. 2004;9(5): 747-756.
[22] Selvaggi TA, Walker RE, Fleisher TA. Development of antibodies to fetal calf serum with arthus-like reactions in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients given syngeneic lymphocyte infusions. Blood. 1997;89(3):776-779.
[23] Bernardi M, Albiero E, Alghisi A, et al. Production of human platelet lysate by use of ultrasound for ex vivo expansion of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. Cytotherapy. 2013;15(8):920-929.
[24] Boos AM, Weigand A, Deschler G, et al. Autologous serum improves bone formation in a primary stable silica-embedded nanohydroxyapatite bone substitute in combination with mesenchymal stem cells and rhBMP-2 in the sheep model. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014;9:5317-5339.
[25] Chimenti I, Gaetani R, Forte E, et al. Serum and supplement optimization for EU GMP-compliance in cardiospheres cell culture. J Cell Mol Med. 2014;18(4):624-634.
[26] Kinzebach S, Bieback K. Expansion of Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal cells under xenogenic-free culture conditions. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2013;129:33-57.
[27] Riordan NH, Madrigal M, Reneau J, et al. Scalable efficient expansion of mesenchymal stem cells in xeno free media using commercially available reagents. J Transl Med. 2015; 13:232.
[28] Kinzebach S, Bieback K. Expansion of Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal cells under xenogenic-free culture conditions. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2013;129:33-57.
[29] Maurer MH. Proteomic definitions of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Int. 2011;2011:704256.
[30] Saeed H, Taipaleenmäki H, Aldahmash AM,et al. Mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEF) exhibit a similar but not identical phenotype to bone marrow stromal stem cells (BMSC). Stem Cell Rev. 2012;8(2):318-328.
[31] Barry FP, Murphy JM. Mesenchymal stem cells: clinical applications and biological characterization. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2004;36(4):568-584.
[32] Kovach TK, Dighe AS, Lobo PI, et al. Interactions between MSCs and immune cells: implications for bone healing. J Immunol Res. 2015;2015:752510.
[33] Kocaoemer A, Kern S, Klüter H, et al. Human AB serum and thrombin-activated platelet-rich plasma are suitable alternatives to fetal calf serum for the expansion of mesenchymal stem cells from adipose tissue. Stem Cells. 2007;25(5):1270-1278.
[34] Shahdadfar A, Frønsdal K, Haug T, et al. In vitro expansion of human mesenchymal stem cells: choice of serum is a determinant of cell proliferation, differentiation, gene expression, and transcriptome stability. Stem Cells. 2005; 23(9):1357-1366.
[35] Hankey DP, McCabe RE, Doherty MJ, et al. Enhancement of human osteoblast proliferation and phenotypic expression when cultured in human serum. Acta Orthop Scand. 2001; 72(4):395-403.
[36] Kobayashi T, Watanabe H, Yanagawa T, et al. Motility and growth of human bone-marrow mesenchymal stem cells during ex vivo expansion in autologous serum. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87(10):1426-1433.
[37] Kuznetsov SA, Mankani MH, Robey PG. Effect of serum on human bone marrow stromal cells: ex vivo expansion and in vivo bone formation.Transplantation. 2000;70(12):1780-1787.
[38] Mar?dziak M, ?mieszek A, Chrz?stek K, et al. Physical Activity Increases the Total Number of Bone-Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Enhances Their Osteogenic Potential, and Inhibits Their Adipogenic Properties. Stem Cells Int. 2015;2015:379093.
[39] Meng YB, Li X, Li ZY, et al. microRNA-21 promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by the PI3K/β-catenin pathway. J Orthop Res. 2015;33(7):957-964.
[40] Raucci MG, Giugliano D, Alvarez-Perez MA, et al. Effects on growth and osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by the strontium-added sol-gel hydroxyapatite gel materials. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2015;26(2):90.
[41] Kim EC, Leesungbok R, Lee SW, et al. Effects of moderate intensity static magnetic fields on human bone marrow- derived mesenchymal stem cells. Bioelectromagnetics. 2015;36(4):267-276.
[42] Aldahmash A, Haack-Sørensen M, Al-Nbaheen M, et al. Human serum is as efficient as fetal bovine serum in supporting proliferation and differentiation of human multipotent stromal (mesenchymal) stem cells in vitro and in vivo. Stem Cell Rev. 2011;7(4):860-868.
|
| [1] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [2] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [5] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [6] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [7] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [8] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [9] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [10] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [11] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [12] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [13] | Li Cai, Zhao Ting, Tan Ge, Zheng Yulin, Zhang Ruonan, Wu Yan, Tang Junming. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB promotes proliferation, differentiation and migration of skeletal muscle myoblast [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1050-1055. |
| [14] | Liu Cong, Liu Su. Molecular mechanism of miR-17-5p regulation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α mediated adipocyte differentiation and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1069-1074. |
| [15] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||