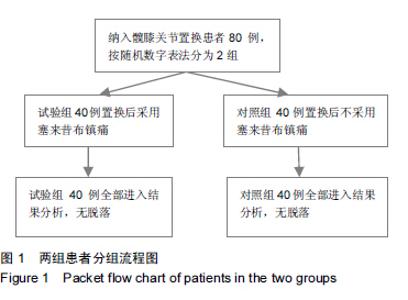
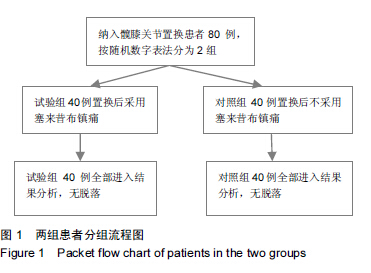
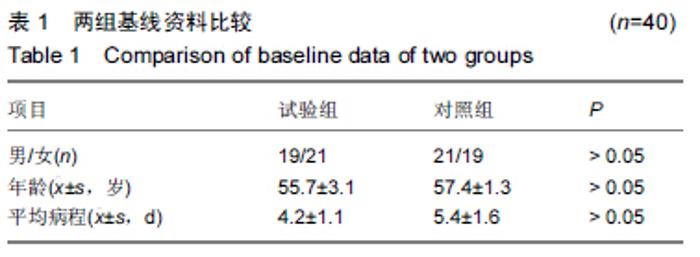
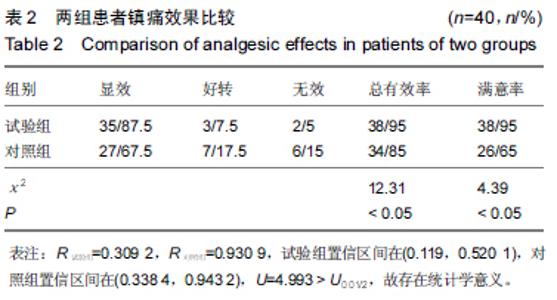
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (44): 7065-7070.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.44.003
Previous Articles Next Articles
Multi-mode analgesia of celecoxib after hip and knee replacement
Xu Feng1, Yang Yu-zhen1, Hao Jie2
- 1Department of Anesthesiology, Chongqing Dongnan Hospital, Chongqing 401336, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 400016, China
-
Received:2015-08-06Online:2015-10-22Published:2015-10-22 -
About author:Xu Feng, Attending physician, Department of Anesthesiology, Chongqing Dongnan Hospital, Chongqing 401336, China
Cite this article
Xu Feng, Yang Yu-zhen, Hao Jie. Multi-mode analgesia of celecoxib after hip and knee replacement[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(44): 7065-7070.
share this article
| [1] 叶坪,寇伯龙,张斌.塞来昔布在髋膝关节置换手术后多模式镇痛的应用[J].中华临床医师杂志:电子版, 2011, 5(3): 844-846. [2] 陈焕诗,金伟,许峰.人工全膝关节置换术治疗膝关节骨关节炎[J].实用骨科杂志,2009,15(7):540-541.
[3] 顾兰珍,艾红珍,姜习凤.多模式镇痛在骨科术后管理中的作用[J].苏州大学学报(医学版),2011,31(1):136-137.
[4] 王炜华,孙建国.腰硬联合麻醉与单纯硬膜外麻醉用于剖宫产手术的比较分析[J].新疆医学,2009,39(1):76-77.
[5] 王琳,田鸣,徐铭军.产程潜伏期腰-硬联合阻滞分娩镇痛的可行性研究[J].中国全科医学,2010,13(6):593-596.
[6] 岳修勤.地佐辛与芬太尼应用于术后静脉镇痛的临床效果比较[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2010,16(4):255-256.
[7] 刘新伟.芬太尼与地佐辛在老年骨科病人镇痛的同时对老年病人循环和呼吸功能的影响的比较[J].现代预防医学,2011,38(23): 4995-4999
[8] 李丽,罗曼,冯洁,等.连续股神经阻滞镇痛对老年人全膝关节置换术后康复功能的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2009,17(15): 1139-1141.
[9] Abdallah FW, Brull R. Is sciatic nerve block advantageous when combined with femoral nerve block for postoperative analgesia following total knee arthroplasty? A systematic review. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2011;36(5):493-498.
[10] Wang SY,Olson-Kellogg B,Shamliyan TA,et al. Physical therapy interventions for knee pain secondary to osteoarthritis: a systematic review. Ann Intern Med. 2012; 157(9): 632-644.
[11] 张永明,范久庆,张德光,等.膝关节置换治疗晚期骨性关节炎[J].中华损伤与修复杂志:电子版,2009,4(2): 165-170.
[12] Su EP,Perna M,Boettner F,et al. A prospective, multi-center, randomised trial to evaluate the efficacy of a cryopneumatic device on total knee arthroplasty recovery.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94(11): 153-156.
[13] 张会东,于松杨,王晓东,等.多模式镇痛的临床研究现状[J].医学综述,2011,17(7): 1072-1075.
[14] 于浩淼,白晓东,马立峰,等.环氧化酶2抑制剂帕瑞昔布、塞来昔布在 TKA 围手术期多模式镇痛中的效果研究[J].中华损伤与修复杂志: 电子版,2014,9(6):634-639.
[15] Ittichaikulthol W,Prachanpanich N,Kositchaiwat C,et al.The post-operative analgesic efficacy of celecoxib compared with placebo and parecoxib after total hip or knee arthroplasty. J Med Assoc Thai. 2010;93(8): 937-942.
[16] 张县华,张洪,周一新,等.全膝关节置换术围手术期多模式镇痛方案的临床研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2008,28(8):647-650.
[17] 高升焘,孙爱娟,张鹏,等.全膝关节置换术后应用连续股神经阻滞镇痛和静脉自控镇痛的效果比较[J].中华关节外科杂志:电子版, 2012,6(1):54-58.
[18] 贾东林,李水清,南兴东,等.罗哌卡因或利多卡因持续股神经阻滞用于膝关节置换术后康复镇痛的临床研究[J].中国疼痛医学杂志, 2008,14(4):214-217.
[19] 符培亮,吴字黎,吴海山,等.全膝置换术后关节内注射鸡尾酒式镇痛混合剂对镇痛效果的评价[J].中华骨科杂志,2008,28(7): 541-545.
[20] Affas F, Nygrds EB, Stiller CO, et al. Pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a randomized trial comparing local infiltration anesthesia and continuous femoral block. Acta Orthop. 2011;82(4):441-447.
[21] 康鹏德,王浩洋,沈彬,等.加入局部浸润镇痛的多模式镇痛在全膝关节置换中的应用[J].中华骨科杂志,2013,33(3): 246-251.
[22] 蒋涛,瞿玉兴,许建安.多模式镇痛在初次全膝关节置换术中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(30):5540-5543.
[23] 张志,范玉伟,张郭瑞,等.多模式镇痛在全膝关节置换术中的疗效评价[J].现代生物医学进展,2011,11(24):4961-4964.
[24] Chan MH, Chen WH, Tung YW, et al. Single-injection femoral nerve block lacks preemptive effect on postoperative pain and morphine consumption in total knee arthroplasty. Acta Anaesthesiol Taiwan. 2012;50(2):54-58.
[25] Wang HJ, Zhang DZ, Li SZ. Comparing the analgesic efficacy of continuous femoral nerve blockade and continuous intravenous analgesia after total knee arthroplasty. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2010;90(33): 2360-2362.
[26] Cappelleri G, Ghisi D, Fanelli A, et al. Does continuous sciatic nerve block improve postoperative analgesia and early rehabilitation after total knee arthroplasty? A prospective, randomized, double-blinded study. Reg Anesth Pain Med.2011; 36(5):489-492.
[27] 乔添柱,滕家松,王东.连续股神经阻滞复合西乐葆对全膝关节置换围手术期镇痛的效果观察[J].中国医药导报,2012,6(9): 46-48.
[28] 郭林,陈昊,杨延伟,等.局部注射含氯诺昔康的镇痛药物抑制痛觉致敏作用对全膝关节置换手术后疼痛控制的影响研究[J].中华关节外科杂志:电子版,2011,5(6):693-697.
[29] 孙向群.沙冰压迫法及中频静电治疗在人工全膝关节置换术后早期功能康复中的应用[J].吉林医学,2012,33(5):916-917.
[30] 秦维龙,孟庆才,方锐,等.中医药镇痛方案在人工膝关节置换术围手术期的疗效观察[J].中医药导报,2010,10(16):43-44.
[31] 曹飞,李超艺,康小红.人工全膝关节置换围手术期多模式联合镇痛的临床研究[J].中国现代医生,2009,47(9):50-52.
[32] 刘德明,王黎明,许春彦.中药熏蒸加手法治疗对全膝关节置换术围手术期的影响[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2012,20(2): 48-49.
[33] Lee AR, Choi DH, Ko JS, et al. Effect of combined single-injection femoral nerve block and patient-controlled epidural analgesia in patients undergoing total knee replacement. Yonsei Med J. 2011;52(1):145-150.
[34] 武迪,段敏,王卫青.全膝关节置换术后膝关节肿胀、疼痛程度对膝关节功能的影响及护理[J].中国医药导报,2012,9(9): 128-134.
[35] 王炜,翁习生,林进,等.洛索洛芬在全膝关节置换的围手术期镇痛与术后镇痛中的研究[J].中国骨与关节外科,2011,4(1): 17-21.
[36] 林荔军,刘登均,张飞,等.多模式联合镇痛在全膝关节置换围手术期中的运用[J].重庆医学,2010,39(14):1871-1874.
[37] Yadeau JT, Liu SS, Rade MC, et al. Performance characteristics and validation of the Opioid-Related Symptom Distress Scale for evaluation of analgesic side effects after orthopedic surgery. Anesth Analg. 2011;113(2): 369-377.
[38] 洪昆达,万甜,李俐,等.不同灸量温针治疗阳虚寒凝型膝骨性关节炎:镇痛及改善症状的比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(41):7748-7750.
[39] Chan MH, Chen WH, Tung YW, et al. Single-injection femoral nerve block lacks preemptive effect on postoperative pain and morphine consumption in total knee arthroplasty. Acta Anaesthesiol Taiwan. 2012;50(2):54-58.
[40] 李恒,隋福革,张宁宁,等.全膝关节置换后鸡尾酒疗法的镇痛效应[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(26):4795- 4796.
[41] Andersen L, Gaarn-Larsen L, Kristensen BB, et al. Subacute pain and function after fast-track hip and knee arthroplasty. Anaesthesia. 2009;64(5):508-513.
[42] Dorr LD, Raya J, Long WT, et al. Multimodal analgesia without parenteral narcotics for total knee arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty. 2008;23(4):502-508.
[43] Mehta A, Hsiao W, King P, et al. Perioperative celecoxib decreases opioid use in patients undergoing testicular surgery: a randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled trial. J Urol. 2013;190(5):1834-1838.
[44] Lu X, Li K.[Multimodal effect of celecoxib on the perioperative analgesia in orthopaedic surgery]. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2009;34(8):815-819.
[45] Huang YM, Wang CM, Wang CT, et al. Perioperative celecoxib administration for pain management after total knee arthroplasty - a randomized, controlled study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2008;9:77.
[46] Reuben SS, Ekman EF, Charron D. Evaluating the analgesic efficacy of administering celecoxib as a component of multimodalanalgesia for outpatient anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery. Anesth Analg. 2007;105(1):222-227.
[47] Reuben SS, Connelly NR. Postoperative analgesic effects of celecoxib or rofecoxib after spinal fusion surgery. Anesth Analg. 2000;91(5):1221-1225.
|
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||