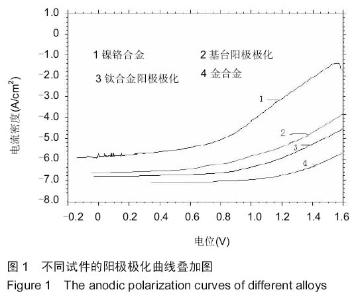
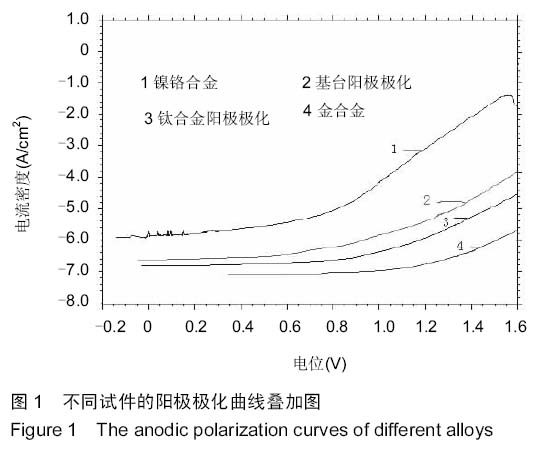
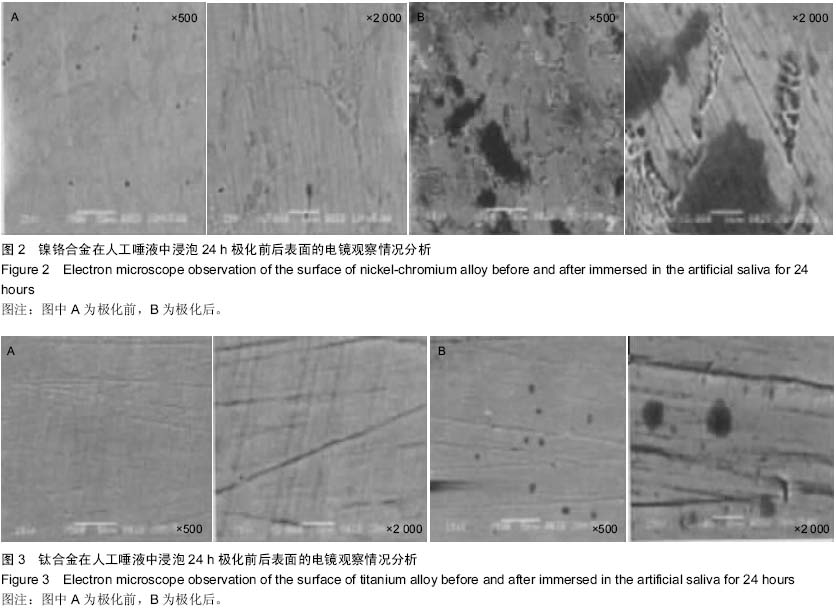
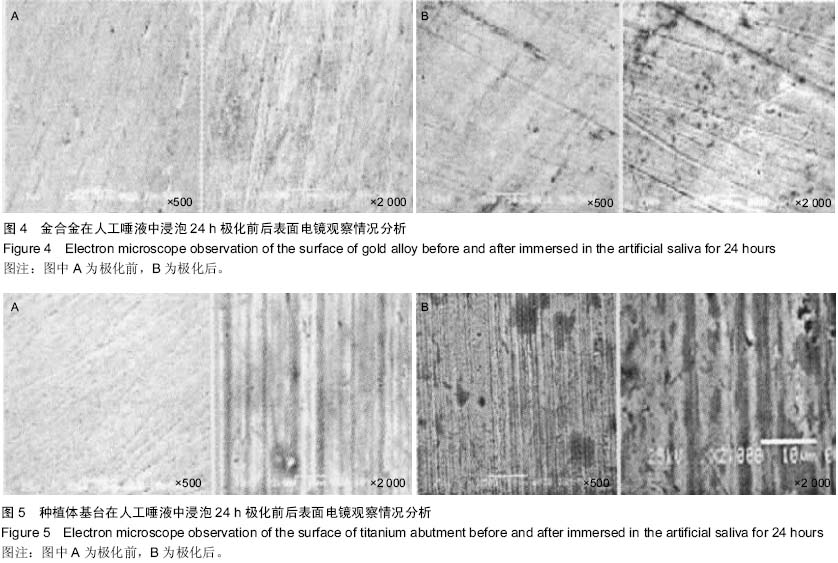
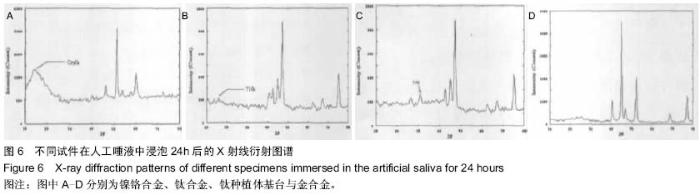
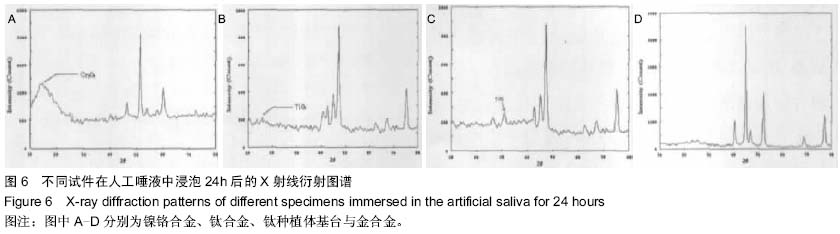
| [1] 刘玉艳,周延民.钛种植体基台与三种合金在人工唾液中腐蚀性能研究[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2006,20(5):485-488.
[2] 汤雅,陈必新.钛种植体基台与种植体上部结构合金的耐腐蚀性能[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(47):7561-7565.
[3] 李梅,杨圣辉,王者玲,等.钛种植体基台的表面粗糙度与细菌粘附[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2001,36(6):431-433.
[4] 李晓军,沙月琴,于春泾,等.不同洁治器械对钛种植体基台表面的影响[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2000,14(1):26-27.
[5] 王卫东,李辉,熊昊,等.两种漱口水对钛种植体基台的影响[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2006,22(8):484-485.
[6] 李晓军,沙月琴,于春泾,等.不同洁治器械对钛种植体基台表面的影响[J].中华口腔医学杂志,1999,14(1):12.
[7] 李智勇,刘学军,赵丽雅,等.不同基台时种植体支持全瓷单冠的应力分析[J].口腔医学研究,2007,23(4):402-404.
[8] 李智勇,牛薇,方伟,等.瓷基台和钛基台用于种植体支持全瓷单冠修复的临床观察[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2007,42(7):391-394.
[9] 王伟嘉.种植体基台与修复冠间粘接界面三维有限元应力分析[D].泸州医学院,2010.
[10] 焦艳军,王珏,潘福勤,等.纯钛种植体的2种表面处理对细菌黏附能力的影响[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2009,25(2):166-169.
[11] 吴小勇,杨娅,顾泽旭,等.2种不同钛基台-氧化锆全瓷修复体用于低位咬合单个磨牙缺失患者种植修复的临床评价[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2013,29(3):394-397.
[12] 王汝丽,曹良菊,夏舟斌,等.氧化锆基台和常规钛基台在前牙区种植修复中的临床应用[J].昆明医科大学学报,2014,35(6): 122-124.
[13] 吴春锋,谢乔,王书明,等.氧化锆瓷基台与钛种植体联合应用中不同连接体设计的有限元分析[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2014,30(3): 140-142.
[14] 焦艳军,王珏,潘福勤,等.钛及钛合金种植体的两种表面处理对细菌黏附能力的影响[J].中国药物与临床,2008,8(11):858-860.
[15] 武斌,巢永烈,隋磊,等.全瓷冠熔附纯钛小基台种植修复体的临床应用[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2007,42(10):622-623.
[16] 任志新.全瓷基台与钛基台种植体支持全瓷单冠的应力分布[D].中国医科大学,2009.
[17] 潘福勤.钛及钛合金种植体的两种表面处理对细菌粘附能力的影响[D].山西医科大学,2006.
[18] 任志新,刘维贤.氧化锆全瓷基台与钛基台种植体支持氧化锆全瓷单冠的应力分布[J].辽宁医学杂志,2009,23(5):245-247.
[19] 杨名辉.软组织水平种植体与平台转移设计的骨水平种植体对后牙区种植体颈部骨量保存的对比研究[D].青岛大学,2013.
[20] 马千里.纯钛牙科种植体材料表面阳极氧化及载银处理的生物学研究[D].第四军医大学,2011.
[21] 王伟嘉,赵峰,龙刚,等.种植体钛基台和全瓷冠间粘接界面的三维有限元应力分析[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2010,15(2):59-62.
[22] 王伟嘉,龙刚,胡嘉伟等.钴铬合金和钛基台与全瓷冠间粘接界面的三维有限元应力分析[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2011, 38(1): 10-13.
[23] 李家奇,孟维艳,周延民,等.不同表面形貌的纯钛种植体对牙龈软组织界面影响的扫描电镜观察[J].吉林大学学报:医学版,2014, 40(1):102-108.
[24] 李俊青,王大山,王永亮,等.氧化锆基台的制作及其与钛基台抗折强度的比较[J].现代生物医学进展,2013,13(14):2640-2643.
[25] 刘霜印,曹保富,付新国,等.钛板携带种植体修复下颌骨缺损的临床应用[J].口腔医学研究,2006,22(3):284-286.
[26] 石茂林,李洪友,陈梦月,等.二段式钛合金种植牙不同弹性模量组件及其组合对骨界面应力分布的影响[J].华侨大学学报:自然科学版,2014,35(4):361-366.
[27] 宋应亮,徐君伍,马轩祥,等.牙龈卟啉菌381对纯钛及钛75合金种植体表面失泽的腐蚀[J].第四军医大学学报,2000,21(8): 915-917.
[28] 宋应亮,徐君伍,马轩祥,等.Aay4对钛及钛75合金表面失泽腐蚀的研究[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2000,35(4):256-258.
[29] 钱棱,王培志.种植体腐蚀及其影响因素的研究进展[J].口腔生物医学,2012,3(2):87-89.
[30] 吕宇鹏,朱瑞富,马泉生,等.医用钛及钛合金种植体材料的研究进展[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2000,5(1):43-49.
[31] 严洪海,赵士芳,陈关福,等.不同温度热氧化处理钛种植体耐腐蚀性能和离子释放速度的体外研究[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2001, 6(3):109-112,115.
[32] 汤雅,王国平.种植体材料钛与种植体上部结构合金间电偶的腐蚀性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(51): 9617- 9620.
[33] 马楚凡,李冬梅,蒋百灵,等.钛种植体表面微弧氧化生物改性的研究[J].第四军医大学学报,2004,25(1):4-7.
[34] 张晓真,汤春波.钛锆合金种植体的研究进展[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2014,19(4):200-204.
[35] 汤雅,王国平,王培志,等.种植体材料钛与种植体上部结构合金问电偶腐蚀性能的研究[J].口腔医学,2008,28(4):195-197.
[36] 宋应亮,徐君伍,马轩祥,等.口腔环境中纯钛及钛75合金种植体覆盖螺丝缝隙腐蚀的研究[J].口腔医学,2000,20(3):113-114.
[37] 汤雅,王国平.影响牙科用钛和钛合金种植体腐蚀性的因素[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2008,35(3):347-349.
[38] 严洪海,胡玲华,黄海蓉,等.不同粗糙表面的纯钛种植体的耐腐蚀性评价[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2008,13(4):175-179.
[39] 王浩,施琥.钛和钛合金在口腔环境中应用腐蚀的研究进展[J].口腔材料器械杂志,2008,17(3):147-149.
[40] 王道强,吴文慧.医用口腔纯钛材料腐蚀性的研究进展[J].临床合理用药杂志,2014,7(14):175-176.
[41] 聂鹤鹏,王国平,夏露. 氟化物对纯钛及钛合金的腐蚀作用[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2013,18(1):51-53.
[42] 邵安良,成艳,奚廷斐,等.TiN/Ti纳米涂层修饰镍钛合金的体外腐蚀行为[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(3):461-464.
[43] 纪文婷.五种超弹性镍钛合金弓丝在人工唾液中抗腐蚀能力的比较[D].大连医科大学:口腔临床医学(硕士),2012.
[44] 尹大宇,朱锦宇,段永宏,等.生物医用镍钛合金表面钽涂层腐蚀行为研究[J].华南国防医学杂志,2011,25(1):52-56.
[45] 朱娴.氟及白蛋白对钛合金抗腐蚀性能影响的研究现状[J].口腔材料器械杂志,2010,19(4):212-214,218.
[46] 曹博玮,陈蕾.氟离子对2种牙科用钛合金耐腐蚀性的影响[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2010,28(3):261-264. |