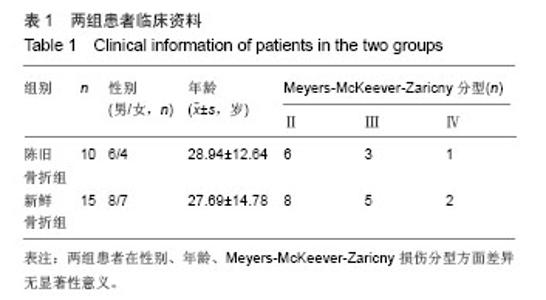
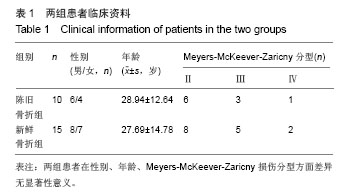
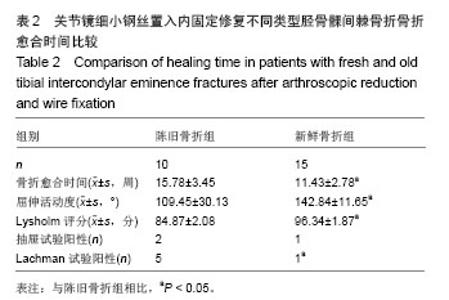
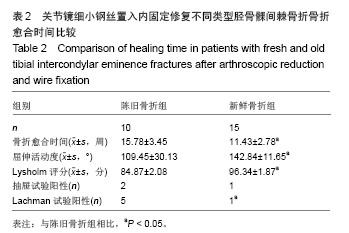
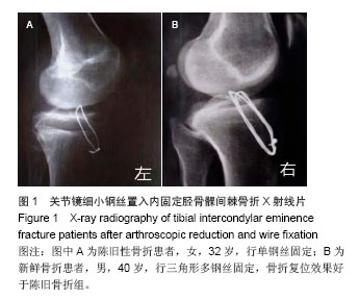
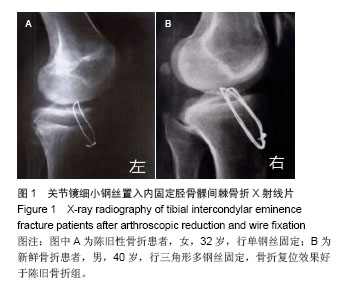
| [1]Vargas B, Lutz N, Dutoit M, et al. Nonunion after fracture of the anterior tibial spine: case report and review of the literature. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2009;18(2):90-92.
[2]陈维东.关节镜下空心螺钉与缝线内固定治疗胫骨髁间棘骨折[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(52):9017-9022.
[3]代振动,袁宏伟,路闯,等.关节镜下克氏针固定治疗胫骨髁间前棘骨折[J].实用骨科杂志,2012,18(8):748-749.
[4]王为.关节镜下可吸收螺钉治疗胫骨髁间棘撕脱骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2012,15(3):353.
[5]孟庆春,王洪,杨述华,等.关节镜下骺板近侧缝线固定治疗儿童胫骨髁间棘骨折的疗效观察[J].华中科技大学学报(医学版),2012, 41(4):473-474.
[6]候江伟,辛若冰,李广贤,等.关节镜下克氏针固定胫骨髁间棘骨折[J].中国实用医刊,2012,39(9):64-66.
[7]杨万波,江红辉,余鹏,等.关节镜下空心螺钉与缝线固定治疗胫骨髁间棘骨折的疗效比较[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2013,1(8): 46-48,51.
[8]郭永智,姜鑫,孙延山,等.关节镜下钢丝三维缝合固定儿童胫骨髁间嵴撕脱骨折的疗效[J].中华小儿外科杂志,2012,33(6): 434-436.
[9]赵建忠,陈新军.关节镜下复位钢丝固定治疗移位的胫骨髁间棘骨折21例报告[J].江苏大学学报(医学版),2012,22(4):359-362.
[10]冯万文,夏亚一,党跃修,等.关节镜下固定移位的胫骨髁间嵴撕脱性骨折[J].中华关节外科杂志:电子版,2012,6(2):40-43.
[11]刘亚云,余智锋.关节镜下钢丝固定与空心螺钉固定治疗胫骨髁间嵴骨折的疗效比较[J].实用临床医学,2013,14(10):50-52,60.
[12]张晓星,邓志龙,曹治东,等.关节镜下PDS线交叉缝合固定治疗胫骨髁间棘骨折[J].创伤外科杂志,2011,13(5):398-400.
[13]Vagras B, Luiz N, Dutoit M, et al. Nonunion after fraeture of the anterior tibial spine:cflse report and review of the literature. J Pediatr Orlhop B. 2009;18(2):90-92.
[14]姜军,陈坚.关节镜下改良双股钢丝前后挤夹固定胫骨嵴撕脱骨折[J].中华医学杂志,2014,94(39):3091-3094.
[15]张鹏,刘开祥.关节镜下双隧道交叉钢丝治疗胫骨髁间棘骨折6例[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2012,21(7):741-742.
[16]赵建忠,陈新军.关节镜下复位钢丝固定治疗移位的胫骨髁间棘骨折21例报告[J].江苏大学学报(医学版),2012,22(4):359-362.
[17]Huang TW, Hsu KY, Cheng LH, et al. Arthroscopic suture fixation of tibial eminence avulsion fractures[J].Arthroscopy. 2008;24(11):1232-1238.
[18]王洪,孙川,孟春庆,等.关节镜下Orthocord缝线固定治疗前交叉韧带胫骨止点撕脱骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2011,26(12): 1067-1069.
[19]刘宇,孙振中,顾三军,等.关节镜下经皮空心螺钉结合钢丝环扎与切开复位治疗髌骨骨折的疗效比较[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2012,6(5):790-793.
[20]董佩龙,唐晓波,王健.关节镜下钢丝和不可吸收缝线"8"字固定前交叉韧带胫骨止点骨折疗效分析[J].东南大学学报(医学版), 2013, 3(2):184-188.
[21]Osti M, Benedetto KP. Results of arthroscopically assisted refixation of fractures of the intercondylar eminence. Z Orthop Unfall. 2010;148(3):288-291.
[22]黄伟,周全,齐克海,等.关节镜下双克氏针张力带钢丝固定治疗胫骨髁间棘骨折[J].西南国防医药,2013,23(3):288-290.
[23]陆振飞,赵金忠.前交叉韧带胫骨止点撕脱骨折的治疗进展[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2008,10(2):186-188.
[24]代振动,袁宏伟,路闯,等.关节镜下克氏针固定治疗胫骨髁间前棘骨折[J].实用骨科杂志,2012,18(8):748-749.
[25]Perugia D, Basiglini L, Vadalà A, et al. Clinical and radiological results of arthroscopically treated tibial spine fractures in childhood. Int Orthop. 2009;33(1):243-248.
[26]王小武,张鹏,黄晓华,等.关节镜下复位“双钢丝四隧道法”固定治疗胫骨髁间嵴骨折[J].实用骨科杂志,2013,19(3):214-217.
[27]张晓星,苟景跃,曹治东,等.关节镜下Herbert钉固定治疗胫骨髁间棘骨折27例分析[J].重庆医学,2012,41(11):1123-1124.
[28]Bonin N, Jeunet L, Obert L, et al. Adult tibial eminence fracture fixation: arthroscopic procedure using K-wire folded fixation. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2007;15(7): 857-862.
[29]唐恒涛,肖鹏,朱旭,等.关节镜下“8”字缝线法治疗前交叉韧带胫骨髁间棘撕脱骨折[J].郑州大学学报(医学版),2014,49(5): 761-764.
[30]金耀峰,陈刚,戴加平,等.关节镜下可吸收缝线套扎治疗儿童ACL胫骨止点撕脱骨折[J].中国微创外科杂志,2014,14(2):166.
[31]项毅,续力民,孙振军.关节镜下经髌旁上入路治疗胫骨髁间棘骨折[J].重庆医学,2011,40(10):980-981.
[32]Li H, Yuan YJ, Yang HH, et al. Arthroscopic treatment of tibial intercondylar eminence fracture in children. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2013;26(9):724-727.
[33]Xu K, Fu X, Li YM, et al. A treatment for large defects of the tibia caused by infected nonunion: Ilizarov method with bone segment extension. Ir J Med Sci. 2014;183(3):423-428.
[34]Zhou Y, Feng F, Qu X, et al. Surgical treatment of antero-medial rotatory instability of knee joint caused by motorcycle. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2012; 26(8):922-925.
[35]Donaldson FE, Pankaj P, Simpson AH. Bone properties affect loosening of half-pin external fixators at the pin-bone interface. Injury. 2012;43(10):1764-1770.
[36]Gan Y, Xu D, Ding J, et al. Tension band wire fixation for anterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture: biomechanical comparison of four fixation techniques. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20(5):909-915.
[37]Fowler TT, Pugh KJ, Litsky AS, et al. Medial malleolar fractures: a biomechanical study of fixation techniques. Orthopedics. 2011;34(8):e349-e355.
[38]Yao ND, Wang FL. Delayed operation on treatment of high-energy distal tibia Pilon fracture. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2011;24(3):256-258.
[39]Lu HD, Zeng C, Dong YX, et al. Treatment of tibial avulsion fracture of the posterior cruciate ligament with open reduction and steel-wire internal fixation. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2011; 24(3):195-198. |