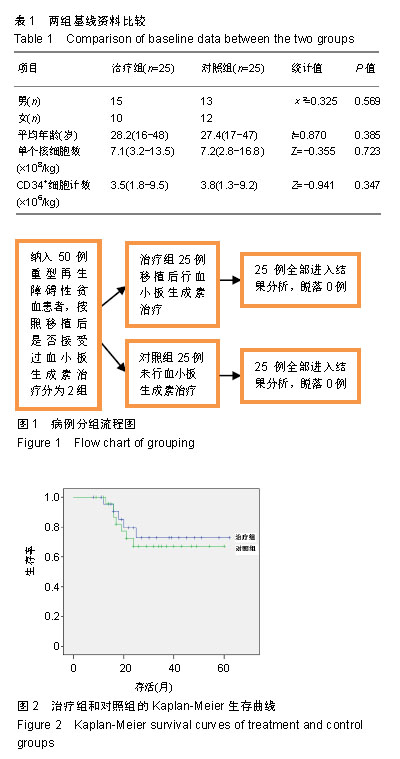
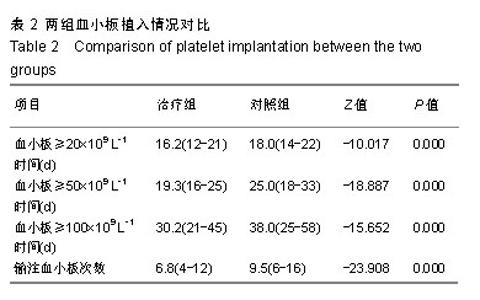
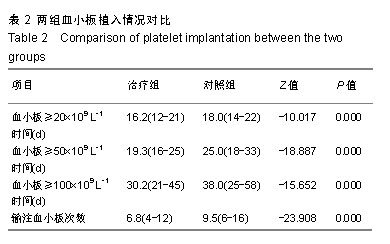
| [1]Park SS, Kwak DH, Jeon YW, et al. Beneficial Role of Low-Dose Antithymocyte Globulin in Unrelated Stem Cell Transplantation for Adult Patients with Acquired Severe Aplastic Anemia: Reduction of Graft-versus-Host Disease and Improvement of Graft-versus- Host Disease-Free, Failure-Free Survival Rate. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2017;23(9):1498-1508.[2]Mori T, Onishi Y, Ozawa Y, et al. Outcome of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in adult patients with hepatitis-associated aplastic anemia. Int J Hematol. 2019;109(6): 711-717.[3]Kim H, Im HJ, Koh KN, et al. Comparable Outcome with a Faster Engraftment of Optimized Haploidentical Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Compared with Transplantations from Other Donor Types in Pediatric Acquired Aplastic Anemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019;25(5):965-974.[4]郭智,刘晓东,杨凯,等.allo-HSCT并使用高剂量环磷酰胺诱导免疫耐受治疗重型再生障碍性贫血[J].中华器官移植杂志,2015,36(6): 356-361.[5]Ghanem KM, Kharfan-Dabaja MA, El-Solh H, et al. Fludarabine-based reduced intensity regimen for matched related donor hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in acquired severe aplastic anemia. Curr Res Transl Med. 2017;65(3):115-119.[6]Shin SH, Jeon YW, Yoon JH, et al. Comparable outcomes between younger (?40 years) and older (>40 years) adult patients with severe aplastic anemia after HLA-matched sibling stem cell transplantation using fludarabine-based conditioning. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2016;51(11):1456-1463.[7]郭智,陈惠仁.单倍体造血干细胞移植后高剂量环磷酰胺诱导免疫耐受治疗再生障碍性贫血的研究[J].中华器官移植杂志,2015,36(12): 753-755.[8]童春,郭智,楼金星,等.单倍型异基因造血干细胞移植治疗重型再生障碍性贫血:回顾性分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(36): 5821-5826.[9]Yahng SA, Park SS, Jeon YW, et al. Successful outcomes of second hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with total nodal irradiation and ATG conditioning for graft failure in adult patients with severe aplastic anemia. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2018; 53(10):1270-1277.[10]Rodeghiero F, Ruggeri M. Treatment of immune thrombocytopenia in adults: the role of thrombopoietin-receptor agonists. Semin Hematol. 2015;52(1):16-24.[11]Elmahdi S, Muramatsu H, Narita A, et al. Markedly High Plasma Thrombopoietin (TPO) Level is a Predictor of Poor Response to Immunosuppressive Therapy in Children With Acquired Severe Aplastic Anemia. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2016;63(4):659-664.[12]Zhang Y, Lin CHS, Kaushansky K, et al. JAK2V617F Megakaryocytes Promote Hematopoietic Stem/Progenitor Cell Expansion in Mice Through Thrombopoietin/MPL Signaling. Stem Cells. 2018;36(11):1676-1684.[13]徐云华,成柏君,陆舜,等.短程间歇预防性给予重组人血小板生成素治疗肺癌化疗诱导的严重血小板减少的疗效[J].中华肿瘤杂志,2011, 33(5):395-399.[14]Bosch-Vilaseca A, García-Cadenas I, Roldán E, et al. Usefulness of thrombopoietin receptor agonists for persistent clinically relevant thrombocytopenia after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Eur J Haematol. 2018;101(3):407-414.[15]Zhang Y, Guo Z, Liu XD, et al. Comparison of Haploidentical Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation and Immunosuppressive Therapy for the Treatment of Acquired Severe Aplastic Anemia in Pediatric Patients. Am J Ther. 2017;24(2):e196-e201.[16]Guo Z, Gao HY, Zhang TY, et al. Analysis of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with high-dose cyclophosphamide-induced immune tolerance for severe aplastic anemia. Int J Hematol. 2016;104(6):720-728.[17]郭智,童春,刘晓东,等.单倍型异基因造血干细胞移植后大剂量环磷酰胺诱导免疫耐受治疗儿童重型再生障碍性贫血[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(32):4818-4824.[18]郭智,陈惠仁,杨凯,等.免疫耐受新方法单倍型造血干细胞移植治疗重型再生障碍性贫血[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(41): 6683-6687.[19]Yang S, Yuan X, Ma R, et al. Comparison of Outcomes of Frontline Immunosuppressive Therapy and Frontline Haploidentical Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Children with Severe Aplastic Anemia Who Lack an HLA-Matched Sibling Donor. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019;25(5):975-980.[20]郭智,陈惠仁,刘晓东,等.低强度预处理联合移植后诱导免疫耐受的单倍体相合Allo-HSCT治疗重型再生障碍性贫血的临床疗效研究[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2016,24(6):1811-1816.[21]郭智,任骅,胡亮钉,等.重型再生障碍性贫血移植后合并肺部侵袭性真菌感染6例临床分析[J].解放军医学杂志, 2017,42(12): 1097-1101.[22]Barbieri D, Elvira-Matelot E, Pelinski Y, et al. Thrombopoietin protects hematopoietic stem cells from retrotransposon-mediated damage by promoting an antiviral response. J Exp Med. 2018; 215(5):1463-1480.[23]程莹,孙延庆,张雯洁,等.重组人血小板生成素促进异基因造血干细胞移植后血小板恢复的Meta分析[J].现代肿瘤医学, 2015,23(10): 1446-1451.[24]孙明玲,王新有,江明,等.重组人血小板生成素联合大剂量地塞米松治疗初治原发性免疫性血小板减少症的临床分析[J].中华内科杂志, 2016,55(3):202-205.[25]Lakhwani S, Perera M, Fernández-Fuertes F, et al. Thrombopoietin receptor agonist switch in adult primary immune thrombocytopenia patients: A retrospective collaborative survey involving 4 Spanish centres. Eur J Haematol. 2017;99(4):372-377.[26]Taylor A, Westwood JP, Laskou F, et al. Thrombopoetin receptor agonist therapy in thrombocytopenia: ITP and beyond. Br J Haematol. 2017;177(3):475-480.[27]Gudbrandsdottir S, Ghanima W, Nielsen CH, et al. Effect of thrombopoietin-receptor agonists on circulating cytokine and chemokine levels in patients with primary immune thrombocytopenia (ITP). Platelets. 2017;28(5):478-483.[28]Blair TA, Moore SF, Walsh TG, et al. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase p110α negatively regulates thrombopoietin-mediated platelet activation and thrombus formation. Cell Signal. 2018;50:111-120.[29]Barbieri D, Elvira-Matelot E, Pelinski Y, et al. Thrombopoietin protects hematopoietic stem cells from retrotransposon-mediated damage by promoting an antiviral response. J Exp Med. 2018; 215(5):1463-1480.[30]苗瞄,吴德沛,曹祥山,等.血小板生成素在异基因造血干细胞移植后促进血小板植入的临床研究[J].中华血液学杂志,2012,33(5): 362-365.[31]江岷,潘欣,徐晨,等.重组人血小板生成素促进异基因造血干细胞移植血小板恢复的随机对照临床试验[J].血栓与止血学,2011,17(6): 247-253.[32]Rodeghiero F, Carli G. Beyond immune thrombocytopenia: the evolving role of thrombopoietin receptor agonists. Ann Hematol. 2017;96(9):1421-1434. |