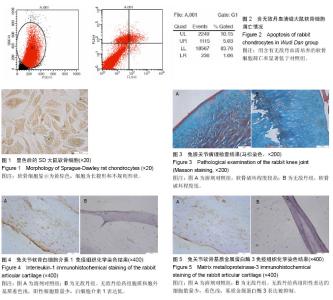
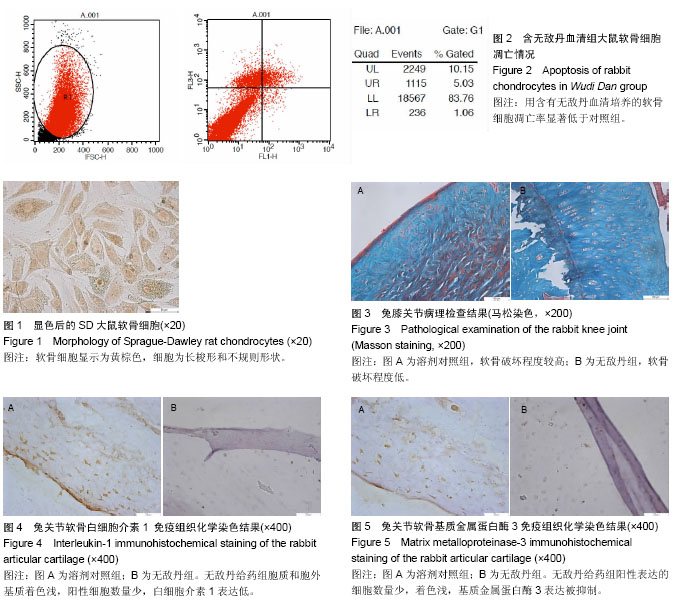
| [1] 杨雪晴,丁长海,徐建华.生物学标记物在骨关节炎中的研究进展[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2014,18(12):843-846.
[2] 王来芳,丁艳杰,赵清,等.吡咯喹啉醌对兔骨关节炎关节软骨保护机制的研究[J].中国生化药物杂志,2014,35(6):59-61.
[3] 陆洋,尹良军. 骨关节炎的临床特征及其治疗进展[J].医学信息, 2015,28(7):335-336.
[4] 刘振峰,方锐,孟庆才.Ⅱ型胶原酶消化法可短时间获得大量纯化大鼠关节软骨细胞[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011, 15(50):9323-9326.
[5] 谢希,高洁生.骨关节炎动物模型研究进展[J].医学综述, 2005, 11(1):67-69.
[6] Marijnissen AC, van Roermund PM, Verzijl N,et al .Steady progression of osteoarthritic features in the canine groove mode,Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2002;10(4):282-289.
[7] 许媛,赵明才.骨关节炎软骨细胞凋亡及其信号通路的研究进展[J].中华临床医师杂志:电子版,2014,8(6):1165-1167.
[8] Blanco FJ, Guitian R, Vazquez-Martul E,et al.Osteoarthritis chondrocytes die by apoptosis. A possible pathway forosteoarthritis pathology. Arthritis Rheum. 1998;41(2): 284-289.
[9] Hashimoto S,Ochs RL,Rosen F,et al.Chondrocyte-derived apoptotic bodies and calcification of articular cartilage.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95(6):3094-3099.
[10] 刘江涛,郭雄.骨关节炎软骨细胞凋亡机制的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2010,16(10):776-780.
[11] 向川.软骨细胞凋亡与骨关节炎[J].国外医学:免疫学分册, 26(2):110.
[12] Malemud CJ.Anticytokine therapy for osteoarthritis: evidence to date. Drugs Aging. 2010;27(2):95-115.
[13] Wojdasiewicz P, Poniatowski ?A, Szukiewicz D.The role of inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis.Mediators Inflamm. 2014; 2014:561459.
[14] Jiang Q, Qiu YT, Chen MJ,et al.Synovial TGF-α1 and MMP-3 levels and their correlation with the progression of temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis combined with disc displacement: A preliminary study.Biomed Rep.2013;1(2): 218-222.
[15] 张荣凯,方航,卢华定,等.MMP3在早期骨关节炎模型软骨下骨的表达及其意义[J].中国病理生理杂志,2011,27(12):2391-2395.
[16] Chen JJ, Huang JF, Du WX,et al.Expression and significance of MMP-3 in synovium of knee joint at different stage in osteoarthritis patients.Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2014;7(4): 297-300. |