Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (5): 787-795.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2444
Previous Articles Next Articles
Biological mechanism of platelet-rich plasma for tendinopathy repair: a visual study based on scientific knowledge map
Qiu Guorong1, 2, He Benxiang1, Wang Chun1
- 1School of Sports Medicine and Health, Chengdu Sport University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China; 2School of Physical Education, Chongqing University of Arts and Science, Chongqing 402160, China
-
Received:2019-04-11Revised:2019-04-19Accepted:2019-05-31Online:2020-02-18Published:2020-01-10 -
Contact:He Benxiang, PhD, Chief physician, School of Sports Medicine and Health, Chengdu Sport University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Qiu Guorong, Doctoral candidate, Associate professor, School of Sports Medicine and Health, Chengdu Sport University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China; School of Physical Education, Chongqing University of Arts and Science, Chongqing 402160, China -
Supported by:the Key Research and Development of Science and Technology Department of Sichuan Province, No. 2017SZ0018; the Key Applied Basic Research Project of Science and Technology Department of Sichuan Province, No. 2016JY0052
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Qiu Guorong, He Benxiang, Wang Chun. Biological mechanism of platelet-rich plasma for tendinopathy repair: a visual study based on scientific knowledge map [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 787-795.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
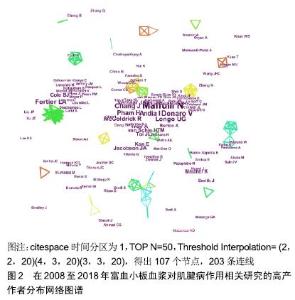
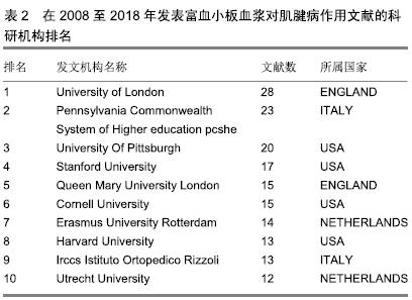
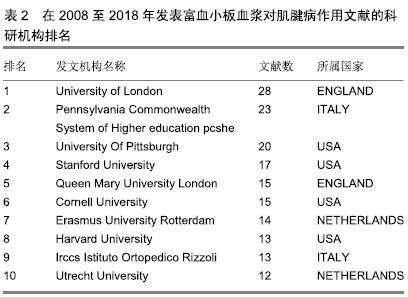
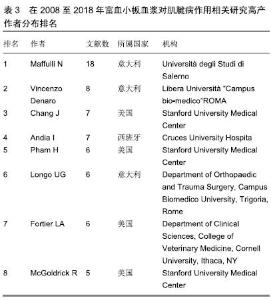
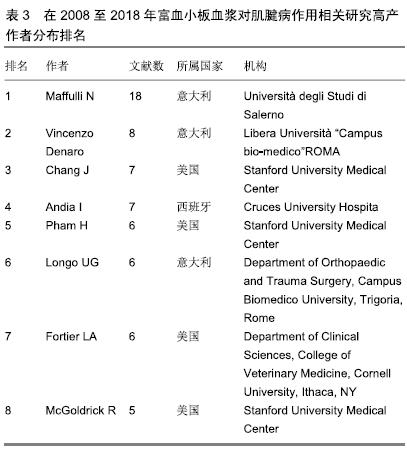
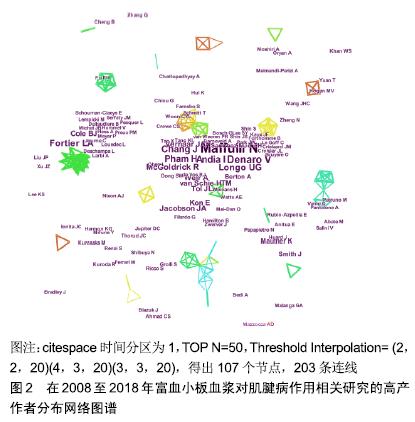
2.1.2 发文作者分布 通过citespace V软件分析得到该研究领域高产发文作者的网络知识图谱(图2)及在该研究领域中发文量排名在前8位的作者列表(表3)。图中每个节点代表一位作者,作者姓名大小与发文量成正比,节点之间的连线代表学者之间的合作强度,连线越粗,合作关系越紧密,线条的颜色代表合作时的年代[15]。将发文量领先的作者定义为该研究领域的核心研究人员。在高产发文作者中,以意大利学者Maffulli N、Vincenzo Denaro和Longo UG为代表的研究团队合作关系紧密,形成了一个聚集度密集的研究群体。这个团队成员关于本研究的成果主要集中于富血小板血浆对肌腱病的临床研究和动物实验模型研究。另一个类似的群体来自于以美国斯坦福大学医学中心的Chang J、Pham H和McGoldrick R为中心的研究团队,该团队成员的研究领域主要为富血小板血浆与其他物质结合对肌腱病的临床实验研究及体外细胞分子生物学研究。从图3中还可以看出,除高产发文作者形成的密集度较高的研究群体外,各群体间的合作关系不多。这些高产发文作者由于来自同一国家或机构,有良好的合作基础与优势,因此彼此间合作非常密切,研究成果也颇为丰硕。"
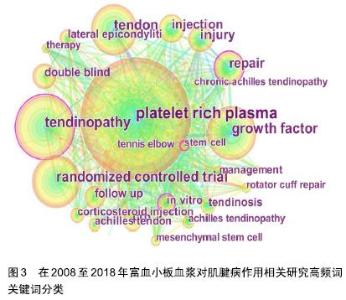
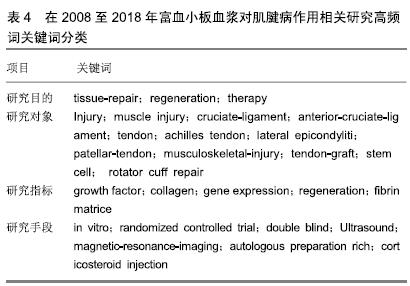
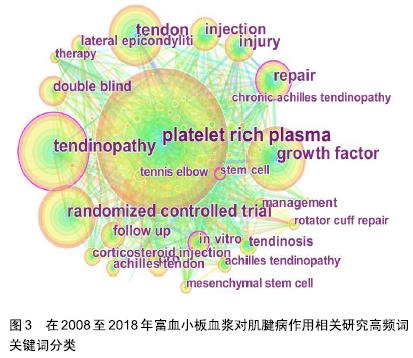
2.2 研究热点分析——关键词共现 关键词作为一篇文章主要内容的提炼,如果某一关键词在其所在的研究领域中不断出现,说明这些词汇是反映该研究领域的热点内容。citespace软件可以通过统计学的相关原理在分析词频出现次数的基础上对关键词的频次及不同关键词之间共现的频次进行提炼,并以可视化方式直观表现出来,从而得出该领域的研究热点[16]。 2.2.1 高频关键词共现分析 通过分析高频关键词得到该领域关键词共现图谱,见图3。将高频关键词按类别划分总结为表4。共现图谱中的每一个节点代表一个关键词,节点及标注词字体的大小与此关键词在研究领域中出现的频率呈正比,节点之间的连线显示各文献关键词之间的联系,连线的粗细与各关键词之间的疏密程度呈正比。 "
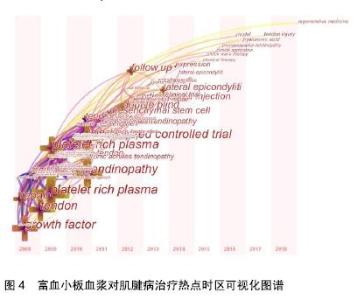
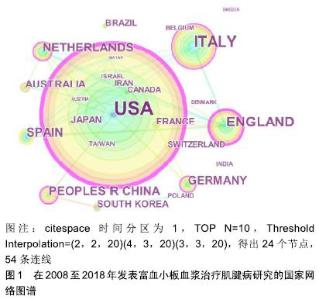
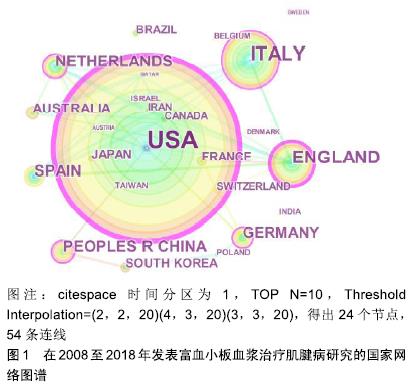
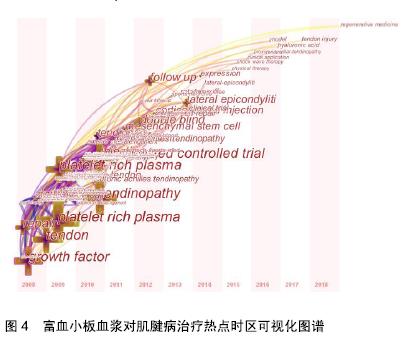
2.2.2 研究热点时区分析 为了更加有效揭示国外富血小板血浆对肌腱病治疗研究热点的动态变化,在citespace V中将节点设为“Keyword”运行程序,以“Time Zone”为可视化结果,得到2008年以来富血小板血浆对肌腱病治疗研究热点变化的时区可视化图谱,见图4,从图中也可以了解到国外富血小板血浆对肌腱病治疗研究进程的关键词演进路径。自2008年以来,关于富血小板血浆对肌腱病治疗的研究热点,已从单纯研究富血小板血浆对疾病治疗的效果研究过渡到研究不同肌腱病中使用富血小板血浆治疗效果及体外研究为主的作用机制研究。值得关注的是,富血小板血浆对肱骨外上髁炎的治疗效果研究在近几年中所占成果比例明显增加。从研究指标的选择来看,2008年研究热点关键词为生长因子(growth factor),它是富血小板血浆的主要有效组成,到2015年,基因表达、表达(gene expression、expression)等词语已成为研究热点关键词,说明研究的重点已从单纯研究富血小板血浆中的组成成分演化为富血小板血浆改变研究对象相关基因表达的研究。在实验方法选择上也更加强调双盲、随意、对照等方法(randomized controlled trial、double blind、controlled trial),增加实验的准确性和可信度。"

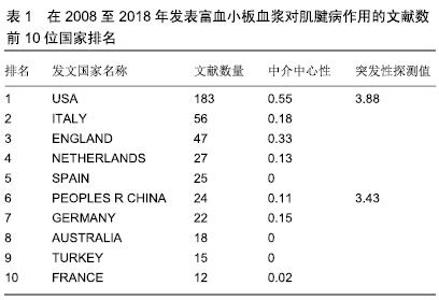
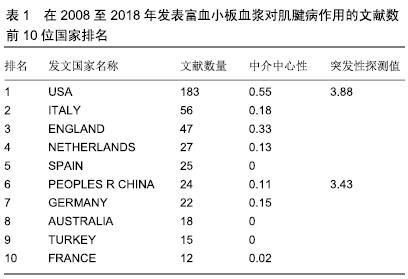
在临床研究中的高被引文献分别涉及到跟腱病(第1、2项研究)、肱骨外上髁炎(第5项研究)和髌腱炎(第8项研究)。有研究表明,发病率最高的几种肌腱病分别是网球肘(肱骨外上髁炎)、肩袖肌腱损伤、跟腱止点末端病、髌腱止点末端病等[18],与高被引文献研究内容吻合。几篇文献采用的研究方法有双盲随机对照法(第1项研究)和实验法(第2、5、8项研究),对于治疗结果的评估,大多采用目测类比评分量表作为检测指标(第1、5、8项研究)。通过一定时间的随访,比较目测类比评分量表数值变化,说明富血小板血浆对肌腱病的治疗效果。通过使用富血小板血浆对不同肌腱病进行治疗,所有临床研究的结果都表明使用富血小板血浆对肌腱病有较好的治疗作用,目测类比评分量表数值在治疗前后有显著性差异。但只有文献1使用双盲随机对照试验。在该研究中,作者发现虽然使用富血小板血浆后患者在随访期间目测类比评分值有明显变化,但和其他对照组比较组未出现显著性差异。 值得一提的是在第5项研究中,研究者首次将自体富血小板血浆与皮质类固醇注射作为非手术治疗失败肱骨外上髁炎患者的一种治疗方法进行了比较,探讨富血小板血浆与皮质类固醇治疗慢性外上髁炎的疗效。在这项研究发表之前,皮质类固醇注射治疗肌腱病曾作为治疗外上髁炎的金标准在使用,该治疗方法虽然有很好的短期期疗效,但在12周随访后经常会出现不良结果[19]。第5项研究结果表明,一次性注射富血小板血浆比皮质类固醇注射液能更好的改善疼痛和功能障碍,而且这些改善随着时间的推移而持续存在。 在体外实验研究中,3篇文献分别选取马指浅屈肌腱(第3项研究),人肌腱细胞(第4、7项研究)作为研究对象,选取不同浓度的富血小板血浆(第3项研究)、富血小板血浆凝块释放物和乏血小板血浆凝块释放物(第4、7项研究)作为培养基对肌腱或肌腱细胞进行培养。经过一段时间培养后,测定肌腱或肌腱细胞中Ⅰ型胶原、Ⅲ型胶原、软骨寡聚基质蛋白、基质金属蛋白酶的表达,以及与肌腱细胞合成代谢相关的蛋白或蛋白基因表达,如血管内皮生长因子、肝细胞生长因子、转化生长因子等,旨在研究富血小板血浆对肌腱细胞合成的相关性研究。 "

| [1] RICKERT M, WANG H, WIELOCH P, et al. Adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of growth and differentiation factor-5 into tenocytes and the healing rat Achilles tendon.Connect Tissue Res. 2005;46(4-5): 175-183. [2] DOCHEVA D, MÜLLER SA, MAJEWSKI M, et al.Biologics for tendon repair.Adv Drug Deliv Rev.2015; 84:222-239. [3] WALDEN G, LIAO X, DONELL S, et al.A clinical, biological, and biomaterials perspective into tendon injuries and regeneration.Tissue Eng Part B Rev.2017;23(1):44-58. [4] MARX RE. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP): what is PRP and what is not PRP? Implant Dent.2001;10(4):225. [5] SAMPSON S, GERHARDT M, MANDELBAUM B. Platelet rich plasma injection grafts for musculoskeletal injuries: a review.Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med.2008;1(3-4):165-174. [6] EVERTS PA, OVERDEVEST EP, JAKIMOWICZ JJ, et al.The use of autologous platelet-leukocyte gels to enhance the healing process in surgery, a review.Surg Endosc.2007; 21(11):2063-2068. [7] ALSOUSOU J, THOMPSON M, HULLEY P, et al.The biology of platelet-rich plasma and its application in trauma and orthopaedic surgery: a review of the literature.Bone Joint J. 2009;91(8): 987-996. [8] FOSTER TE, PUSKAS BL, MANDELBAUM BR, et al. Platelet-rich plasma: from basic science to clinical applications.Am J Sports Med.2009;37(11): 2259-2272. [9] ANDIA I, ABATE M. Platelet-rich plasma: underlying biology and clinical correlates.Regen Med.2013;8(5):645-658. [10] DRAGOO JL, WASTERLAIN AS, BRAUN HJ, et al. Platelet-rich plasma as a treatment for patellar tendinopathy: a double-blind, randomized controlled trial.Am J Sports Med. 2014;42(3):610-618. [11] 陈悦,陈超美,刘则渊,等.CiteSpace 知识图谱的方法论功能[J].科学学研究,2015,33(2):242-253. [12] 孙玉伟.信息行为研究的知识图谱分析[J].情报科学, 2012(5): 102-107,130. [13] 江婉婷,王兴,江志鹏.国外肌肉衰减综合征的运动疗法研究热点与内容分析—基于科学知识图谱的可视化研究[J].体育科学, 2017,37(6):75-83. [14] 李杰,陈超美.CiteSpace:科技文本挖掘及可视化[M].北京:首都经济贸易大学出版社,2016:89. [15] 陈悦,陈超美,胡志刚,等.引文空间分析原理与应用[M].北京:科学出版社,2014:89. [16] 水祎舟,黄竹杭,耿建华.国外足球运动体能训练前沿热点与演化分析—基于科学知识图谱的可视化研究[J].体育科学, 2016 , 36(1):67-78. [17] 陈娟,石习敏,杨均雪,等.国内外健康信息领域演进路径, 热点前沿比较研究—基于科学知识图谱的可视化分析[J]. 现代预防医学,2017,44(1):27. [18] BASS E.Tendinopathy: why the difference between tendinitis and tendinosis matters.Int J Ther Massage Bodywork. 2012; 5(1):14. [19] SMIDT N, VAN DER WINDT DA, ASSENDELFT WJ, et al. Corticosteroid injections, physiotherapy, or a wait-and-see policy for lateral epicondylitis: a randomised controlled trial.Lancet.2002;359(9307):657-662. [20] MCCARREL TM, MINAS T, FORTIER LA.Optimization of Leukocyte Concentration in Platelet-Rich Plasma for the Treatment of Tendinopathy.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012; 94(19):e143. [21] YOSHIDA M, FUNASAKI H, MARUMO K. Efficacy of autologous leukocyte-reduced platelet-rich plasma therapy for patellar tendinopathy in a rat treadmill model.Muscles. 2016; 6(2):205-215. [22] DE VOS RJ, WEIR A, VAN SCHIE HT, et al.Platelet-rich plasma injection for chronic Achilles tendinopathy: a randomized controlled trial.JAMA.2010;303(2):144-149. [23] YAN R, GU Y, RAN J, et al.Intratendon Delivery of Leukocyte-Poor Platelet-Rich Plasma Improves Healing Compared With Leukocyte-Rich Platelet-Rich Plasma in a Rabbit Achilles Tendinopathy Model.Am J Sports Med. 2017; 45(8):1909-1920.。 [24] HANSEN M, BOESEN A, HOLM L, et al.Local administration of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) stimulates tendon collagen synthesis in humans. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2013; 23(5):614-619. [25] KJAER M, LANGBERG H, HEINEMEIER K, et al.From mechanical loading to collagen synthesis, structural changes and function in human tendon.Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2009; 19(4):500-510. [26] ENGEBRETSEN L, STEFFEN K, ALSOUSOU J, et al.IOC consensus paper on the use of platelet-rich plasma in sports medicine.Br J Sports Med.2010;44(15):1072-1081. [27] KON E, FILARDO G, MATTEO BD, et al.Platelet-Rich Plasma in Sports Medicine: New Treatment for Tendon and Cartilage Lesions.Oper Tech Orthop.2012;22(2):78-85. [28] ZHOU Y, WANG JH. PRP Treatment Efficacy for Tendinopathy: A Review of Basic Science Studies.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:9103792. [29] DE JONGE S, DE VOS RJ, WEIR A, et al.One-Year Follow-up of Platelet-Rich Plasma Treatment in Chronic Achilles Tendinopathy A Double-Blind Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial.Am J Sports Med. 2011;39(8): 1623-1629. [30] GOSENS T, PEERBOOMS JC, LAAR WV, et al.Ongoing Positive Effect of Platelet-Rich Plasma Versus Corticosteroid Injection in Lateral Epicondylitis A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial With 2-year Follow-up.Am J Sports Med. 2011;39(6):1200-1208. [31] KROGH TP, FREDBERG U, STENGAARDPEDERSEN K, et al. Treatment of lateral epicondylitis with platelet-rich plasma, glucocorticoid, or saline: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.Am J Sports Med.2013;41(3):625-635. [32] THANASAS C, PAPADIMITRIOU G, CHARALAMBIDIS C, et al. Platelet-rich plasma versus autologous whole blood for the treatment of chronic lateral elbow epicondylitis: a randomized controlled clinical trial.Am J Sports Med. 2011;39(10):2130-2134. [33] ZHANG JY, FABRICANT PD, ISHMAEL CR, et al.Utilization of Platelet-Rich Plasma for Musculoskeletal Injuries: An Analysis of Current Treatment Trends in the United States. Orthop J Sports Med.2016;4(12):2325967116676241. [34] BOESEN AP, HANSEN R, BOESEN MI, et al.Effect of High-Volume Injection, Platelet-Rich Plasma, and Sham Treatment in Chronic Midportion Achilles Tendinopathy: A Randomized Double-Blinded Prospective Study.Am J Sports Med.017;45(9):2034-2043 [35] KROGH TP, ELLINGSEN T, CHRISTENSEN R, et al. Ultrasound-Guided Injection Therapy of Achilles Tendinopathy With Platelet-Rich Plasma or Saline: A Randomized, Blinded, Placebo-Controlled Trial.Am J Sports Med.2016;44(8): 1990-1997. [36] CARMONA JU, LOPEZ C, SANDOVAL JA.Review of the Currently Available Systems to Obtain Platelet Related Products to Treat Equine Musculoskeletal Injuries.Recent Pat Regen Med.2013;3(2):148-159. [37] MAZZOCCA AD, MCCARTHY MB, CHOWANIEC DM, et al. Platelet-rich plasma differs according to preparation method and human variability.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(4): 308-316. [38] WANG JH, NIRMALA X.Application of Tendon Stem/Progenitor Cells and Platelet-Rich Plasma to Treat Tendon Injuries.Oper Tech Orthop.2016;26(2):68-72. [39] DELONG JM, RUSSELL RP, MAZZOCCA AD.Platelet-rich plasma: the PAW classification system.Arthroscopy. 2012; 28(7):998-1009. [40] KEVY SV, JACOBSON MS.Comparison of methods for point of care preparation of autologous platelet gel.J Extra Corpor Technol.2004;36(1):28-35. [41] BEHERA P, DHILLON M, AGGARWAL S, et al. Leukocyte-poor platelet-rich plasma versus bupivacaine for recalcitrant lateral epicondylar tendinopathy.J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2015;23(1):6-10. [42] ALSOUSOU J, ALI A, WILLETT K, et al.The role of platelet-rich plasma in tissue regeneration.Platelets.2013;24(3):173-182. [43] RUBIO-AZPEITIA E, BILBAO AM, SÁNCHEZ P, et al.The Properties of 3 Different Plasma Formulations and Their Effects on Tendinopathic Cells.Am J Sports Med. 2016; 44(8):1952. [44] DRAGOO JL, WASTERLAIN AS, BRAUN HJ, et al. Plateletrich plasma as a treatment for patellar tendinopathy: a doubleblind, randomized controlled trial.Am J Sports Med. 2014;42(3):610-618. [45] DRAGOO JL, BRAUN HJ, DURHAM JL, et al.Comparison of the acute inflammatory response of two commercial platelet-rich plasma systems in healthy rabbit tendons.Am J Sports Med.2012;40(6):1274-1281. [46] FITZPATRICK J, BULSARA M, ZHENG MH.The Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Treatment of Tendinopathy: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Clinical Trials.Am J Sports Med.2017;45(1):226-233. [47] MILLER LE, PARRISH WR, ROIDES B, et al.Efficacy of platelet-rich plasma injections for symptomatic tendinopathy: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised injection-controlled trials.BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. 2017;3(1):e000237. [48] ARIRACHAKARAN A, SUKTHUAYAT A, SISAYANARANE T, et al.Platelet-rich plasma versus autologous blood versus steroid injection in lateral epicondylitis: systematic review and network meta-analysis.Orthop Traumatol.2016;17(2):101-112. [49] KROGH TP, BARTELS EM, ELLINGSEN T, et al.Comparative effectiveness of injection therapies in lateral epicondylitis: a systematic review and network metaanalysis of randomized controlled trials.Am J Sports Med.2013;41(6):1435-1446. [50] MISHRA AK, SKREPNIK NV, EDWARDS SG, et al.Efficacy of platelet-rich plasma for chronic tennis elbow: a double-blind, prospective, multicenter, randomized controlled trial of 230 patients.Am J Sports Med.2014;42(2):463-471. [51] PEERBOOMS JC, SLUIMER J, BRUIJN DJ, et al.Positive effect of an autologous platelet concentrate in lateral epicondylitis in a double-blind randomized controlled trial: platelet-rich plasma versus corticosteroid injection with a 1- year follow-up.Am J Sports Med.2010;38(2):255-262. [52] FILARDO G, DI MATTEO B, KON E, et al.Platelet-rich plasma in tendon-related disorders: results and indications.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2018;26(7):1984-1999. [53] VETRANO M, CASTORINA A, VULPIANI MC, et al. Platelet-rich plasma versus focused shock waves in the treatment of jumper’s knee in athletes.Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(4):795-803. [54] LE ADK, ENWEZE L, DEBAUN MR, et al.Platelet-Rich Plasma.Clin Sports Med.2019;38(1):17-44. [55] GOSENS T, FIEVEZ E, SPIJKER PV, et al.Pain and activity levels before and after platelet-rich plasma injection treatment of patellar tendinopathy: a prospective cohort study and the influence of previous treatments.Int Orthop. 2012;36(9): 1941-1946. [56] WANG JH.Can PRP effectively treat injured tendons? Muscles Ligaments Tendons J.2014;4(1):35-37. [57] NIRMALA X, ZHANG J, WANG HC.Advancements in the Treatment and Repair of Tendon Injuries.Curr Tissue Eng. 2014;3(2):71-81. [58] ALSOUSOU J, THOMPSON M, HARRISON P, et al.Effect of platelet-rich plasma on healing tissues in acute ruptured Achilles tendon: a human immunohistochemistry study.Lancet. 2015;385:S19. [59] KELLY A, LYNCH A, VEREKER E, et al.The anti-inflammatory cytokine, interleukin (IL)-10, blocks the inhibitory effect of IL-1 beta on long term potentiation. A role for JNK.J Biol Chem. 2001;276(49):45564-45572. [60] HUDGENS JL, SUGG KB, GREKIN JA, et al.Platelet-Rich Plasma Activates Proinflammatory Signaling Pathways and Induces Oxidative Stress in Tendon Fibroblasts.Am J Sports Med.2016;44(8):1931-1940. |
| [1] | Jiang Hongying, Zhu Liang, Yu Xi, Huang Jing, Xiang Xiaona, Lan Zhengyan, He Hongchen. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on pressure ulcers after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1149-1153. |
| [2] | Shen Jinbo, Zhang Lin. Micro-injury of the Achilles tendon caused by acute exhaustive exercise in rats: ultrastructural changes and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1190-1195. |
| [3] | Wang Mengting, Gu Yanping, Ren Wenbo, Qin Qian, Bai Bingyi, Liao Yuanpeng. Research hotspots of blood flow restriction training for dyskinesia based on visualization analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1264-1269. |
| [4] | Zhong Hehe, Sun Pengpeng, Sang Peng, Wu Shuhong, Liu Yi. Evaluation of knee stability after simulated reconstruction of the core ligament of the posterolateral complex [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 821-825. |
| [5] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [6] | Ma Ziyue, Ju Xiaochen, Zhang Lei, Sun Rongxin. Tendon-bone healing in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with and without remnant preservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 582-587. |
| [7] | Fan Yinuo, Guan Zhiying, Li Weifeng, Chen Lixin, Wei Qiushi, He Wei, Chen Zhenqiu. Research status and development trend of bibliometrics and visualization analysis in the assessment of femoroacetabular impingement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 414-419. |
| [8] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of multiple implants in treatment of traumatic dislocation of sternoclavicular joint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 443-448. |
| [9] | Lu Yuyun, Huang Mei, Shi Xinlei, Chen Baoyan. Bibliometric and visualization analysis of breast cancer stem cell literature from 2011 to 2020 based on Web of Science database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4001-4008. |
| [10] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [11] | Ren Wenbo, Liao Yuanpeng. Visualization analysis of traumatic osteoarthritis research hotspots and content based on CiteSpace [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3374-3381. |
| [12] | Pan Xuan, Zhao Meng, Zhang Xiumei, Zhao Jie, Zhai Yunkai. Research and application of biological three-dimensional printing technology in the field of precision medicine: analysis of Chinese and English literature [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3382-3389. |
| [13] | Li Wenhui, Liu Guobin. Knowledge mapping analysis on the international research of diabetic foot: a visual analysis based on CiteSpace [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3178-3184. |
| [14] | Zuo Xiuqin, Yin Sasa, Xie Huimin, Jia Zishan, Zhang Lining. Applicability and specifications of platelet-rich plasma in musculoskeletal repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3239-3245. |
| [15] | Zhang Kai, Zhang Xiaobo, Shi Jintao, Wang Keping, Zhou Haiyu. Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration: a bibliometric and visualization analysis based on Web of Science database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3031-3038. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||