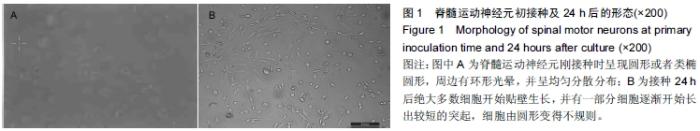
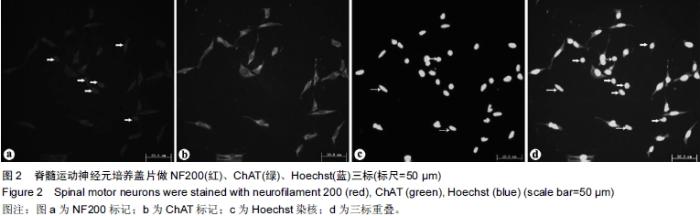
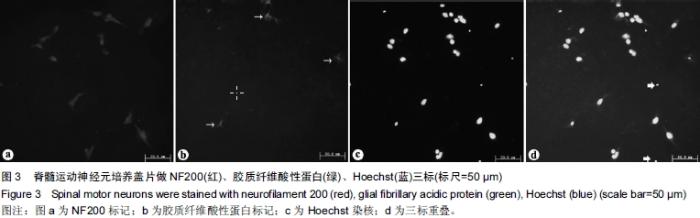
| [1] Kuhn TB.Growing and working with spinal motorneurons. Methods cell Biol.2013;71(1):67-87.
[2] 孙毅,赵冬梅,张烨,等.胎鼠前角运动神经元的取材与培养研究[J].滨州医学院学报,2009,32(6):17-19.
[3] Elliott P,Wallis DI,Foster GA.Ionic mechanisms underlying excitatory effects of serotonin on embryonic rat motoneurons in long-term culture.Neuroscience.2013;90(4):1311-1323.
[4] 赵合庆,杨晓玲,严志强.胚胎大鼠脊髓运动神经元的体外培养与鉴定[J].中华神经科杂志,2004,37(5): 435-437.
[5] 宋学琴,李春岩,吴淑玉,等.胚胎大鼠脊髓运动神经元的体外培养及鉴定[J].基础医学与临床,2004,24(1):83-87.
[6] Son EY, Ichida JK, Wainger BJ, et al.Conversion of Mouse and Human Fibroblasts into Functional Spinal Motor Neurons. Cell Stem Cell. 2011;9(3):205-218.
[7] Haastert K, Grosskreutz J, Jaeckel M, et al.Ratembryonic motoneurons in long -term co-culture with Schwann cells-a system to investigate motoneuron diseases on a cellular level invitro.J Neurosci Method.2012;142(2):275-284.
[8] Das M, Rumsey JW, Gregory CA, et al.Embryonc motoneuron-skeletal muscle co-culture in a defined system. Neuroscience.2014;146(2): 481-488.
[9] Larsen KE, Benn SC, Ay I, et al. Aglial cell line-derived neurotroph factor (GDNF):tetanus tox in fragment C protein conjugate improves delivery of GDNF to spinal cord motor neurons in mice.Brain Res.2006;1120(1):1-12.
[10] Andersona KN, Potterb AC, Piccenna LG, et al. Isolation and culture of motor neurons from the newborn mouse spinal cord.Brain Res Protoc.2014;12: 132-136.
[11] Taguchi T, Huchet M,Roa M,et al. A sub population of embryonic telecephalic neurons survive and develop in vitro in response to factors derived from the periphery. Dev Brain Res.2012;37:125-132.
[12] Rochefort NL,Narushima M,Grienberger C.Development of direction selectivity in mouse cortical neurons.Neuron.2001; (3):425-432.
[13] 杨浩,梁喆,鞠躬,等.体外培养脊髓神经元过程中关于提高细胞产率以及活性的技术探讨[J].解剖学杂志,1997,20(3):239-242.
[14] 杨浩,王春婷,鞠躬.不同方法纯化体外培养脊髓神经元的比较[J].中国组织化学与细胞化学杂志2000,9(3).
[15] Rakowicz WP,Staples CS,Milbrandt J. Glial cell line-derived neuro-trophic factor promotes the survival of early postnatal spinal motor neurons in the lateral and medial motor columns in slice culture.J Neurosci.2012;22:3953-3962.
[16] Carriedo SG,Yin HZ,Weiss JH.Motor neurons are selectively vulnerable to AMPA/Kainate receptor-mediated injury in vitro. J Neurosci.2006;16:4069-4079.
[17] 赵林普.某些神经营养因子对培养大鼠脊髓腹侧神经元生长分化作用[J].细胞生物学杂志, 2010(增刊),117(3).
[18] Bataille S,Potalier P,Coulon P.Influence of acety-l2 cholinesterase on embryonic spinal rat motoneurous grousth in culture:a quantitative morphometric study.Eur J Neurosci. 2008;10:560-572.
[19] 宋学琴,王丽琴,吴淑玉.生长底物对培养胚胎大鼠脊髓运动神经元的作用[J].中国免疫学杂志,2004,20(6): 405-409.
[20] 杨晓玲,赵合庆,严志强.体外培养大鼠脊髓运动神经元的存活率及形态观察[J].基础医学与临床,2007,27(3):344-345.
[21] Martin FC,Wiley CA.A serum-free,pyruvate-free medium that supports neonatal/ glial cultures.J Neurosci Res.2005; 41(2): 246.
[22] Banker GA,Cowan WM.Rat hippocampal neurons in dispersed cell culture.Brain Res.2012;126(2):397.
[23] Taylor AR, Robinson MB, Milligan CE.In vitro methods to prepare astrocyte and motoneuron cultures for the investigation of potential in vivo interactions. Nat Protoc.2007; 2(6):1499-1507.
[24] 余磊, 潘树义, 秦建强.脊髓神经细胞培养的方法.中国临床解剖学杂志,2002,20(4),267.
[25] Lin LF,Doherty DH,Lile JD.GDNF:a glia cell line-derived neurotrophic factor for midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Science. 2013;260(5111):1130.
[26] Zum AD,Baetge EE,Hammang JP.Glia cell line-derived neurotrophic factor(GDNF),a new neurotrophic factor for motoneurons.Neuro Report.2014;6(1):113.
[27] 陈波,袁琼兰.胶质细胞源性神经营养因子与突触可塑性[J].四川解剖学杂志,2006(4):38-39,44.
[28] 宋学琴,吴淑玉,王丽琴.胚胎大鼠脊髓运动神经元体外培养方法的优化.河北医科大学学报,2004,25(3),133-135.
[29] Lucius R, Mentlein R.Development of a culture system for pure rat neurons: advantages of a sandwich technique.Anat Anz.2013;177(5):447-454.
[30] 司徒镇强,吴军正.细胞培养[M].西安:世界图书出版公司,2004: 150-152. |