Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (2): 196-203.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0006
Previous Articles Next Articles
Biomechanical finite element analysis on the bone interface of posterior mandibular area under different setting forces after inclined implantation with angled abutment
- Department of Stomatology, the Second Hospital of Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300201, China
-
Received:2017-11-30Online:2018-01-18Published:2018-01-18 -
About author:Liu Li-ping, Studying for master’s degree, Associate chief physician, Department of Stomatology, the Second Hospital of Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300201, China -
Supported by:the Applied Basic and Cutting-Edge Technology Research Plan of Tianjin, No. 15JCZDJC38200
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Li-ping, Lv Xiao-fei, Deng Shu, Peng Cheng .
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
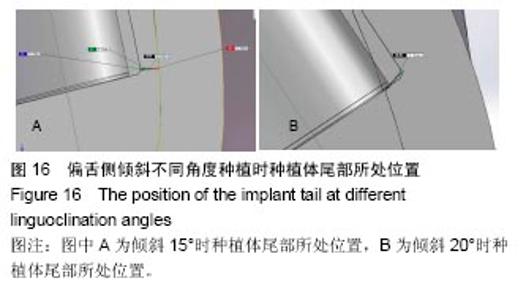
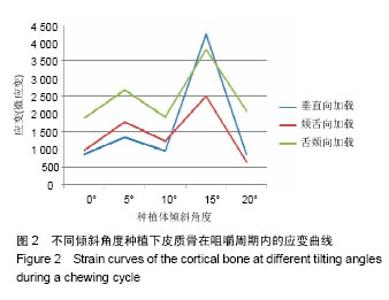
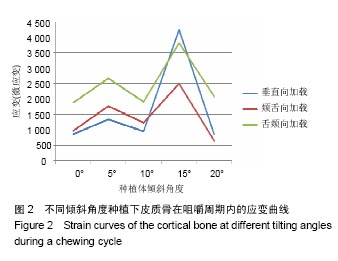
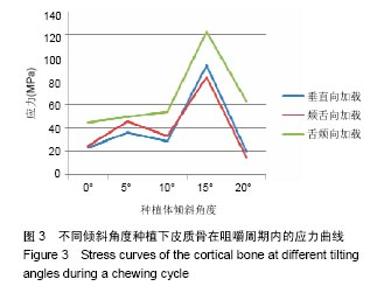
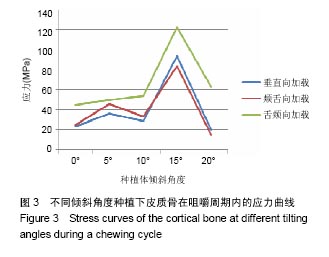
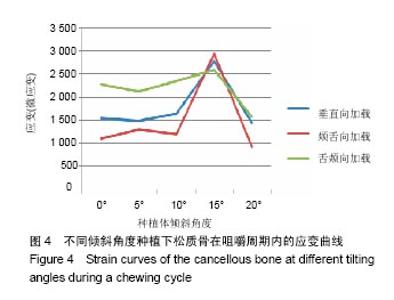
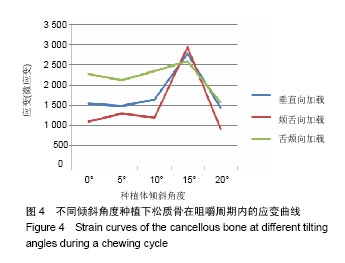
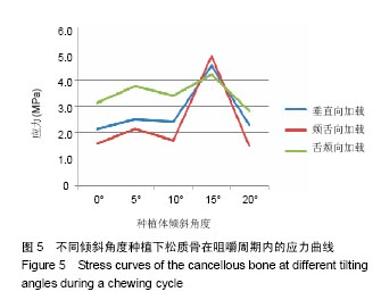
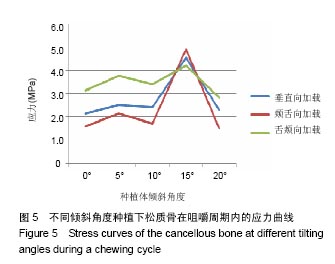
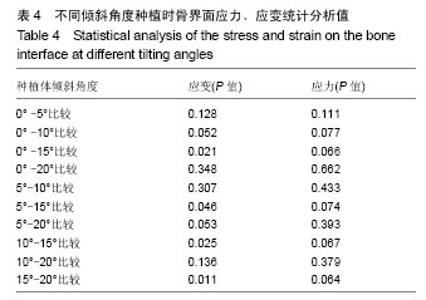
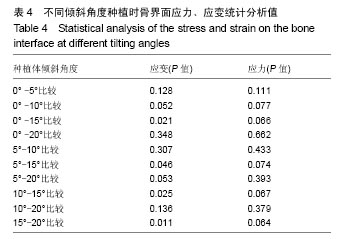
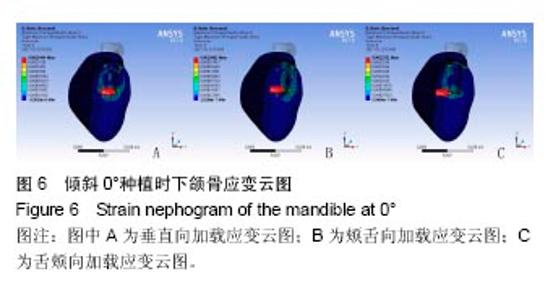
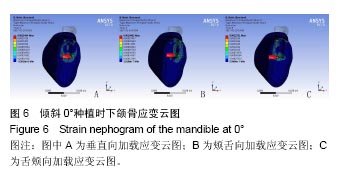
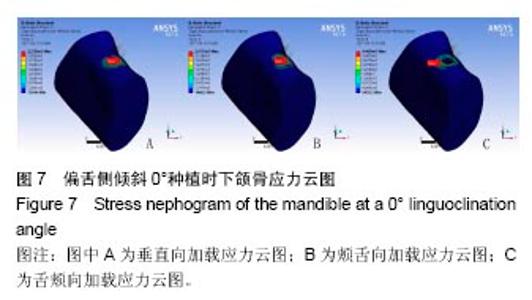
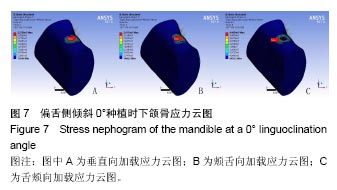
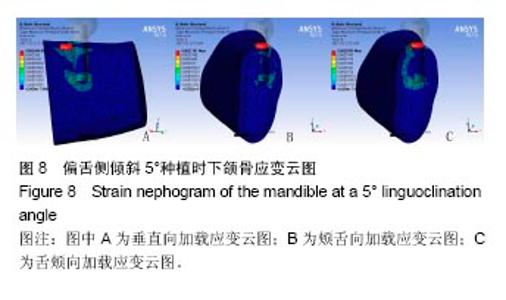
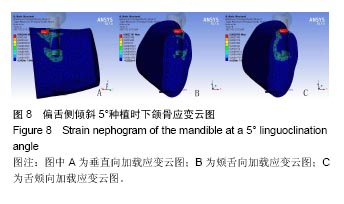
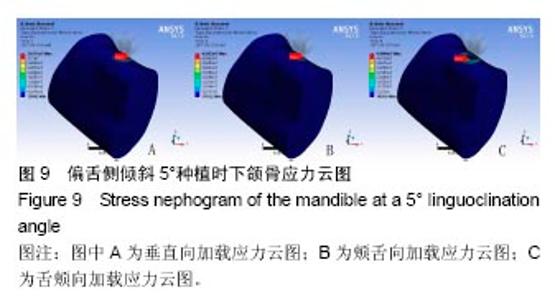
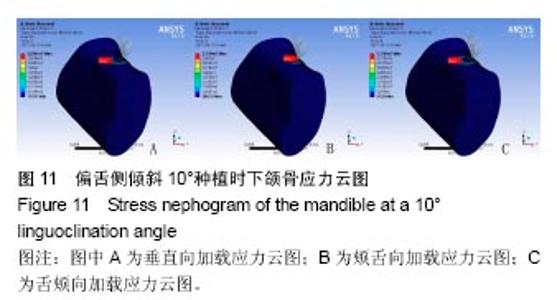
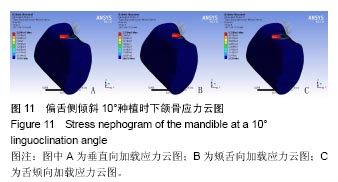
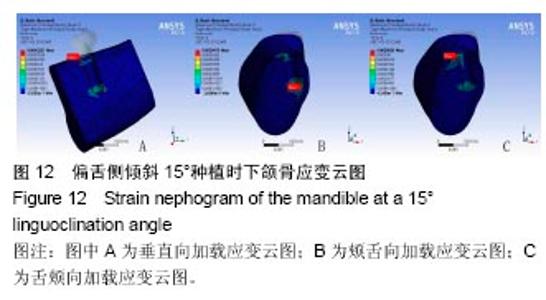
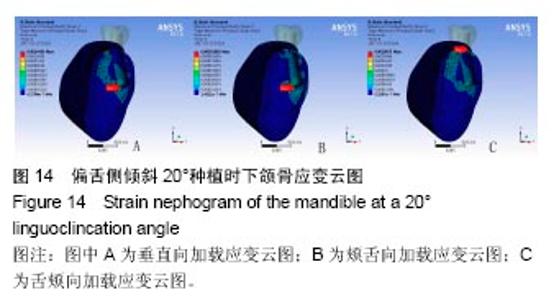
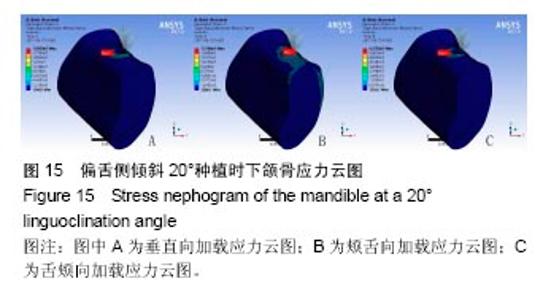
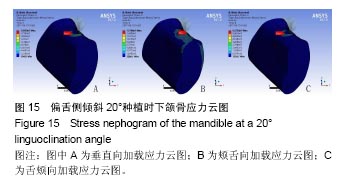
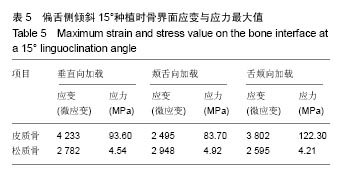
2.4 特殊情况 根据以上结果,有以下两种特殊情况:①如图16A所示,当种植体向舌侧倾斜15°时,其周围骨组织最大微应变为3 802微应变。这是由于种植体尾部接近皮质骨、松质骨交界面,距离仅有0.58 mm,此处松质骨厚度过小,从而不能提供有效的支撑力,造成种植体颈部处的皮质骨、种植体尾部处的松质骨应变、应力较大;②如图16B所示,当种植体向舌侧倾斜20°时,其周围骨组织最大微应变为 2 088微应变。角度增大微应变却变小。其原因是由于种植体尾部接触皮质骨,种植体尾部进入皮质骨内0.56 mm深度,由皮质骨对种植体尾部形成支撑,下颌骨受力主要由皮质骨承担,而皮质骨弹性模量较大,所以应变、应力较小。"
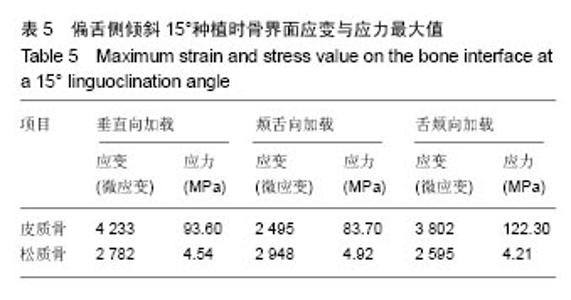
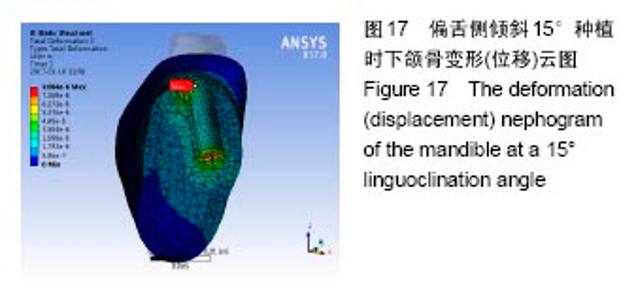
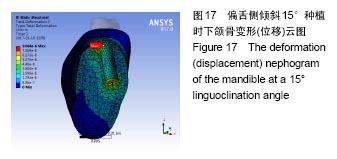
2.4.1 偏舌侧倾斜15°种植时骨界面应力、应变最大值的数值变化 此时,骨界面(皮质骨、松质骨)的应变、应力数据(最大值)统计见表5。并且,在此角度下,皮质骨、松质骨在各个受力状态下产生的应力、应变均大于其余种植角度。观察此研究模型,在偏舌侧倾斜15°种植时,种植体尾部接近皮质骨、松质骨交界面,根据材料力学的变形协调原理[25],在不同材质的交界面处,变形(材料在受力状态下产生的绝对位移)是连续的(图17)。所以,皮质骨、松质骨交界处的变形是连续的。然而,应变是绝对位移与物体几何尺寸的比值,是一个相对量,由于皮质骨、松质骨的物体几何尺寸不同,所以,应变在交界面处不连续。并且,由于材料弹性模量不同,应力也是不连续的。 2.4.2 倾斜20°种植时骨界面的应力、应变最大值数值变化 此时,种植体周围骨组织应变、应力较倾斜15°种植明显降低,最大值与倾斜10°种植时较接近。 "
| [1]宿玉成.现代口腔种植学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2004: 46,96-97.[2]林野.解剖条件不良时的种植与特殊处理[J].中国口腔种植学杂志, 2009,14(2):38.[3]Johansson B,Friberg B,Nilson H.Digitally planned,immediately loaded dental implants with prefabricated prostheses in the reconstruction of edentulous maxillae:a 1-year prospective, multicenter study.Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2009;11(3): 194-200.[4]吴轶群,黄伟,张志勇,等.倾斜种植体在上颌后牙区骨量不足患者中的应用[J].上海口腔医学,2011,20(5):506-510.[5]Krekmanov L,Kahn M,Rangert B,et al.Tilting of posterior mandibular and maxillary implants for improved prosthesis support.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.2000;15(3):405-414.[6]Aparicio C,Perales P,Rangert B.Tilted implants as an alternative to maxillary sinus grafting; a clinical,radiologic,and periotest study.Clin Implant Dent Relat Res.2001;3(1):39-49.[7]张卉卉.上颌后牙区严重骨萎缩的种植修复设计[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2009,14(2):136-137.[8]Eberhardt JA,Torabinejad M,Christiansen EL.A computed tomographic study of the distances between the maxillary sinus floor and the apices of the maxillary posterior teeth.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol.1992;73(3):345-346.[9]ten Bruggenkate CM,Oosterbeek HS,Krekeler G,et al.The placement of angled implants in the edentulous maxillae for the use of overdentures.J Prosthet Dent.1991;66(6):807-809.[10]邓丽,黄震,章福保,等.下颌神经管颌骨内走行方向的锥形束CT测量分析[J].中国医学影像学杂志,2014,22(3):161-163.[11]吴碧林,邓飞龙.上颌后牙区骨量不足条件下种植技术的应用现况[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2016,21(1):43-46.[12]Al-Abdullah K,Zandparsa R,Finkelman M,et al.An in vitro comparison of the accuracy of implant impressions with?coded healing abutments and different implant angulations.J Prosthet Dent.2013;110(2):90-100.[13]Balshi TJ,Ekfeldt A,Stenberg T,et al.Three-year evaluation of Brånemark implants connected to angulated abutments.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.1997;12(1):52-58.[14]Chrcanovic BR,Albrektsson T,Wennerberg A.Tilted versus axially placed dental implants;a meta-analysis.J Dent. 2015; 43(2):149-70.[15]陈祖贤,王超,王立军,等.上颌后牙区倾斜种植的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(33):5957-5962.[16]皮昕.口腔解剖生理学[M].6版.北京:人民卫生出版社, 2007: 288-289.[17]李晓宇,左雯鑫,朱啸,等.连续动态加载下单种植体周围骨组织应力的三维有限元分析[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2011,27(1):26-29.[18]盛潇,朱敏.颞下颌关节三维有限元建模方法进展[J].口腔颌面外科杂志, 2011,21(1):68-71.[19]Ferreira MB,Baro VA,Faverani LP,et al.The role of super- structure material on the stress distribution in mandibular full-arch implant-supported fixed dentures.A CT-based 3D-FEA.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2014;35:92-99.[20]周晖,孙迎春,朱保民,等.种植修复上部义齿不同牙尖斜度设计的三维有限元分析[J].天津医科大学学报,2003,9(2):249-252.[21]程玉叶,周文清,高美琴,等.两组不同牙尖斜度咬(牙合)设计对种植体周围组织的影响研究[J].南通大学学报(医学版), 2015,35(6): 517-521.[22]Paul S,Padmanabhan TV,Swarup S.Comparison of strain genera- ted in bone by”platform-switched” and ”non-platform-switched” implants with straight and angulated abutments under vertical and angulated load;a finite element analysis study.Indian J Dent Res.2013;24(1):8-13.[23]徐明志,王燕,刘洪臣.颊舌减径对固定修复后基牙牙周受力影响的三维有限元研究[J].口腔医学研究,2007,23(3):249-251.[24]Edlich RF,Cross CL,Dahlstrom JJ,et al.Modern concepts of the diagnosis and treatment of necrotizing fasciitis.J Emerg Med.2010;39(2):261-265.[25]刘鸿文.材料力学[M].5版.北京:高等教育出版社,2012:8-11.[26]Rungruanganunt P,Taylor T,Eckert SE,et al.The effect of static load on dental implant survival;a systematic review.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.2013;28(5):1218-1225.[27]Chrcanovic BR,Albrektsson T,Wennerberg A.Reasons for failures of oral implants.J Oral Rehabil. 2014;41(6):443-476.[28]Robling AG,Castillo AB,Turner CH.Biomechanical and molecular regulation of bone remodeling. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2006;8:455-498.[29]Frost HM.Bone” mass” and the ”mechanostat”. A Proposal Anat Rec.1987;219:1-9.[30]Luo SL,Yuan KF,Lai QG,et al.Study on angle of immediate loading of immediate implant placement.Craniofac Surg. 2015; 26(3):700-705.[31]Küçükkurt S,Alpaslan G,Kurt A.Biomechanical comparison of sinus floor elevation and alternative treatment methods for dental implant placement.Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2017;20(3):284-293. |
| [1] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [3] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [4] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [5] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [6] | Xu Yulin, Shen Shi, Zhuo Naiqiang, Yang Huilin, Yang Chao, Li Yang, Zhao Heng, Zhao Lu. Biomechanical comparison of three different plate fixation methods for acetabular posterior column fractures in standing and sitting positions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 826-830. |
| [7] | Cai Qunbin, Zou Xia, Hu Jiantao, Chen Xinmin, Zheng Liqin, Huang Peizhen, Lin Ziling, Jiang Ziwei. Relationship between tip-apex distance and stability of intertrochanteric femoral fractures with proximal femoral anti-rotation nail: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 831-836. |
| [8] | Song Chengjie, Chang Hengrui, Shi Mingxin, Meng Xianzhong. Research progress in biomechanical stability of lateral lumbar interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 923-928. |
| [9] | Liu Zhao, Xu Xilin, Shen Yiwei, Zhang Xiaofeng, Lü Hang, Zhao Jun, Wang Zhengchun, Liu Xuzhuo, Wang Haitao. Guiding role and prospect of staging and classification combined collapse prediction method for osteonecrosis of femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 929-934. |
| [10] | Xie Chongxin, Zhang Lei. Comparison of knee degeneration after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with or without remnant preservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 735-740. |
| [11] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [12] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [13] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [14] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [15] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||