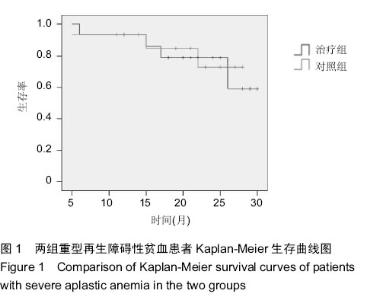
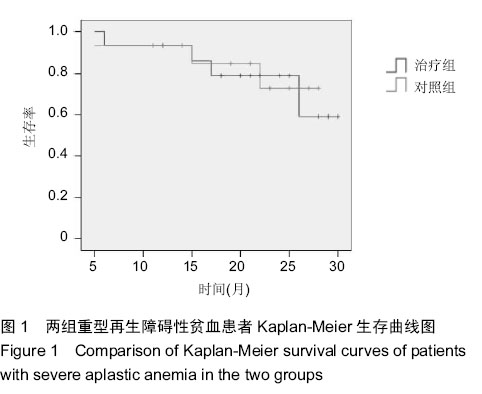
| [1] Miano M, Dufour C. The diagnosis and treatment of aplastic anemia: a review. Int J Hematol. 2015;101(6):527-535.
[2] 徐勇,欧阳建,陈兵,等.HLA全相合异基因造血干细胞移植与免疫抑制剂治疗重型再生障碍性贫血的比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(45):8513-8517.
[3] Pillai A, Hartford C, Wang C, et al. Favorable preliminary results using TLI/ATG-based immunomodulatory conditioning for matched unrelated donor allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in pediatric severe aplastic anemia. Pediatr Transplant. 2011;15(6):628-634.
[4] 葸瑞,白海,王存邦. 异基因造血干细胞移植治疗重型再生障碍性贫血[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2015,19(6):908-912.
[5] 郭智,陈惠仁,刘晓东,等.单倍型异基因造血干细胞移植治疗儿童重型再生障碍性贫血[J]. 中华实用儿科临床杂志,2014,29(15): 1145-1148.
[6] Ciceri F, Lupo-Stanghellini MT, Korthof ET. Haploidentical transplantation in patients with acquired aplastic anemia. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013;48(2):183-185.
[7] Kamio T, Ito E, Ohara A, et al. Relapse of aplastic anemia in children after immunosuppressive therapy: a report from the Japan Childhood Aplastic Anemia Study Group. Haematologica. 2011;96(6):814-819.
[8] 赵焱,谢晓恬. 重型获得性再生障碍性贫血治疗新进展[J].中华实用儿科临床杂志, 2015,30(3):236-238.
[9] 马肖容,杨楠,王瑾,等. 免疫抑制治疗成人重型再生障碍性贫血的近期疗效及长期生存情况随访研究[J].中国实验血液学杂志, 2015,23(2):471-476.
[10] 苏雁,吴润晖,马洁,等. 兔抗胸腺细胞球蛋白联合环孢素免疫抑制治疗儿童重型再生障碍性贫血的疗效[J].中华实用儿科临床杂志,2015,30(3):189-193.
[11] 徐学聚,吴爽,张园,等. 抗胸腺细胞球蛋白联合环孢素治疗儿童再生障碍性贫血后复发相关因素分析[J]. 中华实用儿科临床杂志,2013,28(15):1181-1183.
[12] 陈欣,冯四洲. 异基因造血干细胞移植治疗重型再生障碍性贫血研究进展[J].中华血液学杂志,2012,33(11):963-967.
[13] Bacigalupo A. Bone marrow transplantation for acquired severe aplastic anemia. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2014; 28(6):1145-1155.
[14] Hutspardol S, Sirachainan N, Anurathapan U, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for children with severe aplastic anemia. J Med Assoc Thai. 2013;96 Suppl 1:S18-24.
[15] Yoshida N, Kobayashi R, Yabe H, et al. First-line treatment for severe aplastic anemia in children: bone marrow transplantation from a matched family donor versus immunosuppressive therapy. Haematologica. 2014;99(12): 1784-1791.
[16] 陈惠仁,楼金星,张媛,等. 非血缘HLA相合供者造血干细胞移植治疗重型再生障碍性贫血的临床分析[J].中国实验血液学杂志, 2012,20(4):959-964.
[17] 万鼎铭,石聪聪,谢新生,等.父母供子女单倍型造血干细胞移植治疗恶性血液病[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(10):1753-1760.
[18] Clay J, Kulasekararaj AG, Potter V, et al. Nonmyeloablative peripheral blood haploidentical stem cell transplantation for refractory severe aplastic anemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014;20(11):1711-1716.
[19] 朱玲,薛梅,王志东,等. 异基因造血干细胞移植治疗重型再生障碍性贫血的疗效研究[J].中国全科医学,2011,14(6):1925-1927.
[20] Wang Z, Zheng X, Yan H, et al. Good outcome of haploidentical hematopoietic SCT as a salvage therapy in children and adolescents with acquired severe aplastic anemia. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2014;49(12):1481-1485.
[21] Kanda Y, Oshima K, Kako S, et al. In vivo T-cell depletion with alemtuzumab in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: Combined results of two studies on aplastic anemia and HLA-mismatched haploidentical transplantation. Am J Hematol. 2013;88(4):294-300.
[22] Peinemann F, Bartel C, Grouven U. First-line allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation of HLA-matched sibling donors compared with first-line ciclosporin and/or antithymocyte or antilymphocyte globulin for acquired severe aplastic anemia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;7: CD006407.
[23] Im HJ, Koh KN, Seo JJ. Haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in children and adolescents with acquired severe aplastic anemia. Korean J Pediatr. 2015;58(6): 199-205.
[24] 陈惠仁,何学鹏,司英健,等. 氟达拉滨替代环磷酰胺的预处理方案用于单倍型造血干细胞移植[J].中华血液学杂志,2009, 30(8): 514-517.
[25] Kim H, Kim BS, Kim DH, et al. Comparison between matched related and alternative donors of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cells transplanted into adult patients with acquired aplastic anemia: multivariate and propensity score-matched analysis. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2011;17(9):1289- 1298.
[26] Huang XJ, Xu LP, Liu KY, et al. Partially matched related donor transplantation can achieve outcomes comparable with unrelated donor transplantation for patients with hematologic malignancies. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15(14):4777-4783.
[27] Esteves I, Bonfim C, Pasquini R, et al. Haploidentical BMT and post-transplant Cy for severe aplastic anemia: a multicenter retrospective study. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2015;50(5):685-689. |