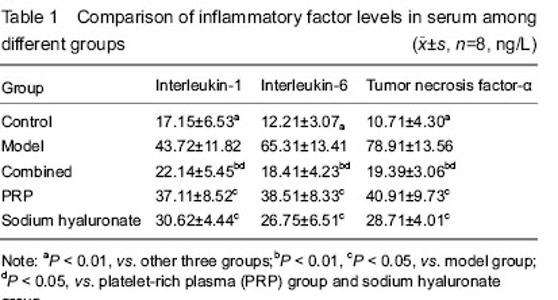
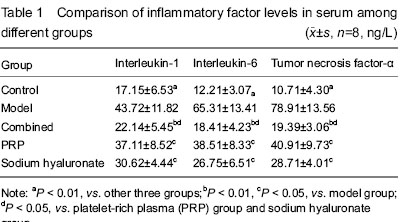
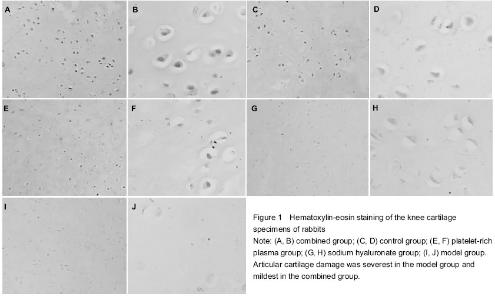
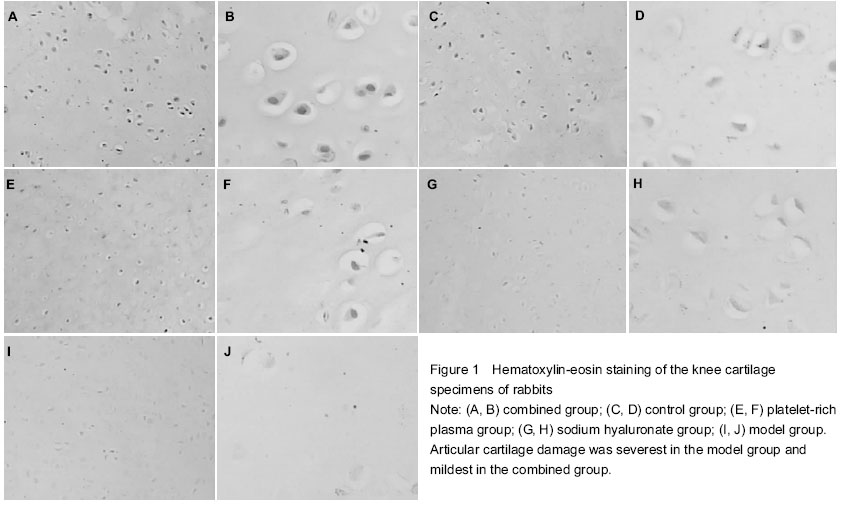
| [1] Huang ZF, Zhao B, Liu ZR, et al. Clinical research for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis with the method combined with oral and external use which under the guidance of The Juanbizhuanggu theory. Zhongguo Xiandai Yisheng. 2013; 51(33):86-87.
[2] Liu MH, Dong JW. Voltaren emulgel treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a clinical observation. Zhongguo Yiyao Zhinan. 2011;9 (32):88-89.
[3] Neogi T. Clinical significance of bone changes in osteoarthritis. Ther Adv MusculoskeletDis. 2012;4(4):259-567.
[4] Kapidzi?-Basi? N, Kikanovi? S, Hoti Hadziefendi? A, et al. Changes in social relations as a consequence of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Reumatizam. 2013;60(1):42-46.
[5] Wang SD, Wang YZ, Zeng LY, et al. Research progress of the induction and detection methods of chondrocyte sapoptosis in vitro. Zhongguo Guzhi Shusong Zazhi. 2014;(1):100-104.
[6] Ou Y, Tan C, An H, et al. Selective COX-2 inhibitor ameliorates osteoarthritis by repressing apoptosis of chondrocyte. Med Sci Monit. 2012;18(6):BR247-252.
[7] Zamli Z, Adams MA, Tarlton JF, et al. Increased chondrocyte apoptosis is associated with progression of osteoarthritis in spontaneous Guinea pig models of the disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(9):17729-17743.
[8] Intekhab-Alam NY, White OB, Getting SJ, et al. Urocortin protects chondrocytes from NO-induced apoptosis: a future therapy for osteoarthritis? Cell Death Dis. 2013;4:e717.
[9] Zhao Z, Ji H, Jing R, et al. Extracorporeal shock-wave therapy reduces progression of knee osteoarthritis in rabbits by reducing nitric oxide level and chondrocyte apoptosis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012;132(11):1547-1553.
[10] Turajane T, Tanavaree A, Labpiboonpong V, et al. Outcomes of intra-articular injection of sodium hyaluronate for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee. J Med Assoc Thai. 2007;90(9):1845-1852.
[11] Kato Y, Mukudai Y, Okimura A, et al. Effects of hyaluronic acid on the release of cartilage matrix proteoglycan and fibronectin from the cell matrix layer of chondrocyte cultures: interactions between hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate glycosaminoglycan. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1995;43:158-159.
[12] Homandberg GA, Hui F, Wen C, et al. Hyaluronic acid suppresses fibronectin fragment mediated cartilage chondrolysis: I. In vitro. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 1997;5(5):309-319.
[13] Conaghan PG. A turbulent decade for NSAIDs: update on current concepts of classification, epidemiology, comparative efficacy, and toxicity. Rheumatol Int. 2012;32(6):1491-1502.
[14] Hochberg MC, Altman RD, April KT, et al. American College of Rheumatology 2012 recommendations for the use of nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic therapies in osteoarthritis of the hand, hip, and knee. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012;64(4):465-474.
[15] Ragle RL, Sawitzke AD. Nutraceuticals in the management of osteoarthritis : a critical review. Drugs Aging. 2012;29(9):717-731.
[16] Kahan A, Uebelhart D, De Vathaire F, et al. Long-term effects of chondroitins 4 and 6 sulfate on knee osteoarthritis: the study on osteoarthritis progression prevention, a two-year, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(2):524-533.
[17] Lee KS, Wilson JJ, Rabago DP, et al. Musculoskeletal applications of platelet-rich plasma: fad or future? AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;196(3):628-636.
[18] Su JM, Jin Y, Qu Q, et al. The expression of microRNA130a during chondrogenic differentiation of rat bone mesenchymal stem cells. Jichu Yixue yu Linchuang. 2010;30(5):520-523.
[19] Moser C. Response to: cytokine profile of autologous conditioned serum for treatment of osteoarthritis, in vitro effects on cartilage metabolism and intra-articular levels after injection. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(6):410.
[20] Pan HL, Yao Y, Wang GW, et al. Variety and significance of IL-1 levels in blood and syn ovial fluid of osteoarthritis model animals. Haerbin Yike Daxue Xuebao. 2001;35(3):192-194.
[21] Jiao YT, Wang DZ, Hu J. Effect of IL-1 and dexamethasone on proliferation, metabolization and precollagen gene expression of human condylar cartilage cells.Zhonghua Chuangshang Zazhi. 2000;16(2):94-95.
[22] Westacott CI, Sharif M. Cytokines in osteoarthritis: mediators or markers of joint destruction? Semin Arthritis Rheum.1996;25(4):254-272.
[23] Pelletier JP, DiBattista JA, Roughley P, et al. Cytokines and inflammation in cartilage degradation. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1993;19(3):545-568.
[24] Kotake S, Sato K, Kim KJ, et al. Interleukin-6 and soluble interleukin-6 receptors in the synovial fluids from rheumatoid arthritis patients are responsible for osteoclast-like cell formation. J Bone Miner Res. 1996;11(1):88-95.
[25] Reboul P, Pelletier JP, Tardif G, et al. The new collagenase, collagenase-3, is expressed and synthesized by human chondrocytes but not by synoviocytes. A role in osteoarthritis. J Clin Invest. 1996;97(9):2011-2019.
[26] Zheng SM, Dong TH, Liu JE. Determination of tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6 in kneen osteoarthritis patients. Zhonghua Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 1998;5(6):544.
[27] Neidal J, Sihulze M, Sova L, et al. Practical significance of cytokine determination in joint fluid in patients with arthroses or rheumatoid arthritis. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb. 1996;134(4):381-385.
[28] Turajane T, Tanavaree A, Labpiboonpong V, et al. Outcomes of intra-articular injection of sodium hyaluronate for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee. J Med Assoc Thai. 2007;90(9):1845-1852. |