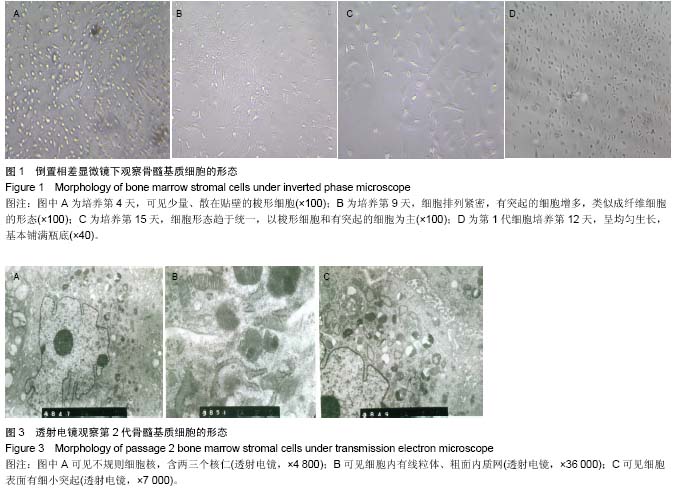
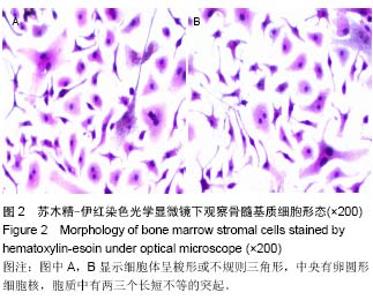
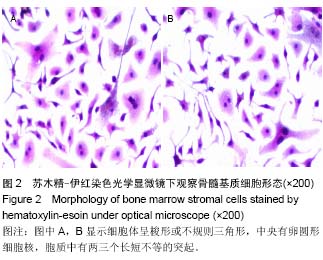
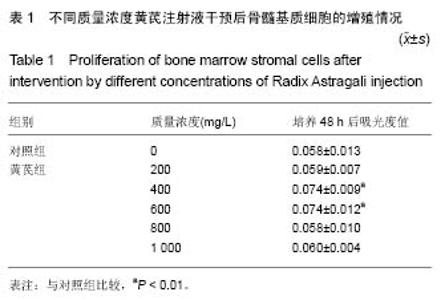
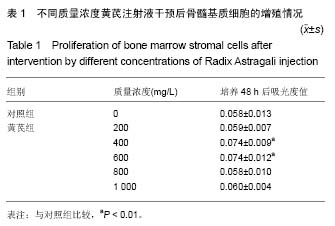
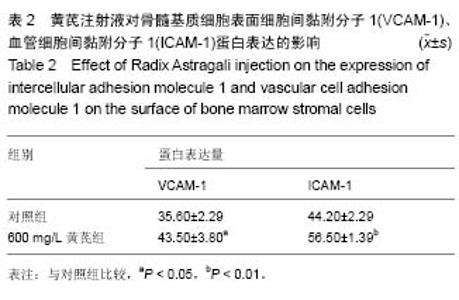
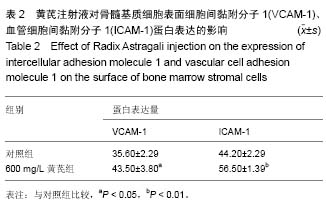
| [1] 高磊,王健民.造血干/祖细胞归巢的重要影响因素[J].国外医学:输血及血液学分册,2003,26(3):252-254.
[2] 罗成基. 造血微环境基质细胞的研究概况及前景[J].解放军医学杂志,1999,24(1):1-3.
[3] Dexter TM, Allen TD, Lajtha LG. Conditions controlling the proliferation of haemopoietic stem cells in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 1977;91(3):335-344.
[4] 王亚平,王建伟,吴宏,等.干细胞衰老与疾病[M].北京:科学出版社, 2009:103-104.
[5] 景鹏伟,胡文煦,宋小英,等.衰老大鼠模型骨髓基质细胞的生物学特点[J]. 解剖学报,2015,46(1):44-50.
[6] Lam BS, Adams GB. Hematopoietic stem cell lodgment in the adult bone marrow stem cell niche. Int J Lab Hematol. 2010; 32(6 Pt 2):551-558.
[7] Vayssade M, Nagel MD. Stromal cells. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009;14:210-224.
[8] Law S, Chaudhuri S. Mesenchymal stem cell and regenerative medicine: regeneration versus immunomodulatory challenges. Am J Stem Cells. 2013;2(1): 22-38.
[9] Wu KH, Tsai C, Wu HP, et al. Human application of ex vivo expanded umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells: enhance hematopoiesis after cord blood transplantation. Cell Transplant. 2013;22(11):2041-2051.
[10] Peled A, Kollet O, Ponomaryov T, et al. The chemokine SDF-1 activates the integrins LFA-1, VLA-4, and VLA-5 on immature human CD34(+) cells: role in transendothelial/ stromal migration and engraftment of NOD/SCID mice. Blood. 2000;95(11):3289-3296.
[11] Yu WM, Hawley TS, Hawley RG, et al. Role of the docking protein Gab2 in beta(1)-integrin signaling pathway-mediated hematopoietic cell adhesion and migration. Blood. 2002; 99(7):2351-2359.
[12] Sundberg LJ, Galante LM, Bill HM, et al. An endogenous inhibitor of focal adhesion kinase blocks Rac1/JNK but not Ras/ERK-dependent signaling in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(32):29783-29791.
[13] Richards CA, Austin EA, Huber BE. Transcriptional regulatory sequences of carcinoembryonic antigen: identification and use with cytosine deaminase for tumor-specific gene therapy. Hum Gene Ther. 1995;6(7):881-893.
[14] Zhang XH, Chen JJ. The mechanism of astragaloside IV promoting sciatic nerve regeneration.Neural Regen Res. 2013;8(24): 2256-2265.
[15] 刘清尧. 黄芪的药理作用与临床应用研究[J].世界最新医学信息文摘:电子版, 2013, 13(21): 179,185.
[16] 熊明彪. 黄芪的药理作用及临床研究进展[J].亚太传统医药, 2013,9(10):70-71.
[17] 陈图刚,谭维羚,马战清,等.黄芪注射液对外周血内皮祖细胞数量及功能的影响[J].中药新药与临床药理,2007,18(5):364-368.
[18] 邓成珊.当代中西医结合血液病学[M].北京:中国医药科技出版社,1997;362.
[19] 李美芬,蒋德昭.黄芪促进小鼠粒系造血[J].湖南医科大学学报, 1991,16(2):135-136.
[20] 徐展望,张鹏,谭国庆,等.谈中西药物对骨髓基质细胞增殖分化的影响[J].山东中医药大学学报,2005,29(4):263-264.
[21] 王乾兴,金华,何国平,等.黄芪多糖对衰老小鼠造血干细胞细胞周期调控蛋白的影响[J].遵义医学院学报,2014,37(2):144-146.
祝晓玲,祝彼得,刘军,等.黄芪诱导贫血小鼠骨髓基质细胞产生SCF的研究[J].中药药理与临床,2001,17(5):19-20. |