Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (1): 146-151.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2154
Previous Articles Next Articles
Application and function of autologous blood concentrate in tissue regeneration
Wang Ning, Zhong Weijian
- Stomatological Hospital of Stomatology College of Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116023, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2020-01-17Revised:2020-01-19Accepted:2020-03-09Online:2021-01-08Published:2020-11-20 -
Contact:Zhong Weijian, Associate professor, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Stomatological Hospital of Stomatology College of Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116023, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Wang Ning, Master candidate, Physician, Stomatological Hospital of Stomatology College of Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116023, Liaoning Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Ning, Zhong Weijian. Application and function of autologous blood concentrate in tissue regeneration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 146-151.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
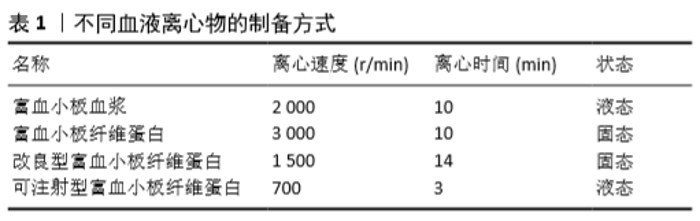
2.1 自体血液浓缩物的发展历程 1954年,KINGSLEY[1]在与凝血有关的实验中首次发现血凝块可以加快创口愈合。1970年,MATRAS[2]通过在离体血液中加入凝血酶和钙制作出一种“纤维蛋白凝胶”,可以促进大鼠皮肤创伤的愈合,但由于供体血液中纤维蛋白原浓度较低,导致纤维蛋白凝胶的质量和稳定性较差,促进伤口愈合的效果不理想。随后在1975至1978年间学者们提出了血液提取物的概念,并将其命名为“血小板-纤维蛋白-凝血酶混合物”[3]。直至1984年,ASSOIAN等[4]通过离心加了抗凝剂的自体血液,首次制成了第1代血小板浓缩制品——富血小板血浆。在富血小板血浆中加入促凝剂激活血小板可释放出多种生长因子,这些生长因子可以促进软硬组织再生[5],但其制备过程复杂、成本较高,同时由于使用了抗凝剂可能存在免疫排斥及过敏反应等问题。 2000年,CHOUKROUN等[6]开发了第2代血小板浓缩制品——富血小板纤维蛋白。将血液置入不含任何添加剂的离心管中,离心后可观察到血液在管内分成3层,分别为顶层的贫血小板血浆、中间层的富血小板纤维蛋白和底层的红细胞碎片。富血小板纤维蛋白中的白细胞、血小板含量较高,同时具有较为坚韧的纤维蛋白网状结构,可作为细胞生长的支架。这种纤维蛋白网状结构还能够附着大量的血小板和生长因子,形成一个缓释系统,更有效地促进软硬组织再生[7-11]。RODELLA等[12]介绍了浓缩生长因子的新概念,通过使用特制的离心机,在范围为2 400-2 700 r/min的离心速率下变速离心血液,获得的纤维蛋白块更大,生长因子更多,强度更高。2009年,DOHAN EHRENFEST等[13]首次对自体血液浓缩物提出了分类标准,该标准根据2个关键参数即白细胞含量和纤维蛋白结构的不同分成4类:①纯血小板血浆(P-PRP);②富白细胞-血小板血浆(L-PRP);③纯血小板纤维蛋白(P-PRF);④富白细胞-血小板纤维蛋白(L-PRF)。2014年CHOUKROUN[14]介绍了一种改良型富血小板纤维蛋白 (advanced platelet-rich fibrin,A-PRF),改良后制备出的富血小板纤维蛋白含有更多的白细胞和生长因子。TUNALI等[15]认为钛是一种血小板活化剂,使用钛制离心管制作的富血小板纤维蛋白质地更加坚韧,促进软硬组织再生的能力更强。 2015年,MOUR?O等[16]对可注射型富血小板纤维蛋白(injectable platelet-rich fibrin,I-PRF)的制备做出了详细的技术说明,其认为在3 300 r/min下离心2 min可以制作出流动状态的富血小板纤维蛋白,可以直接给患者注射或混合骨移植材料用于骨缺损区。2016年,CHOUKROUN等[17]分别使用高、中、低不同离心速率制备可注射型富血小板纤维蛋白,证实了低速离心下制作的可注射型富血小板纤维蛋白可以含有更多的血小板和白细胞。 不同血液离心物的制备方式见表1。"
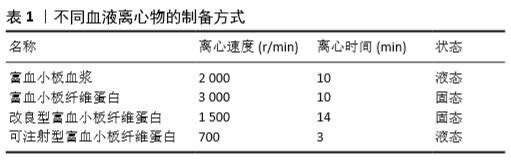
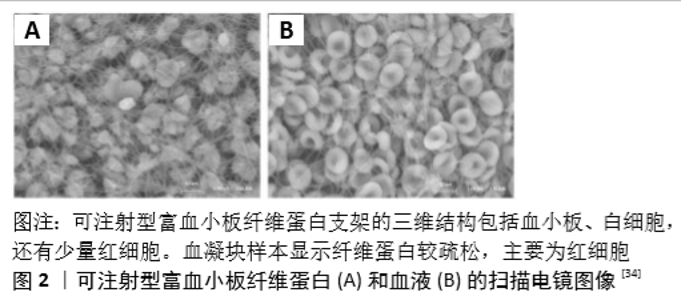
2.2 自体血液浓缩物的基础研究现状 2.2.1 富血小板血浆的基础研究 目前国际上富血小血浆的制备方式并没有统一标准,按照离心次数的不同可以分为一次离心法、二次离心法和三次离心法,其中一次离心法收集的富血小板血浆中血小板数量有限,三次离心法需要多次转移样品,操作复杂且容易受外界污染,二次离心法操作相对简便,血小板含量较多,是临床上的主要制备方式,其制备过程如下:①抽取前臂静脉血置于含有枸橼酸钠的离心管中,以2 000 r/min的转速离心10 min;②吸取上层清液及少量邻近中层的红细胞并转移到另一个无菌离心管中;③不改变离心速度再次离心10 min,中间层即为富血小板血浆,加入凝血酶和氯化钙即为富血小板血浆凝胶[4]。 关于富血小板血浆的作用机制和再生效果的基础研究颇多。陶海荣等[18]在兔股骨头坏死模型中分别使用富血小板血浆混合磷酸三钙和单纯磷酸三钙进行治疗,结果表明富血小板血浆混合磷酸三钙组的骨修复重建效果显著优于单纯使用磷酸三钙组。AKEDA等[19]的一项体外实验发现在富血小板血浆的影响下猪椎间盘细胞的增殖速度变快,细胞外基质代谢速率增强。但由于富血小板血浆没有统一的制备方式,不同方式制作出的富血小板血浆的血小板、白细胞和血浆的含量也各不相同。由于富血小板血浆在制备过程中使用枸橼酸钠、异种凝血酶和氯化钙作为添加剂可能会存在免疫排斥和过敏反应等问题,富血小板血浆在临床已逐渐被富血小板纤维蛋白替代。 2.2.2 富血小板纤维蛋白的生物学特性 富血小板纤维蛋白是将血液置入无添加剂的离心管内,以3 000 r/min的转速离心10 min获得的[6]。DOHAN EHRENFEST等[20]学者利用扫描电镜观察离心管底部的红色部分,发现此处有大量红细胞聚集,只存在少数松散且不成熟的纤维蛋白网络。在红黄交界处可以观察到大量白细胞和血小板聚集,其中白细胞呈球形结构,表面呈现不规则突起。血小板通常相互嵌合,附着在纤维蛋白网络上。富血小板纤维蛋白黄色固体部分有大量的血小板和纤维蛋白,由于血小板广泛聚集而形成了坚固厚实的纤维蛋白网络,此处的血小板似乎被高度激活。 DOHAN等[21]体外细胞培养分析认为富血小板纤维蛋白中的血小板被激活后可以释放出5种生长因子,包括转化生长因子β1、血小板衍生生长因子、血管内皮生长因子、表皮生长因子和胰岛素样生长因子Ⅰ。最早对转化生长因子β1的研究主要在其控制炎症和影响组织发育方面,近年来发现转化生长因子β1对成纤维细胞和成骨细胞的生长及分化功能都有明显的调控作用[22]。血小板衍生生长因子是一种来源于血小板内的肽类调节因子,可以刺激成纤维细胞分裂增生,正常生理状态下不发挥作用。血小板衍生生长因子位于血小板的α颗粒内,当血小板被激活时释放出来并且发挥作用,能够启动并加速组织愈合[23]。血管内皮生长因子可以有效促进血管内皮细胞生长,诱导毛细血管增生。表皮生长因子可以诱导角化细胞和成纤维细胞增殖分化,促进伤口愈合,同时可以与其他生长因子产生协同作用。胰岛素样生长因子Ⅰ可以促进细胞有丝分裂,有效增强成骨细胞活性[24]。实验证明胰岛素样生长因子Ⅰ在创伤愈合过程中发挥作用,在损伤的神经、肌肉细胞中胰岛素样生长因子Ⅰ的浓度有所增加[25]。 GIANNINI等[26-27]发现富血小板纤维蛋白中白细胞的数量占全部血液中的65%,而且在富血小板纤维蛋白的制备过程中这些白细胞不会受到损伤。因此,富血小板纤维蛋白干预后对炎症的调控也能起到理想的效果[28]。KAWASAKI等[29]学者通过扫描电镜观察发现富血小板纤维蛋白中有大量血小板和白细胞聚集在纤维蛋白网络上,这种网状结构可以为组织修复提供一个场所,同时纤维蛋白网络表面有益于上皮细胞的增殖,可以进一步起到促进创面愈合的作用。 2.2.3 改良型富血小板纤维蛋白的生物学特性 改良型富血小板纤维蛋白是将自体血液置于无添加剂的离心管内,在 1 500 r/min的转速下离心14 min获得。KOBAYASHI等[30]学者在体外对富血小板血浆、富血小板纤维蛋白、改良型富血小板纤维蛋白进行观察分析,分别在15 min,60 min,8 h,1 d,3 d和10 d对生长因子释放量进行评估,结果表明改良型富血小板纤维蛋白10 d内释放的各项生长因子总量明显高于富血小板血浆和富血小板纤维蛋白,而10 d后两者基本全部代谢完成。在不同时间点观察各项生长因子释放量可以发现,富血小板血浆虽然在1 h内释放了较多的生长因子,但富血小板纤维蛋白和改良型富血小板纤维蛋白在10 d内逐步释放的生长因子总量更多。与富血小板纤维蛋白相比,改良型富血小板纤维蛋白随着时间的推移释放了更多的生长因子,在临床上对软硬组织的生长都更加有利[31]。Masson染色观察发现改良型富血小板纤维蛋白凝块的网状结构松散,为血小板和白细胞的聚集提供了更多的空间。通过细胞计数发现改良型富血小板纤维蛋白与富血小板纤维蛋白相比含有更多的血小板和白细胞,并且改良型富血小板纤维蛋白凝块中的细胞分布更加均匀[32]。 2.2.4 可注射型富血小板纤维蛋白的生物学特性 可注射型富血小板纤维蛋白是将自体血液置于无添加剂的塑料离心管中,在700 r/min转速下离心3 min获得。这种仍具有流动性的自体血液浓缩物称为可注射型富血小板纤维蛋白。FUJIOKA- KOBAYASH 等[33]认为使用“低速离心”方法只有少量的血小板及白细胞向离心管底部移动,更多的聚集在中间部分。通过电镜观察发现,与自体血凝块比,可注射型富血小板纤维蛋白中只含少量红细胞并且纤维蛋白网络更加致密,网络链条的直径从 20 nm到 200 nm不等,平均直径为90 nm[34],见图2。可注射型富血小板纤维蛋白中白细胞和血小板分布相比于富血小板纤维蛋白更加均匀,与其他植骨材料混合后操作方便。 GHANAATI等[35]利用扫描电镜观察发现,与天然血凝块比,可注射型富血小板纤维蛋白中形成的纤维蛋白网络更紧密,并且可注射型富血小板纤维蛋白中可以观察到活化的血小板、白细胞和红细胞嵌入复杂的三维纤维蛋白网络中。 2.3 自体血液浓缩物的临床应用 2.3.1 富血小板血浆的临床应用 (1)富血小板血浆在骨科中的应用:目前临床上主要使用自体骨、异体骨、异种骨和人工骨作为骨移植材料。自体骨来源有限且要开辟第二术区,加重患者的术后反应。异体骨和异种骨存在免疫排斥和传播疾病等问题。人工骨只有骨传导性,没有骨诱导能力,单纯使用时成骨效果不佳。DALLARI等[36]进行了一项随机对照研究,将33例接受胫骨截骨术治疗膝内翻的患者根据骨移植材料的不同随机分组,12周后使用富血小板血浆混合冻干骨组的骨愈合率达到45%,而单纯使用冻干骨组骨愈合率只有20%,他们得出的结论是富血小板血浆可以激活植骨区的成骨潜能。BIELECKI[37]在治疗肱骨骨不连患者时首次使用了富血小板血浆凝胶,将富血小板血浆凝胶注射到骨不连的间隙中诱导骨组织再生,在降低手术创伤的同时得到了理想的效果。 (2)富血小板血浆在皮肤科中的应用:皮肤烧伤后,除了烧伤皮肤表面存在创伤,机体其他临近组织也会受到损伤,因此烧伤创口往往愈合较慢。刘哲伟等[38]将68例患者的烧伤创面平均分为2个部分,一部分用富血小板血浆敷在创面上,另一部分使用磺胺嘧啶银霜进行治疗。比较两组愈合时间和炎症发生率等,他们发现富血小板血浆组各项指标均优于磺胺嘧啶银霜组。 (3)富血小板血浆在口腔科中的应用:富血小板血浆取自患者本身,在口腔门诊收集相对容易,在口腔科中有较为广泛的应用。OLUFEMI等[39]在一项研究中对比了30例富血小板血浆凝胶填充下颌第三磨牙拔牙窝和30例单纯血凝块填充下颌第三磨牙拔牙窝,比较两组间术后疼痛、肿胀和开口度的差异,结果表明富血小板纤维蛋白凝胶可以有效减少患者第三磨牙拔除后的各项术后反应。TOPCUOGLU等[40]报道了3例患者将富血小板血浆注入根尖未发育完成的根管中,术后随访时患者并未出现不适症状,叩诊正常,X射线示根管壁增厚,根尖口封闭,均达到了理想的质量效果。 (4)富血小板血浆在其他领域中的应用:随着对富血小板血浆基础研究的逐渐完善,越来越多的领域开始关注并使用富血小板血浆。CERVELL等[41]通过激光治疗、脂肪移植和富血小板血浆等技术联合应用处理创伤后形成的瘢痕,其疗效显著强于使用单一方式进行治疗。在运动医学中,RADICE等[42]在一项前瞻性单盲研究中指出,辅助富血小板血浆注射治疗50名交叉韧带断裂运动员的平均愈合时间可缩短48%。 2.3.2 富血小板纤维蛋白的临床应用 富血小板纤维蛋白由于其良好的生物相容性、容易获取、操作方法简单、无感染风险,目前已在口腔治疗各方面得到广泛的应用[43]。 (1)富血小板纤维蛋白促进骨组织再生的应用:在口腔颌面外科中用富血小板纤维蛋白来促进植骨区的骨改建,最常用的方法是在种植位点的骨缺损处将富血小板纤维蛋白与骨粉混合进行骨增量[44]。白冰等[45]对富血小板纤维蛋白联合Bio-Oss骨粉进行引导骨组织再生进行研究,将40例患者分为单纯Bio-Oss组和Bio-Oss混合富血小板纤维蛋白组进行引导骨组织再生,术后20周通过锥形束CT发现Bio-Oss混合富血小板纤维蛋白组成骨量和密度均高于Bio-Oss组,结果表明Bio-Oss联合富血小板纤维蛋白能取得更好的成骨效果。CHOUKROUN等[46]比较富血小板纤维蛋白混合冻干同种异体骨和单纯冻干同种异体骨用于上颌窦开窗提升术促进种植体周围骨再生的效果,发现富血小板纤维蛋白混合冻干同种异体骨组有更多的新生骨。TAJIMA等[47]为6例患者进行9次(其中3例患者双侧)上颌窦开窗提升术并植入富血小板纤维蛋白,同期种植17枚种植体,术后6个月锥形束CT示植骨区充满了高密度的骨样组织且种植体稳定不松动,说明富血小板纤维蛋白单独应用可以促进骨再生。富血小板纤维蛋白也可以用于拔牙位点保存,通常情况下牙齿拔除后如果不对拔牙窝进行处理,牙槽嵴顶宽度和高度都会有明显降低。在拔牙窝内植入富血小板纤维蛋白后,不但会加快牙槽窝愈合,而且牙槽窝愈合后骨量高度、宽度也能得到很好地维持[48]。ZHANG等[49]将28例患者根据拔牙位点处理方式不同将患者分为实验组和对照组,实验组在拔牙位点内植入富血小板纤维蛋白膜,对照组拔牙窝不作处理。患者在术后7 d、1个月和3个月拍摄锥形束CT,观察拔牙位点的骨质密度和骨量变化,并在3个月时利用套筒钻取材进行组织学观察,结果发现实验组早期牙龈愈合良好,疼痛肿胀程度较轻,锥形束CT发现颊舌侧和牙槽嵴宽度变化量较小,组织学研究观察到新骨成分更多,说明富血小板纤维蛋白在拔牙位点保存时可以有效降低术后反应,很大程度避免了骨量丧失,增加新骨密度。HAUSER等[50]研究指出在微创拔牙同时于拔牙位点内填入富血小板纤维蛋白可以有效保存拔牙位点的硬组织。另外有研究发现拔牙窝内填塞富血小板纤维蛋白后干槽症的发生率也会明显降低[51]。 在牙周病的治疗中富血小板纤维蛋白也能发挥很大作用,可用于牙周骨缺损的修复。SHARMA等[52]在56例慢性牙周炎患者中随机选择28例患者在翻瓣刮治后于骨缺损处填入富血小板纤维蛋白,并使用富血小板纤维蛋白膜覆盖窗口,另外28例患者单纯进行翻瓣刮治,术后9个月观察发现实验组探诊深度降低值显著高于对照组,牙周附着水平和骨缺损处的骨充填率也高于对照组。THORAT等[53]将32例重度牙周炎患者随机分为2组,实验组16例进行翻瓣刮治联合富血小板纤维蛋白治疗,对照组16例常规翻瓣刮治,术后9个月时观察菌斑指数、探针出血情况和探诊深度,结果发现实验组所有测量结果均优于对照组,说明常规翻瓣治疗慢性牙周炎过程中使用富血小板纤维蛋白可以有效提高治疗效果。SHARMA等[54]对18例Ⅱ度根分叉病变患者进行治疗时随机将患者分为常规治疗联合富血小板纤维蛋白组和单纯常规治疗组,比较菌斑指数、探诊出血指数、探测深度、附着水平、牙龈边缘水平和X射线观察骨缺损情况,结果表明根分叉处填入富血小板纤维蛋白组各项数据均好于常规治疗组。NAGAVENI等[55]对牙周病患者进行翻瓣治疗后将富血小板纤维蛋白膜覆盖在牙周缺损上,不填入其他骨移植材料,术后患者无自述不适,3个月随访时牙周袋探诊深度正常,6个月X射线片发现填充富血小板纤维蛋白的区域有新骨生成。 (2)富血小板纤维蛋白在治疗神经损伤中的应用:最近也有学者指出下牙槽神经移位术后会不可避免的出现下唇麻木等下牙槽神经损伤症状,但利用富血小板纤维蛋白膜包裹移位神经后神经损伤症状恢复速度明显加快。KHOJASTEH等[56] 回顾了14例进行过下牙槽神经移位术患者,其中7例在用富血小板纤维蛋白膜包裹下牙槽神经再将其复位作为实验组,剩余7例直接复位作为对照组,在术后3,6,12个月进行随访,评估神经功能障碍情况,结果术后3个月时实验组有1例患者表示感觉正常,剩余13例患者均出现麻木症状。术后6个月时实验组全部患者恢复正常,对照组有3例患者症状减轻。术后12个月除对照组1例患者外全部恢复正常。结果表明富血小板纤维蛋白可以加速下牙槽神经移位术后神经症状的恢复。 改良型富血小板纤维蛋白为术区提供了更多的血小板和白细胞,因此在相同使用方法中会有更好的效果[32]。 2.3.3 可注射型富血小板纤维蛋白的应用 有学者将可注射型富血小板纤维蛋白注射在面部皮肤老化部位的真皮深层和皮下层,在平均观察6个月后患者均获得了满意的效果,皮肤老化皱纹部位得到明显改善[57]。ALBILIA等[58]每隔2周给37例颞下颌关节疼痛患者(共48个颞下颌关节)注射 1.5 mL可注射型富血小板纤维蛋白,48个颞下颌关节中有33个在第8周开始得到了明显的改善,研究结果表明可注射型富血小板纤维蛋白对大多数颞下颌关节疼痛患者具有长期的镇痛作用。在骨增量方面,有学者通过比较上颌窦开窗提升时使用Bio-Oss骨粉混合可注射型富血小板纤维蛋白和单纯应用Bio-Oss骨粉作为骨移植材料,比较其成骨效果,术后4个月Bio-Oss骨粉混合可注射型富血小板纤维蛋白组的种植体稳定系数显著高于单纯使用Bio-Oss骨粉组,术后6个月Bio-Oss骨粉混合可注射型富血小板纤维蛋白组的新生骨高度显著高于单纯使用Bio-Oss骨粉组[59]。"
| [1] KINGSLEY CS. Blood coagulation; evidence of an antagonist to factor VI in platelet-rich human plasma. Nature. 1954;173(4407):723-724. [2] MATRAS H. Effect of various fibrin preparations on reimplantations in the rat skin. Osterr Z Stomatol. 1970;67(9):338-359. [3] ROSENTHAL AR, EGBERT PR, HARBURY C, et al. Use of platelet-fibrinogen-thrombin mixture to seal experimental penetrating corneal wounds. Albrecht Von Graefes Arch Klin Exp Ophthalmol. 1978;207(2):111-115. [4] ASSOIAN RK, GROTENDORST GR, MILLER DM, et al. Cellular transformation by coordinated action of three peptide growth factors from human platelets. Nature. 1984;309(5971):804-806. [5] MARX RE, CARLSON ER, EICHSTAEDT RM, et al. Platelet-rich plasma: Growth factor enhancement for bone grafts. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1998;85(6):638-646. [6] CHOUKROUN J,ADDA F,SCHOEFFLER C.Une opportunité en Paro-implantologie: Le PRF. Implantodontie.2000;42:55-62. [7] MIRON RJ, FUJIOKA-KOBAYASHI M, BISHARA M, et al. Platelet-Rich Fibrin and Soft Tissue Wound Healing: A Systematic Review. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2017;23(1):83-99. [8] ALI S, BAKRY SA, ABD-ELHAKAM H. Platelet-Rich Fibrin in Maxillary Sinus Augmentation: A Systematic Review. J Oral Implantol. 2015;41(6):746-753. [9] LOPEZ-JORNET P, SANCHEZ PEREZ A, AMARAL MENDES R, et al. Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: Is autologous platelet concentrate application effective for prevention and treatment? A systematic review. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2016;44(8):1067-1072. [10] MALAVOLTA EA, ASSUNÇÃO JH, GRACITELLI ME, et al. Comments on: Evaluation of platelet-rich plasma and fibrin matrix to assist in healing and repair of rotator cuff injuries: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Rehabil. 2016;30(7):726-727. [11] MORASCHINI V, BARBOZA EDOS S. Use of Platelet-Rich Fibrin Membrane in the Treatment of Gingival Recession: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Periodontol. 2016;87(3):281-290. [12] RODELLA LF, FAVERO G, BONINSEGNA R, et al. Growth factors, CD34 positive cells, and fibrin network analysis in concentrated growth factors fraction. Microsc Res Tech. 2011;74(8):772-777. [13] DOHAN EHRENFEST DM, RASMUSSON L, ALBREKTSSON T. Classification of platelet concentrates: from pure platelet-rich plasma (P-PRP) to leucocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin (L-PRF). Trends Biotechnol. 2009;27(3):158-167. [14] CHOUKROUN J. Advanced PRF and i-PRF: Platelet concentrate or blood concentrate. Periodontal Med Clin Pract. 2014;13:64-68. [15] TUNALI M, ÖZDEMIR H, KÜÇÜKODACI Z, et al. In vivo evaluation of titanium-prepared platelet-rich fibrin (T-PRF): a new platelet concentrate. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013;51(5):438-443. [16] MOURÃO CF, VALIENSE H, MELO ER, et al. Obtention of injectable platelets rich-fibrin (i-PRF) and its polymerization with bone graft: technical note. Rev Col Bras Cir. 2015;42(6):421-423. [17] CHOUKROUN J, GHANAATI S. Reduction of relative centrifugation force within injectable platelet-rich-fibrin (PRF) concentrates advances patients’ own inflammatory cells, platelets and growth factors: the first introduction to the low speed centrifugation concept. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2018; 44(1):87-95. [18] 陶海荣,张长青,曾炳芳.磷酸三钙结合PRP修复股骨头坏死的研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2005,19(3):170-173. [19] AKEDA K, AN HS, PICHIKA R, et al. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) stimulates the extracellular matrix metabolism of porcine nucleus pulposus and anulus fibrosus cells cultured in alginate beads. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(9): 959-966. [20] DOHAN EHRENFEST DM, DEL CORSO M, DISS A, et al. Three-dimensional architecture and cell composition of a Choukroun’s platelet-rich fibrin clot and membrane. J Periodontol. 2010;81(4):546-555. [21] DOHAN DM, CHOUKROUN J, DISS A, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second-generation platelet concentrate. Part II: platelet-related biologic features. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006;101(3):e45-50. [22] NOH KC, LIU XN, ZHUAN Z, et al. Leukocyte-Poor Platelet-Rich Plasma-Derived Growth Factors Enhance Human Fibroblast Proliferation In Vitro. Clin Orthop Surg. 2018;10(2):240-247. [23] JOHNSSON A, HELDIN CH, WESTERMARK B, et al. Platelet-derived growth factor: identification of constituent polypeptide chains. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982;104(1):66-74. [24] 孟祥倩. STAT3蛋白在IGF-I介导的成肌细胞增殖中的作用[D].济南:山东大学,2014. [25] YUAN Y, DUAN R, WU B, et al. Gene expression profiles and bioinformatics analysis of insulin-like growth factor-1 promotion of osteogenic differentiation. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019;7(10):e00921. [26] GIANNINI S, CIELO A, BONANOME L, et al. Comparison between PRP, PRGF and PRF: lights and shadows in three similar but different protocols. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015;19(6):927-930. [27] DOHAN EHRENFEST DM, DISS A, ODIN G, et al. In vitro effects of Choukroun’s PRF (platelet-rich fibrin) on human gingival fibroblasts, dermal prekeratinocytes, preadipocytes, and maxillofacial osteoblasts in primary cultures. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2009; 108(3):341-352. [28] DEL CORSO M, SAMMARTINO G, DOHAN EHRENFEST DM. Re: “Clinical evaluation of a modified coronally advanced flap alone or in combination with a platelet-rich fibrin membrane for the treatment of adjacent multiple gingival recessions: a 6-month study”. J Periodontol. 2009;80(11): 1694-1697; author reply 1697-1699. [29] KAWASAKI J, KATORI N, KODAKA M, et al. Electron microscopic evaluations of clot morphology during thrombelastography. Anesth Analg. 2004;99(5):1440-1444. [30] KOBAYASHI E, FLÜCKIGER L, FUJIOKA-KOBAYASHI M, et al. Comparative release of growth factors from PRP, PRF, and advanced-PRF. Clin Oral Investig. 2016;20(9):2353-2360. [31] EL BAGDADI K, KUBESCH A, YU X, et al. Reduction of relative centrifugal forces increases growth factor release within solid platelet-rich-fibrin (PRF)-based matrices: a proof of concept of LSCC (low speed centrifugation concept). Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2019;45(3):467-479. [32] 周延民,付丽.富血小板纤维蛋白在口腔软硬组织再生中的作用——回顾与展望[J].口腔医学,2018,38(11):961-965. [33] FUJIOKA-KOBAYASHI M, MIRON RJ, HERNANDEZ M, et al. Optimized Platelet-Rich Fibrin With the Low-Speed Concept: Growth Factor Release, Biocompatibility, and Cellular Response. J Periodontol. 2017;88(1):112-121. [34] VARELA HA, SOUZA JCM, NASCIMENTO RM, et al. Injectable platelet rich fibrin: cell content, morphological, and protein characterization. Clin Oral Investig. 2019;23(3):1309-1318. [35] GHANAATI S, BOOMS P, ORLOWSKA A, et al. Advanced platelet-rich fibrin: a new concept for cell-based tissue engineering by means of inflammatory cells. J Oral Implantol. 2014;40(6):679-689. [36] DALLARI D, SAVARINO L, STAGNI C, et al. Enhanced tibial osteotomy healing with use of bone grafts supplemented with platelet gel or platelet gel and bone marrow stromal cells. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(11):2413-2420. [37] BIELECKI TM. Percutaneous injection of autogenous growth factors in patient with monunion of the humerus. A case report. Orthopaedics. 2006; 3(3): e15. [38] 刘哲伟,苏开新,陈军,等.富含血小板血浆外敷在深Ⅱ度烧伤创面修复中的临床应用[J].天津医药,2014,42(12):1213-1215. [39] OGUNDIPE OK, UGBOKO VI, OWOTADE FJ. Can autologous platelet-rich plasma gel enhance healing after surgical extraction of mandibular third molars? J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011;69(9):2305-2310. [40] TOPÇUOĞLU G, TOPÇUOĞLU HS. Regenerative Endodontic Therapy in a Single Visit Using Platelet-rich Plasma and Biodentine in Necrotic and Asymptomatic Immature Molar Teeth: A Report of 3 Cases. J Endod. 2016; 42(9):1344-1346. [41] CERVELLI V, NICOLI F, SPALLONE D, et al. Treatment of traumatic scars using fat grafts mixed with platelet-rich plasma, and resurfacing of skin with the 1540 nm nonablative laser. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2012;37(1):55-61. [42] RADICE F, YÁNEZ R, GUTIÉRREZ V, et al. Comparison of magnetic resonance imaging findings in anterior cruciate ligament grafts with and without autologous platelet-derived growth factors. Arthroscopy. 2010;26(1):50-57. [43] 戴勇中,叶平.富血小板纤维蛋白的研究进展[J].中华口腔医学杂志, 2011,46(6):382-384. [44] NAIK B, KARUNAKAR P, JAYADEV M, et al. Role of Platelet rich fibrin in wound healing: A critical review. J Conserv Dent. 2013;16(4):284-293. [45] 白冰,郭泽清,姚江武.含PRF骨粉诱导骨组织再生的临床观察[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2015,31(12):739-741. [46] CHOUKROUN J, DISS A, SIMONPIERI A, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second-generation platelet concentrate. Part V: histologic evaluations of PRF effects on bone allograft maturation in sinus lift. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006;101(3):299-303. [47] TAJIMA N, OHBA S, SAWASE T, et al. Evaluation of sinus floor augmentation with simultaneous implant placement using platelet-rich fibrin as sole grafting material. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2013;28(1):77-83. [48] CHOUKROUN J, DISS A, SIMONPIERI A, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second-generation platelet concentrate. Part IV: clinical effects on tissue healing. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006;101(3): e56-60. [49] ZHANG Y, RUAN Z, SHEN M, et al. Clinical effect of platelet-rich fibrin on the preservation of the alveolar ridge following tooth extraction. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15(3):2277-2286. [50] HAUSER F, GAYDAROV N, BADOUD I, et al. Clinical and histological evaluation of postextraction platelet-rich fibrin socket filling: a prospective randomized controlled study. Implant Dent. 2013;22(3):295-303. [51] HOAGLIN DR, LINES GK. Prevention of localized osteitis in mandibular third-molar sites using platelet-rich fibrin. Int J Dent. 2013;2013:875380. [52] SHARMA A, PRADEEP AR. Treatment of 3-wall intrabony defects in patients with chronic periodontitis with autologous platelet-rich fibrin: a randomized controlled clinical trial. J Periodontol. 2011;82(12):1705-1712. [53] THORAT M, PRADEEP AR, PALLAVI B. Clinical effect of autologous platelet-rich fibrin in the treatment of intra-bony defects: a controlled clinical trial. J Clin Periodontol. 2011;38(10):925-932. [54] SHARMA A, PRADEEP AR. Autologous platelet-rich fibrin in the treatment of mandibular degree II furcation defects: a randomized clinical trial. J Periodontol. 2011;82(10):1396-1403. [55] NAGAVENI NB, KUMARI KN, POORNIMA P, et al. Management of an endo-perio lesion in an immature tooth using autologous platelet-rich fibrin: a case report. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 2015;33(1):69-73. [56] KHOJASTEH A, HOSSEINPOUR S, NAZEMAN P, et al. The effect of a platelet-rich fibrin conduit on neurosensory recovery following inferior alveolar nerve lateralization: a preliminary clinical study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2016;45(10):1303-1308. [57] 张敏,易阳艳,王朝慧,等.可注射PRF联合自体脂肪移植矫正上睑凹陷的疗效[J].实用医学杂志,2019,35(15):2394-2398. [58] ALBILIA JB, HERRERA-VIZCAINO C, WEISLEDER H, et al. Liquid platelet-rich fibrin injections as a treatment adjunct for painful temporomandibular joints: preliminary results. Cranio. 2018:1-13 [59] 谢慧,解永富,刘勤,等.注射型PRF在上颌窦外提升术中的应用效果[J].上海口腔医学,2019,28(1):71-75. |
| [1] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [2] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [3] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [4] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [5] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [6] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [7] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [8] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [9] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [10] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [11] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [12] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [13] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [14] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [15] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||