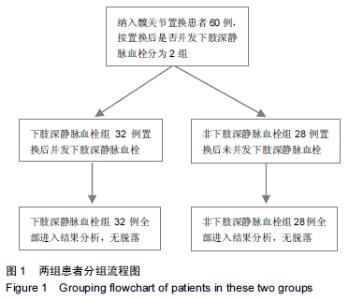
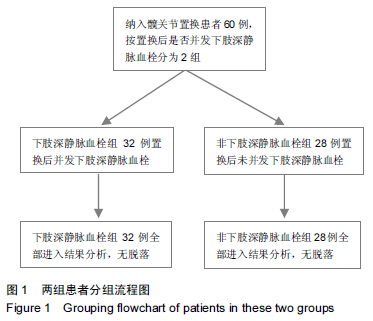
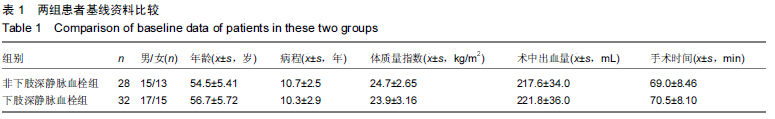
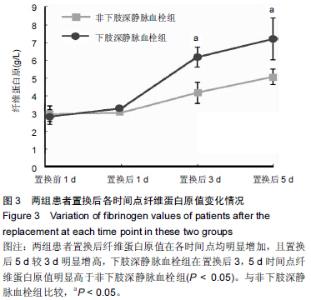
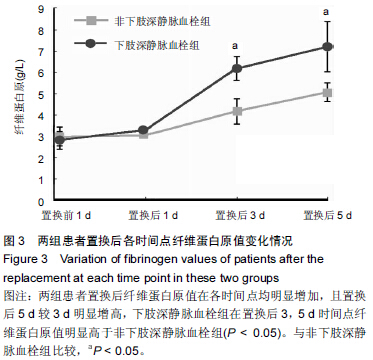
[2] 余鑫,余昌俊,余康敏,等.CD62p、CD63、D-二聚体与下肢深静脉血栓形成的关系[D].安徽:安徽医科大学,2011:7.
[3] Kierkegaard A.Incidence of acute deep vein thrombosis in two districts.A phlebographic study.Acta Chir Scand. 1980;146(4): 267-269.
[4] 吴立华.肝素治疗下肢深静脉血栓与血液流变学的关系[J].中国血液流变学杂志,2003,13(1):43.
[5] 吴建平,徐根方.深静脉血栓病人血浆同型半胱氨酸水平探讨[J].江苏大学学报(医学版),2003,13(5):459-461.
[6] 冯周琴.实用血栓病学[M].郑州:河南科学技术出版社,1995:257.
[7] Bertina RM.Genetic approach to thrombophilia.Thromb Haemost. 2001;86(1):92-103.
[8] Chi YW,Woods TC.Clinical risk factors to predict deep venous thrombosis post-endovenous laser ablation of saphenous veins. Phlebology. 2014;29(3):150-153.
[9] Haake DA,Berkman SA.Venous thromboembolic disease after hip surgery.Risk factors,prophylaxis,and diagnosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989;(242):212-231.
[10] White RH,Gettner S,Newman JM,et al.Predictors of rehospitalization for symptomatic venous thromboembolism after total hip arthroplasty. N Engl J Med. 2000;343(24): 1758-1764.
[11] 胡钦胜,沈彬,杨静,等.动态检测D-二聚体与血浆纤维蛋白原预测全髋置换术后下肢深静脉血栓的价值[J].中国骨与关节杂志, 2013,2(3):133-137.
[12] 李洪军,王海,何成彦,等.血浆纤维蛋白原及D-二聚体检测对老年下肢骨折并发深静脉血栓的早期诊断价值[J].中国实验诊断学, 2007,11(8):1053-1054.
[13] 高丽,屈波,黄敏.人工关节置换术后血流变改变与下肢深静脉血栓形成的相关性探讨[J].现代护理,2004,10(7):601-602.
[14] 肖超,陈臣,陈荣富.全膝关节置换术后并发下肢深静脉血栓患者血液动力学及流变学改变[J].重庆医学,2014,43(23): 3083-3085.
[15] Chung LH,Chen WM,Chen CF,et al.Deep vein thrombosis after total knee arthroplasty in asian patients without prophylactic anticoagulation. Orthopedics. 2011;34(1):15.
[16] Kim YH,Yoo JH,Kim JS.Factors leading to decreased rates of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism after total knee arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty. 2007;22(7):974-980.
[17] 姚晨,史冬泉,蒋青.人工关节置换术后深静脉血栓形成的基因多态性研究进展[J].中华外科杂志,2009,47(11):871-873.
[18] 蒋青.人工关节置换术后深静脉血栓形成的基因多态性研究进展[J].中华外科杂志,2009,47(11):871-873.
[19] Wang H,Duan Q,Wang L,et al.Analysis on the pathogenesis of symptomatic pulmonary embolism with human genomics. Int J Med Sci. 2012;9(5):380-386.
[20] Lippi G,Franchini M,Targher G,et al.Help me,Doctor!My D-dimer is raised. Ann Med. 2008;40(8):594-605.
[21] Stang LJ.D-dimer and fibrinogen/fibrin degradation products. Methods Mol Biol. 2013;992:415-427.
[22] Zhu R,Wei S,Wu S,et al.Early diagnosis of lower limb deep vein thrombosis after major orthopedic surgeries. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2010;24(6):730-734.
[23] Yuan XZ,Wu XM,Chen M,et al.Incidence of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) in patients undergoing thoracotomy and changes of hemostasis. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao. 2004;36(5): 529-532.
[24] Wells PS,Anderson DR,Rodger M,et al.Evaluation of D-dimer in the diagnosis of suspected deep-vein thrombosis. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(13):1227-1235.
[25] Elf JL,Strandberg K,Svensson PJ.The diagnostic performance of APC-PCI complex determination compared to D-dimer in the diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2010;29(4):465-470.
[26] Lippi G,Mengoni A,Manzato F.Plasma D-dimer in the diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis. JAMA. 1998;280(21): 1828-1829.
[27] Lippi G,Favaloro EJ.D-dimer measurement and laboratory feedback. J Emerg Med. 2009;37(1):82-83.
[28] 张黄丽,张潮旭,葛衡江.髋关节置换术围术期凝血功能改变及其临床意义[J].武警医学,2009,20(1):35-39.
[29] 喻德富,王友华,姜胜华,等.人工全髋关节置换对血液流变学影响的研究[J].实用骨科杂志,2008,14(8):464-466.
[30] 郭建斌.人工关节置换术后下肢深静脉血栓的血液学检测与相关危险因素分析[J].西安:第四军医大学,2013.