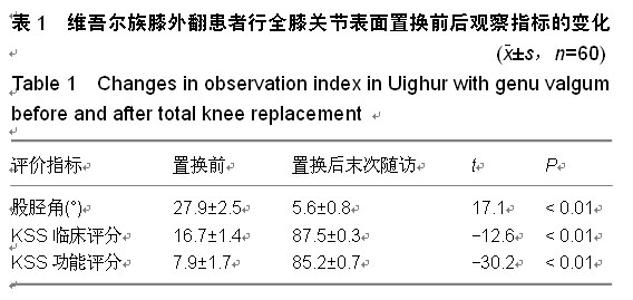
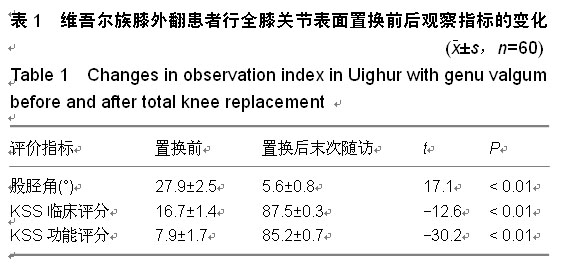
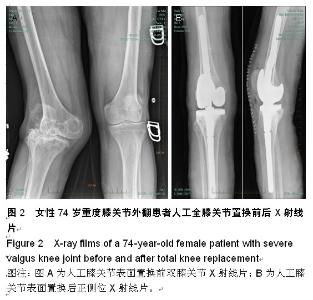
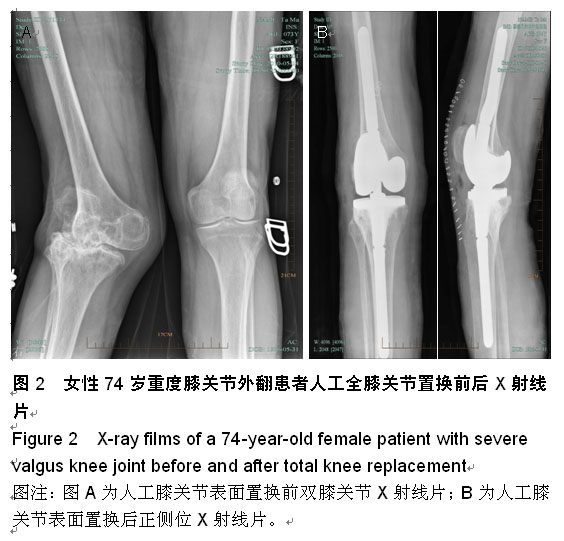
| [1] 刘凤祥,朱振安,毛远清.全膝关节置换术后髌股关节并发症的病因与预防[J].中华关节外科杂志:电子版,2008,2(6): 688-691.
[2] Sasanuma H,Sekiya H,Takatoku K,et al. evaluate soft-tissue balance during versus after total knee arthroplasty.J Orthop Surg ( Hong Kong). 2011;18:26-30.
[3] Merie-Vincent F,Couris CM,Schott AM,et al.Cross-sectional study of pain and disabilily at knee replacement surgery for osteoarthritis in 299patients.Joint Bone Spine. 2007;74(6): 612-616.
[4] 中华医学会.临床诊疗指南—骨科学分册[M]北京:人民卫生出版,2008.
[5] Ceccarelli F,Perricone C,Alessandri C,et al.Exploratory data analysis on the effects of non pharmacological treatment for knee osteoarthritis.Clin Exp Rheumato. 2010;2:250-253.
[6] 尚延春,陈龙海,王战朝.全膝关节置换术后伸膝装置并发症分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2007,15(11):869-871.
[7] Bruzzone M,Ranawat A,Castoldi F,et al.The risk of direct peroneal nerve injury using the Ranawat“inside-out”lateral release technique invalgus total knee arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty, 2010,25:161-165.
[8] 周殿阁,张斌,寇伯龙,等.膝外翻全膝关节置换外侧髌旁入路的手术方法探讨[J].中华医学杂志,2007,87(27): 1885-1889.
[9] 马军,牛东生,孙玺淳,等. 个体化的软组织平衡技术在膝外翻全膝关节置换术中的应用[J].中华关节外科杂志:电子版,2012,6(5):到695-701.
[10] 王国栋,郭艾,强华,等.活动平台假体人工骤关节置换看的中期随访[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(26):4101-4107.
[11] Kim S,Meehan JP,White R.Operative risk of staged bilateral knee arthrop lasty is underestimated in retrospective studies.J Arthroplasty.2011;26:1198-1204.
[12] Husted H,Troelsen A,Otte KS,et al.Fast-track surgery for bilateral total knee replacement.J Bone Joint Surg Br.2011; 93:351-336.
[13] Hu J,Liu Y, Lv Z,et al.Mortality and morbidity associated with simultaneous bilateral or staged bilateral to tall knee arthroplasty:ameta-analysis.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2011; 131(9):1291-1298.
[14] 符培亮,李晓华,吴宇黎,等.初次全膝关节置换股内侧肌中间入路与内侧髌旁入路置入假体的优势对比[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(9):1793-1796.
[15] Ranawat AS,Ranawat CS,Elkus M,et al.Total knee arthroplasty for severe valgus deformity.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87: 271-284.
[16] 徐杰,刘春华,周仕国,等.全膝关节置换:股内侧肌下与内侧髌旁入路的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(35):6240-6246.
[17] Walter F,Haynes MB,Markel DC.Arandomized prospective study ev- aluating the efect of patellar eversion on the early functional Outcomes in primary to total knee arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty.2007;22(4):509-514.
[18] Mukherjee Press J,Hockings M.Mid-vastus vs medial para-patellar approach in total knee replacement-time to discharge.Lowa Orthop J. 2009;29:19-22.
[19] ln Y,Kim JM,Choi NY,et al.Large thigh girth is are lative contraindication for the subvastus approach in primary total knee arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty.2007;22(4):569-573.
[20] 符培亮,吴字黎,吴海山,等.全膝置换术后关节内注射鸡尾酒式镇痛混合剂对镇痛效果的评价[J].中华骨科杂志,2008,28(7): 541-545.
[21] Markert SE.The use of cryotherapy after a total kneereplacement:aliterature review.Orthop Nurs. 2011; 30(1):29-36.
[22] 高升焘,孙爱娟,张鹏,等.全膝关节置换术后应用连续股神经阻滞镇痛和静脉自控镇痛的效果比较[J].中华关节外科杂志:电子版,2012,6(1):54-58.
[23] 方锐,梁治权,孟庆才.同期双侧全膝关节置换与选择性单侧全膝关节置换后的早期功能恢复[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(9):1549-1552.
[24] 方锐,梁治权,孟庆才.一期双膝关节与单膝关节置换的早期评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(4):599-603.
[25] Ekinci Y, Oner M, Karaman I, et al.Comparison of simultaneous bilatera with unilateral total knee arthroplasty. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc.2014;48(2)127-135.
[26] Memtsoudis SG, Mantilla CB, Parvizi J, et al.Have bilateral total knee arthroplasties become safe?Apopulation-based trend analysis.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2013;471(1):17-25.
[27] Memtsoudis SG, Ma Y, Chiu YL, et al.Bilateral total knee arthroplasty:risk factors formajor morbidity and mortality. Anesth Analg. 2011;113(4):784-790.
[28] Peskun C, Mayne I, Malempati H, et al.Cardiovascular disease predicts complications following bilateral total knee arthroplasty under a single anesthetic.Knee.2012;19(5):580-584.
[29] Spicer E, Thomas GR, Rumble EJ.Comparison of the major intraoperative and postoperative complications between unilateral and sequential bilateral total knee arthroplasty in a high-volume community hospital.Can J Surg.2013;56(5):311-317.
[30] 韦兆祥,商晓军,王益民,等.软组织平衡对全膝关节置换时膝外翻畸形的矫正作用观察[J].解放军医学杂志,2011,36(6):682.
[31] 吴小春,韩为,路晓.人工全膝关节表面置换术20例体会[J].临床骨科杂志,2010,13(2):221.
[32] 郭景泉,郭景丽,董纪元.人工全膝关节置换术治疗膝关节炎22 例分析[J].军医进修学院学报,2011,32(9):914.
[33] Gong L, Dong JY, Li ZR.Effects of combined application of muscle relaxants and celecoxib administration after total knee arthroplasty (TKA) on early recovery:a randomized,doubleblind, controlled study.J Arthroplasty. 2013;2:12-16.
[34] 赵合意,徐生产.64例应用国产膝关节假体行全膝关节置换术的近期疗效观察[J].中华关节外科杂志:电子版,2012,6(3):80-81.
[35] Roberts VI,Harper WM.A 15-year follow-up study of 4606 primary total knee replacements.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007; 89:1452-1456.
[36] Leese PT, Hubbard RC, Karim A,et al.Effects of celecoxib,a novel cyclooxy- ge nase-2 inhibitor,on platelet function in healthy adults:arandomized,controlled trial. J Clin Pharmaeol. 2000;40:124.
[37] Ekman EF, Wahba M.Analgeic efficacy of perioperative celecoxib in ambulatory arthroseopic knee surgery:a double-blind,placebo-controlled study.J Arthroscopy. 2006; 22;635.
[38] Lin J, Zhang L, Yang H.Perioperative administration of selective cyclooxygen-ase-2 inhibitors for postoperative pain management in patients after total knee arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty. 2013;28;207-213.
[39] Huang YM, Wang CM, Wang CT, et al.Perioperative celecoxib administration for pain management after total knee arthroplasty-arandomized, controlled study.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2008;9:77.
[40] Maniar RN,Baviskar JV, Singhi T,et al.Influence of bilateral sequential total knee arthroplasty on functional recovery. Indian J Orthop. 2013;47(1):23-30.
[41] Poultsides LA,Ghomrawi HM,Lyman S, et al.Change in preoperative expectations in patients undergoing stagged bilateral primary total knee or total hiparthroplasty.J Arthroplasty.2012;27(9):1609-1615.e1. |