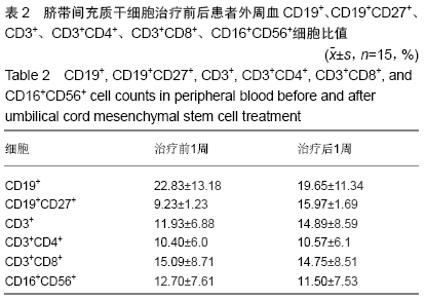
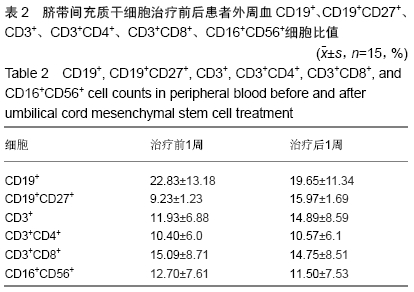
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (13): 2034-2038.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2039
Previous Articles Next Articles
Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of refractory chronic graft-versus-host disease
Zhang Ling, Sun Yanling, Wang Xiaozhen, Long Bing , Liu Jiajun
- Department of Hematology, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Institute of Hematology, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510630, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2019-08-08Revised:2019-08-10Accepted:2019-09-07Online:2020-05-08Published:2020-03-09 -
Contact:Liu Jiajun, MD, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Hematology, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Institute of Hematology, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510630, Guandong Province, China -
About author:Zhang Ling, Master, Attending physician, Department of Hematology, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Institute of Hematology, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510630, Guandong Province, China -
Supported by:Medical Research Foundation of Guangdong Province, No. A2017512; the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, No. 2014A030312012
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Ling, Sun Yanling, Wang Xiaozhen, Long Bing , Liu Jiajun. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of refractory chronic graft-versus-host disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(13): 2034-2038.
share this article
| [1] ARAI S, ARORA M, WANG T, et al. Increasing incidence of chronic graft-versus-host disease in allogeneic transplantation: a report from the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant.2015;21(2):266-274. [2] HERRMANN R, STURM M, SHAW K, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell therapy for steroid-refractory acute and chronic graft versus host disease: a phase 1 study. Int J Hematol. 2012;95(2):182-188. [3] GHANNAM S, BOUFFI C, DJOUAD F, et al. Immunosuppression by mesenchymal stem cells: mechanisms and clinical applications. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2010;1(1):2. [4] LI J, LI D, JU X, et al. Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells retain immunomodulatory and anti-oxidative activities after neural induction. Neural Regen Res. 2012;7(34):2663-2672. [5] CAMPAGNOLI C, ROBERTS IA, KUMAR S, et al. Identification of mesenchymal stem/progenitor cells in human first-trimester fetal blood, liver, and bone marrow. Blood. 2001;98(8):2396-2402. [6] IGURA K, ZHANG X, TAKAHASHI K, et al. Isolation and characterization of mesenchymal progenitor cells from chorionic villi of human placenta. Cytotherapy. 2004;6(6):543-553. [7] LEE SJ, KLEIN JP, BARRETT AJ, et al. Severity of chronic graft-versus-host disease: association with treatment-related mortality and relapse. Blood.2002;100(2):406-414. [8] TOGHRAIE F, RAZMKHAH M, GHOLIPOUR MA, et al. Scaffold-free adipose-derived stem cells (ASCs) improve experimentally induced osteoarthritis in rabbits. Arch Iran Med. 2012;15(8):495-499. [9] 庞荣清,何洁,李福兵,等.一种简单的人脐带间充质干细胞分离培养方法[J].中华细胞与干细胞杂志(电子版),2011,1(2):30-33. [10] LEE SJ, WOLFF D, KITKO C, et al. Measuring therapeutic response in chronic graft-versus-host disease. National Institutes of Health consensus development project on criteria for clinical trials in chronic graft-versus-host disease: IV. The 2014 Response Criteria Working Group report. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015;21(6):984-999. [11] WEISS ML, ANDERSON C, MEDICETTY S, et al. Immune properties of human umbilical cord Wharton's jelly-derived cells. Stem Cells. 2008; 26(11):2865-2874. [12] LE BLANC K, RASMUSSON I, SUNDBERG B, et al. Treatment of severe acute graft-versus-host disease with third party haploidentical mesenchymal stem cells. Lancet. 2004;363(9419):1439-1441. [13] 陈广华,杨婷,田竣,等.脐带间充质干细胞治疗糖皮质激素耐药的严重型急性移植物抗宿主病19例分析[J].中华血液学杂志, 2012, 33(4):303-306. [14] ZHAO K, HUANG F, PENG YW, et al. Clinical observation of mesenchymal stem cell as salvage treatment for refractory acute graft-versus-host disease. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2013;34(2): 122-126. [15] 陆英,张祥忠,刘相富,等.间充质干细胞输注对移植物抗宿主病中不同受损器官的治疗效果[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(23):3676-3681. [16] WENG JY, DU X, GENG SX, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell as salvage treatment for refractory chronic GVHD. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2010; 45(12):1732-1740. [17] INTRONA M, LUCCHINI G, DANDER E, et al. Treatment of graft versus host disease with mesenchymal stromal cells: a phase I study on 40 adult and pediatric patients. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014; 20(3):375-381. [18] 张乐施,刘启发,黄科.间充质干细胞治疗糖皮质激素耐药性慢性移植物抗宿主病临床疗效观察[J].中华内科杂志, 2009,48(7):542-546. [19] 张玲,张祥忠,李晓青,等.脐带间充质干细胞治疗难治性慢性移植物抗宿主病的疗效观察[J]. 器官移植,2016,11(7):459-462. [20] ERBEY F, ATAY D, AKCAY A, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Treatment for Steroid Refractory Graft-versus-Host Disease in Children: A Pilot and First Study from Turkey. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:1641402. [21] FRASER CJ, SCOTT BAKER K. The management and outcome of chronic graft-versus-host disease. Br J Haematol. 2007;138(2): 131-145. [22] PARKER PM, OPENSHAW H, FORMAN SJ. Myositis associated with graft-versus-host disease. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 1997;9(6):513-519. [23] SRINIVASAN M, FLYNN R, PRICE A, et al. Donor B-cell alloantibody deposition and germinal center formation are required for the development of murine chronic GVHD and bronchiolitis obliterans. Blood. 2012;119(6):1570-1580. [24] JURADO M, DE LA MATA C, RUIZ-GARCÍA A, et al. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cells as part of therapy for chronic graft-versus-host disease: A phase I/II study. Cytotherapy. 2017;19(8):927-936. [25] PENG Y, CHEN X, LIU Q, et al. Alteration of naïve and memory B-cell subset in chronic graft-versus-host disease patients after treatment with mesenchymal stromal cells. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2014;3(9): 1023-1031. [26] NORDLANDER A, MATTSSON J, RINGDÉN O, et al. Graft-versus-host disease is associated with a lower relapse incidence after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2004;10(3): 195-203. [27] KOH LP, CHEN CS, TAI BC, et al. Impact of postgrafting immunosuppressive regimens on nonrelapse mortality and survival after nonmyeloablative allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant using the fludarabine and low-dose total-body irradiation 200-cGy. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2007;13(7):790-805. [28] VAN DER STRAATEN HM, FIJNHEER R, DEKKER AW, et al. Relationship between graft-versus-host disease and graft-versus- leukaemia in partial T cell-depleted bone marrow transplantation. Br J Haematol. 2001;114(1):31-35. [29] KIM N, IM KI, LIM JY, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment and prevention of graft-versus-host disease: experiments and practice. Ann Hematol. 2013;92(10):1295-1308. [30] BARON F, LECHANTEUR C, WILLEMS E, et al. Cotransplantation of mesenchymal stem cells might prevent death from graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) without abrogating graft-versus-tumor effects after HLA-mismatched allogeneic transplantation following nonmyeloablative conditioning. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2010;16(6):838-847. [31] KUZMINA LA, PETINATI NA, PAROVICHNIKOVA EN, et al. Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells for the Prophylaxis of Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease-A Phase II Study. Stem Cells Int. 2012; 2012:968213. |
| [1] | Chen Xiao, Guo Zhi, Chen Lina, Liu Xuanyong, Zhang Yihuizhi, Li Xumian, Wang Yueqiao, Wei Liya, Xie Jing, Lin Li. Factors affecting the mobilization and collection of autologous peripheral blood hematopoietic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2958-2962. |
| [2] | Cao Linlin, Ding Kaiyang, Song Hao, Wu Guolin, Hu Maogui, Fan Dandan, Zhou Chenyang, Wang Cuicui, Feng Yuanyuan. Efficacy and influencing factors of autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in the treatment of malignant lymphoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 1993-1998. |
| [3] | Zhang Suping, Sun Ling, Wan Dingming, Cao Weijie, Li Li, Liu Changfeng, Liu Yufeng, Wang Dao, Guo Rong, Jiang Zhongxing, Xie Xinsheng. Effectiveness of unrelated peripheral blood stem cell transplantation in the treatment of severe aplastic anemia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(31): 4994-5001. |
| [4] | Wei Yuanfeng, Huang Dongping. Current status of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in the treatment of aplastic anemia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(19): 3093-3100. |
| [5] | Xue Hui, Feng Shuqing, Hu Yongchao, Liu Zhibin, Li Xiaoyu, Gao Feng. Stratification therapy for cytomegalovirus infection after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(5): 756-760. |
| [6] | Chen Xiaoling, Deng Huilan, Lu Quanyi, Hong Xiuli, Hu Jiasheng. Pure red cell aplasia follows allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a two-case report and literature review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(5): 761-766. |
| [7] | Guo Zhi, Ren Hua, Ji Yong, Chen Liping, Chen Lina, Liu Xuanyong, Zheng Shanshan, Liu Xiaodong, Chen Huiren. Thrombopoietin improves platelet recovery after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for severe aplastic anemia: an assessment of safety and efficacy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(33): 5269-5274. |
| [8] | Liu Jiao, Wang Daming, An Taixue, Hu Xuesong, Li Nankai, Wang Hongfu, Ma Wen, Nie-He Zhongrong, Xiao Lijia, Zhou Yiwen, Zheng Lei. Expression profile analysis of miRNAs in serumal exosomes as sensitive biomarkers in patients with graft-versus-host disease following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(21): 3418-3425. |
| [9] | Wang Xiaoning, Chen Ying, Zhu Huachao, Zhang Mei, He Pengcheng. Protective effect of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on acute drug-induced liver injury after conditioning in haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(17): 2690-2695. |
| [10] | Wei Yuanfeng, Wei Zhongling, Yang Yuqiong, Qi Jing, Yan Jiawei, Huang Dongping. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for severe aplastic anemia in 10 cases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(13): 2042-2048. |
| [11] | Wan Ding-ming, Sun Lin-lin, Xie Xin-sheng, Guo Rong, Cao Wei-jie, Zhang Su-ping, Li Li, Chen Xiao-na, Liu Yu-ye. Peripheral blood haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adults: monitoring minimal residual diseases to intervene recurrence [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(9): 1413-1418. |
| [12] | Wan Ding-ming, Liu Yu-ye, Cao Wei-jie, Xing Hai-zhou, Xie Xin-sheng, Wang Dao, Zhang Su-ping, Li Li, Chen Xiao-na, Sun Lin-lin. Genetic haploidentical peripheral blood stem cell transplantation for treatment of myelodysplastic syndrome: a 2-year follow-up visit of 21 cases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(5): 662-668. |
| [13] | Ren Juan, Zhao Juan, Wang Xiao-ning. Co-transplantation of umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells and haploidentical hematopoietic stem cells for treatment of severe aplastic anemia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(33): 5297-5302. |
| [14] | Wang Kun, Han Jun-yong, Chen Jin-yan, Liu Shen-min, Xue Shi-jie, Jin Jing-jun. Measurements of T-cell receptor excision cycles in early stage of immune reconstitution after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(29): 4643-4649. |
| [15] | Feng You-fan, Wei Xiao-fang, Zhang Qi-ke. Detection of minimal residual disease prior to allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in middle-aged and elderly acute myeloid leukemia patients: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(29): 4692-4697. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||