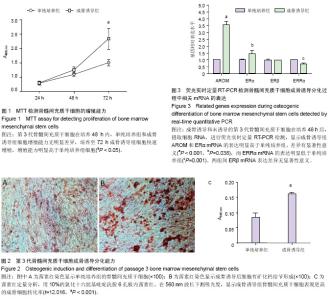
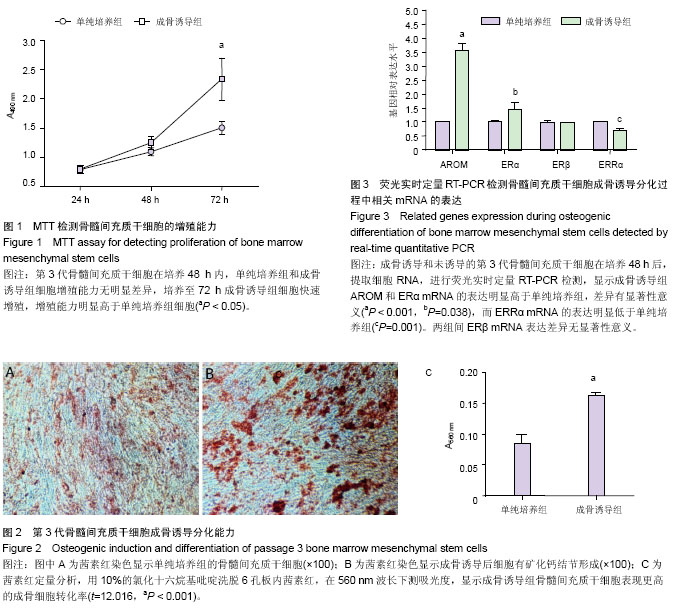
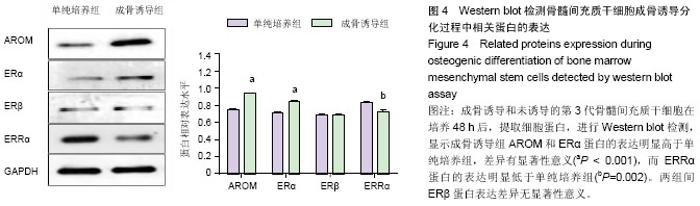
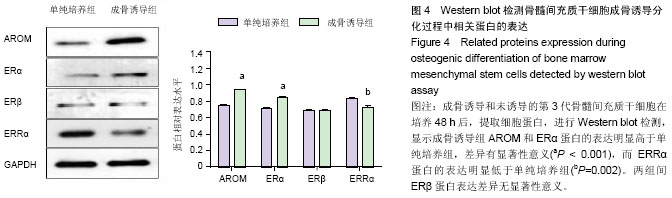
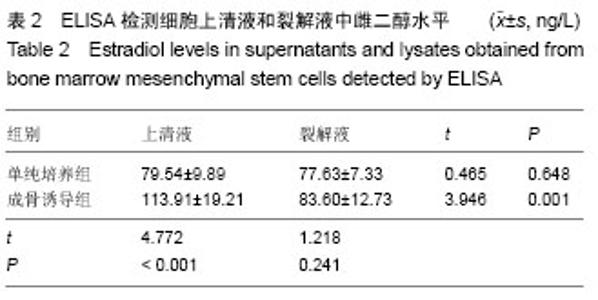
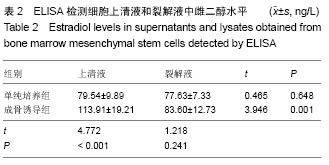
| [1] Fan JZ, Yang L, Meng GL, et al. Estrogen improves the proliferation and differentiation of hBMSCs derived from postmenopausal osteoporosis through notch signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014;392(1-2):85-93.
[2] Lv H, Che T, Tang X, et al. Puerarin enhances proliferation and osteoblastic differentiation of human bone marrow stromal cells via a nitric oxide/cyclic guanosine monophosphate signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2015;12(2): 2283-2290.
[3] Perez EA, Weilbaecher K. Aromatase inhibitors and bone loss. Oncology (Williston Park). 2006;20(9):1029-1039.
[4] Riancho JA, Sañudo C, Valero C, et al. Association of the aromatase gene alleles with BMD: epidemiological and functional evidence. J Bone Miner Res. 2009;24(10): 1709-1718.
[5] Riancho JA, Zarrabeitia MT, Valero C, et al. A gene-to-gene interaction between aromatase and estrogen receptors influences bone mineral density. Eur J Endocrinol. 2006; 155(1): 53-59.
[6] 王俊玲,黄思敏,魏秋实,等.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞及不同组织中17β-雌二醇的表达情况[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2015, 31(6):905-907.
[7] Shoukry A, Shalaby SM, Etewa RL, et al. Association of estrogen receptor β and estrogen-related receptor α gene polymorphisms with bone mineral density in postmenopausal women. Mol Cell Biochem. 2015;405(1-2):23-31.
[8] Li L, Yao XL, He XL, et al. Role of mechanical strain and estrogen in modulating osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) from normal and ovariectomized rats. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2013; Suppl 59:OL1889-1893.
[9] Zhou S, Zilberman Y, Wassermann K, et al. Estrogen modulates estrogen receptor alpha and beta expression, osteogenic activity, and apoptosis in mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) of osteoporotic mice. J Cell Biochem Suppl. 2001; Suppl 36:144-155.
[10] Francis WR, Owens SE, Wilde C, et al. The temporal expression of estrogen receptor alpha-36 and runx2 in human bone marrow derived stromal cells during osteogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;453(3):552-556.
[11] Bonnelye E, Aubin JE. Estrogen receptor-related receptor alpha: a mediator of estrogen response in bone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90(5):3115-3121.
[12] Bonnelye E, Laurin N, Jurdic P, et al. Estrogen receptor-related receptor-alpha (ERR-alpha) is dysregulated in inflammatory arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008;47(12):1785-1791.
[13] Cai C, Yuan GJ, Huang Y, et al. Estrogen-related receptor α is involved in the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells isolated from human periodontal ligaments. Int J Mol Med. 2013;31(5):1195-1201.
[14] Bonnelye E, Aubin JE. Differential expression of estrogen receptor-related receptor alpha and estrogen receptors alpha and beta in osteoblasts in vivo and in vitro. J Bone Miner Res. 2002;17(8):1392-1400.
[15] Ai N, Krasowski MD, Welsh WJ, et al. Understanding nuclear receptors using computational methods. Drug Discov Today. 2009;14(9-10):486-494.
[16] Seals DR, Jablonski KL, Donato AJ. Aging and vascular endothelial function in humans. Clin Sci (Lond). 2011;20(9): 357-375.
[17] Luo D, Liu Y, Zhou Y, et al. Association between dietary phytoestrogen intake and bone mineral density varied with estrogen receptor alpha gene polymorphisms in southern Chinese postmenopausal women. Food Funct. 2015;6(6): 1977-1983.
[18] Bojar I, Gujski M, Raczkiewicz D, et al. Estrogen receptor alpha polymorphisms, estradiol level, and occurrence of atherosclerosis risk factors in healthy postmenopausal women. Med Sci Monit. 2015;21:970-979.
[19] Kurt O, Yilmaz-Aydogan H, Uyar M, et al. Evaluation of ERα and VDR gene polymorphisms in relation to bone mineral density in Turkish postmenopausal women. Mol Biol Rep. 2012;39(6):6723-6730.
[20] Erdogan MO, Y?ld?z H, Artan S, et al. Association of estrogen receptor alpha and collagen type I alpha 1 gene polymorphisms with bone mineral density in postmenopausal women. Osteoporos Int. 2011;22(4):1219-1225.
[21] Ikeda K, Tsukui T, Horie-Inoue K, et al. Conditional expression of constitutively active estrogen receptor α in osteoblasts increases bone mineral density in mice. FEBS Lett. 2011; 585(9):1303-1309.
[22] Vanderschueren D, Laurent MR, Claessens F, et al. Sex steroid actions in male bone. Endocr Rev. 2014;35(6):906-960.
[23] He YX, Liu Z, Pan XH, et al. Deletion of estrogen receptor beta accelerates early stage of bone healing in a mouse osteotomy model. Osteoporos Int. 2012;23(1):377-389.
[24] Auld KL, Berasi SP, Liu Y, et al. Estrogen-related receptor α regulates osteoblast differentiation via Wnt/β-catenin signaling. J Mol Endocrinol. 2012;48(2):177-191.
[25] Delhon I, Gutzwiller S, Morvan F, et al. Absence of estrogen receptor-related-alpha increases osteoblastic differentiation and cancellous bone mineral density. Endocrinology. 2009; 150(10):4463-4472.
[26] Teyssier C, Gallet M, Rabier B, et al. Absence of ERRalpha in female mice confers resistance to bone loss induced by age or estrogen-deficiency. PLoS One. 2009;4(11):e7942.
[27] Wang BL, Sun W, Shi ZC, et al. Decreased proliferation of mesenchymal stem cells in corticosteroid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head. Orthopedics. 2008;31(5):444.
[28] Sheng H, Sheng CJ, Cheng XY, et al. Pathomorphological changes of bone marrow adipocytes in process of steroid-associated osteonecrosis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013; 6(6):1046-1050. |