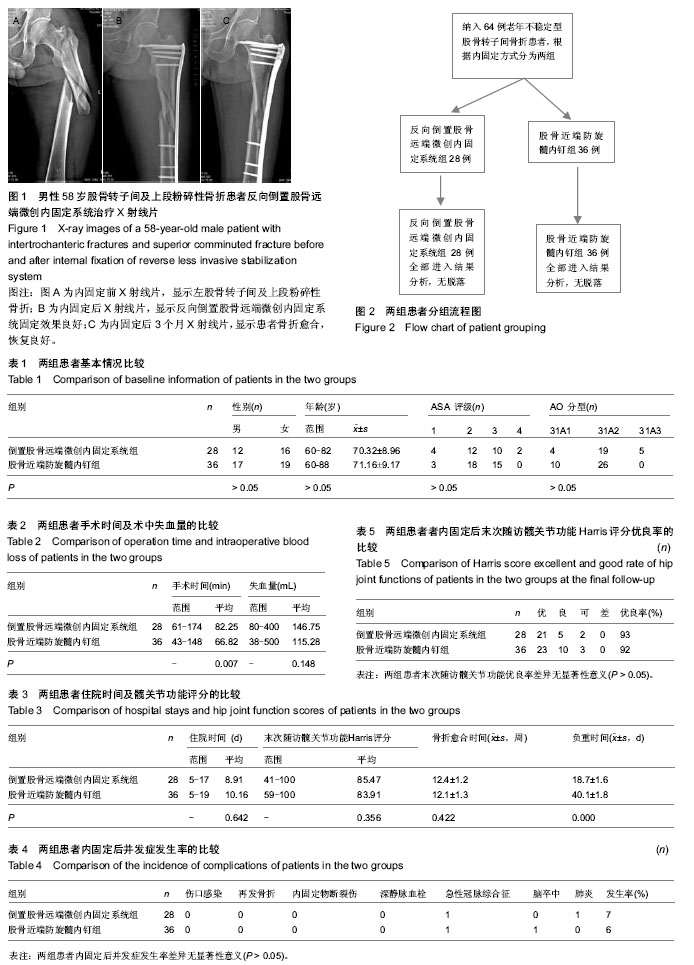
| [1] 管英.股骨近端锁定钢板术治疗老年股骨转子间骨折52例效果分析[J].中国老年学杂志,2011,31(10):1890-1891.
[2] 焦广俊,刘海春,王洪亮,等.股骨近端防旋髓内钉与Gamma 钉固定治疗成人股骨转子间骨折的Meta分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2011,19(22):1858-1859.
[3] 何正华,胡阿威,夏春明,等.股骨近端解剖型锁定钢板在老年股骨粗隆间骨折治疗中的应用[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2010, 25(4):316-317.
[4] 黄成国,叶君健.3种不同方式治疗老年股骨转子间骨折的病例对照试验[J].中国骨伤,2012,25(7):549-553.
[5] 顾华,付建,张波涛,等.DHS与PFNA治疗老年不稳定股骨转子间骨折的疗效比较[J].川北医学院学报,2012,27(3):288-292.
[6] 陈海良,庞瑞明,刘洪财,等.PFNA治疗骨质疏松性股骨转子间骨折的临床观察[J].海南医学院学报,2011,17(4):532-534.
[7] 吴翔,史作兵.股骨髁LISS钢板反向使用治疗股骨转子下骨折疗效分析[J].浙江医学,2013,35(9):805-807.
[8] 缪海雄,王斌,刘伟乐,等.反向LISS-DF与PFNA治疗股骨转子间骨折疗效分析[J].亚太传统医药,2013,9(5):136-138.
[9] 荆浩,周越,南庞,等.DHS与倒置LISS 治疗股骨粗隆间骨折临床疗效比较[J].宁夏医科大学学报,2013,34(4):463-467.
[10] 王利宏,蒋恒,徐国红,等.倒置股骨远端LISS与DHS治疗股骨转子间骨折的疗效分析[J].中华关节外科杂志,2011,5(3): 374-378.
[11] 陈兴华,刘涛,黄珍谷.长、短股骨近端防旋髓内钉固定股骨转子间骨折的对比[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(4):595-600.
[12] Pui CM, Bostrom MP, Westrich GH,et al. Increased Complication Rate Following Conversion Total Hip Arthroplasty After Cephalomedullary Fixation For Intertrochanteric Hip Fractures: A Multi-center Study.J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(8 Suppl):45-47.
[13] 杨国跃,江汉,韩立强.PFNA治疗老年外侧壁不完整型股骨转子间骨折的疗效分析[J].天津医药,2014,42(7):713-718.
[14] 李康养,马楚平,梁江山,等.DHS、PFNA及人工关节治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折临床疗效分析[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2011, 19(7): 25-27.
[15] 丁华,章洪喜,袁即山,等.股骨近端髓内钉-螺旋刀片内固定与人工股骨头置换术治疗老年股骨转子间不稳定型骨折的疗效比较[J].生物医学工程与临床,2013,17(5):450-454.
[16] 胡福云.老年股骨粗隆间骨折股骨近端防旋髓内钉的治疗效果及其对生活质量的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2012,32(9): 1926-1927.
[17] 王渊,张智勇,封国刚.倒LISS钢板治疗高龄股骨转子间骨折22例临床分析[J].中国煤炭工业医学杂志,2012,15(3):336-339.
[18] 孙源,张长青,金东旭,等.倒置股骨远端微创内固定系统接骨板治疗老午股骨转子间骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2011,13(3): 208-212.
[19] 唐少龙,江敞.微创内固定系统倒置与防旋股骨近端髓内钉治疗高龄复杂不稳定型股骨粗隆间骨折的比较[J].中国骨伤,2011, 24(5):366-369.
[20] 洪方业,叶斌,李双.倒置 LISS钢板内固定治疗高龄患者股骨转子间粉碎性骨折可行性研究[J].淮海医药,2012,30(5):386-389.
[21] 黄伟杰,罗涛,沈波.股骨近端防旋髓内钉内固定治疗股骨转子间骨折的并发症分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2010,12(8):790-792.
[22] 赵光辉,王浩.LISS钢板治疗高龄股骨转子间粉碎骨折的疗效观察[J].实用骨科杂志,2009,15(12):892-894.
[23] 盛加根,张长青.倒置股骨远端微创内固定系统治疗股骨近段骨不连[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2008,10(11):1013-1015.
[24] 谢晨学,许效坤,冯青,等.PFNA和倒置股骨髁LISS钛板治疗股骨粗隆间骨折的疗效[J].医学临床研究,2014,31(8):1500-1502.
[25] 王恒龙,王志刚,姜振国,等.LISS钢板治疗老年股骨远端及胫骨近端骨折[J].实用骨科杂志,2011,17(8):760-762.
[26] Pryce Lewis JR, Ashcrolt GP.Reverse LISS plating for proximal segmental femoral fractures in the polytrauma pabent; A case report. Injury. 2007;38(4):235-239.
[27] 杨云海,林卓锋,张松生,等.LISS钢板治疗老年人股骨粗隆间骨折的疗效分析[J].国际医药卫生导报,2011,17(14):1718-1720.
[28] 李鹏,苗娜,王维彬.LISS在股骨远端关节骨折中的应用及与传统解剖钢板疗效对比[J].河北医药,2014,36(3):357-358.
[29] 张建明,邓波.微创股骨LISS钢板治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折的优越性[J].中国医药指南,2013,11(24):248-249.
[30] 苟琦,杨忠义.PFNA及倒置LISS钢板治疗股骨近端骨折效果比较[J].中国卫生产业,2014,11(9):1-2.
[31] 陈路遥,黄俭,吴玮伟,等.LISS钢板治疗股骨远端骨折临床研究[J].中国伤残医学,2013,21(11):66-68.
[32] 林彩龙.四种方法治疗股骨粗隆间骨折对比观察[J].中外医学研究,2013,11(19):36-37.
[33] Nielsen KD,Dammen I.Late symptoms after hip fracture with displacement of the lesser trochanter-a case report. Acta Orthop Scand. 2003;74(4):500-501
[34] 李杰,黄健华,霍维玲,等.反向Liss与PFNA治疗股骨粗隆间粉碎性骨折的疗效分析[J].医学信息,2013,(28):115-117.
[35] Zhang CQ,Sun Y,Zeng BF, et al. Reverse LISS plating for intertrochanteric hip fractures in elderly patients. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2010;11:166. |