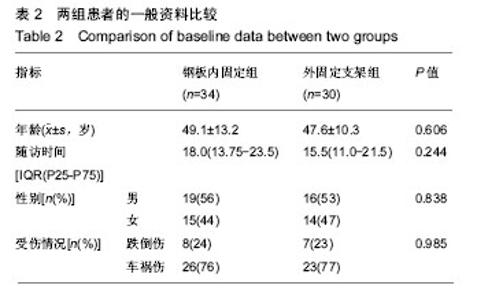
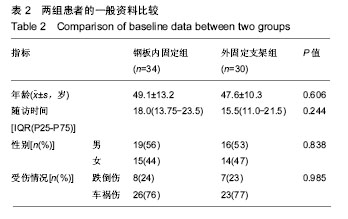
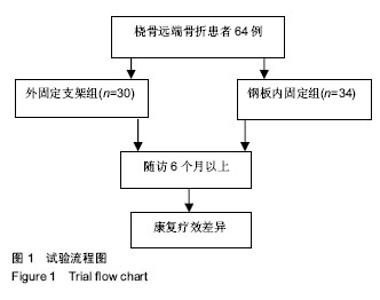
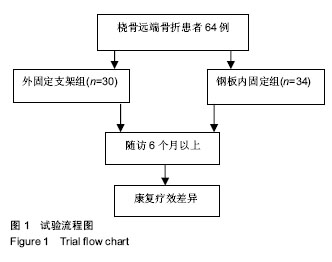
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (8): 1196-1202.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1061
Previous Articles Next Articles
Open reduction and plate fixation versus closed reduction and external fixation for distal radius fractures: scores and linear regression analysis
Ke Wei, Li Ke, Wang Sibo, Du Xinhui, Qiu Zhongpeng, Kang Zhilin, Wang Weishan, Li Gang
- Orthopedics Center, the First Affiliated Hospital of the Medical College, Shihezi University, Shihezi 832000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Online:2019-03-18Published:2019-03-18 -
Contact:Li Gang, Chief physician, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Orthopedics Center, the First Affiliated Hospital of the Medical College, Shihezi University, Shihezi 832000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Ke Wei, Master candidate, Orthopedics Center, the First Affiliated Hospital of the Medical College, Shihezi University, Shihezi 832000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 31760270 (to WSB)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ke Wei, Li Ke, Wang Sibo, Du Xinhui, Qiu Zhongpeng, Kang Zhilin, Wang Weishan, Li Gang . Open reduction and plate fixation versus closed reduction and external fixation for distal radius fractures: scores and linear regression analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1196-1202.
share this article
| [1] Ma C, Deng Q, Pu H, et al. External fixation is more suitable for intra-articular fractures of the distal radius in elderly patients. Bone Res. 2016;4(1):39-47. [2] Arora R, Lutz M, Deml C et al. A prospective randomized trial comparing nonoperative treatment with volar locking plate ?xation for displaced and unstable distal radial fractures in patients sixty-?ve years of age and older. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93:2146-2153. [3] Wang JH, Sun T. Comparison of effects of seven treatment methods for distal radius fracture on minimizing complex regional pain syndrome. Arch Med Sci. 2017;13(1):163-173. [4] Snoddy MC, An TJ, Hooe BS, et al. Incidence and reasons for hardware removal following operative fixation of distal radius fractures. J Hand Surg. 2015;40(3):505. [5] Satake H, Hanaka N, Honma R, et al. Complications of distal radius fractures treated by volar locking plate fixation. Orthopedics. 2016;39(5):1-4. [6] Esenwein P, Sonderegger J, Gruenert J, et al. Complications following palmar plate fixation of distal radius fractures: a review of 665 cases. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013;133(8): 1155-1162. [7] Lichtman DM, Bindra RR, Boyer MI, et al. Treatment of distal radius fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2010;18(3):180. [8] Orbay JL, Touhami A. Current concepts in volar fixed-angle fixation of unstable distal radius fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;445(445):58-67. [9] Loisel F, Kielwasser H, Faivre G, et al. Treatment of distal radius fractures with locking plates: an update. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2018. doi: 10. 1007/s00590-018-2274-z. [10] Levin SM, Nelson CO, Botts JD, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of volar locking plates for distal radius fractures. Hand. 2008;3(1):55-60. [11] Egol KA, Kubiak EE, Kummer FJ, et al. Biomechanics of locked plates and screws. J Orthop Trauma. 2004;18(8): 488-493. [12] Freeland AE, Luber KT. W3-biomechanics and biology of plate fixation of distal radius fractures. Hand Clin. 2009; 21(3):27-36. [13] Loisel F, Bouilloux X, Uhring J, et al. Early postoperative improvements in the Quick DASH score after distal radius fracture are related to the type of surgical treatment. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2015;25(5):865-869. [14] Obert L, Rey PB, Uhring J, et al. Fixation of distal radius fractures in adults: a review. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2013;99(2):216-234. [15] Duramaz A, Bilgili MG, Karaali E, et al. Volar locking plate versus K-wire-supported external fixation in the treatment of AO/ASIF type C distal radius fractures: a comparison of functional and radiological outcomes. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2018;24(3):255-262. [16] Bentohami A, Bijlsma TS, Goslings JC, et al. Radiological criteria for acceptable reduction of extra-articular distal radial fractures are not predictive for patient-reported functional outcome. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2013;38(5):524. [17] 邵佳申,郑占乐,吕红芝,等.双反牵引微创治疗后外侧胫骨平台骨折的疗效分析[J].中华老年骨科与康复电子杂志,2017,3(5): 302-305.[18] Chilakamary VK, Lakkireddy M, Koppolu KK, et al. Osteosynthesis in distal radius fractures with conventional bridging external fixator; tips and tricks for getting them right. J Clin Diagn Res. 2016;10(1):RC05. [19] 裴福兴,陈安民.骨科学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2016.[20] Athar SM, Ashwood N, Aerealis G, et al. Is external fixation a better way than plaster to supplement K-wires in non-comminuted distal radius fractures? Postgrad Med J. 2017;94(1107):20-24. [21] Kodama N, Takemura Y, Ueba H, et al. Acceptable parameters for alignment of distal radius fracture with conservative treatment in elderly patients. J Orthop Sci. 2014;19(2):292. [22] 邱贵兴,裴福兴,胡侦明,等.中国骨质疏松性骨折诊疗指南(骨质疏松性骨折诊断及治疗原则)[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2015, 8(5):85-88.[23] 潘达德,顾玉东,侍德,等.中华医学会手外科学会上肢部分功能评定试用标准[J].中华手外科杂志,2000,16(3):130-135.[24] Imaeda T, Uchiyama S, Wada T, et al. Reliability, validity, and responsiveness of the Japanese version of the Patient-Rated Wrist Evaluation. J Orthop Sci. 2010;15(4):509-517. [25] 崔秀仁,赵勇,张兴平,等.持续牵引在纠正桡骨远端不稳定骨折中桡骨短缩的作用机制探讨[J].中国骨伤,2009,22(5):376-377.[26] Canale ST,Beaty JH.坎贝尔骨科手术学(创伤骨科第12版;第6卷)[M].北京:人民军医出版社,2015.[27] Jeudy J, Steiger V, Boyer P, et al. Treatment of complex fractures of the distal radius: a prospective randomised comparison of external fixation 'versus' locked volar plating. Injury. 2012;43(2):174-179. [28] Monaco NA, Dwyer CL, Ferikes AJ, et al. Hand surgeon reporting of tendon rupture following distal radius volar plating. Hand. 2016;11(3):278. [29] Asadollahi S, Keith PP. Flexor tendon injuries following plate fixation of distal radius fractures: a systematic review of the literature. J Orthop Traumatol. 2013;14(4):227-234. [30] Selvan DR, Machin DG, Perry D, et al. The role of fracture reduction and plate position in the aetiology of flexor pollicis longus tendon rupture after volar plate fixation of distal radius fractures. Hand. 2015;10(3):497-502. [31] 秦泗河.Ilizarov技术概述[J].中华骨科杂志,2006,26(9):642-645.[32] Gouk C, Bindra RR, Tarrant DJ, et al. Volar locking plate fixation versus external fixation of distal radius fractures: a meta-analysis. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2018;43(9):954-960. [33] Hansen T B, Snerum L. Radiolucency around external fixation pins in distal radius fractures is not a part of a deep infection. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2013;38(8):905-906. [34] Kumbaraci M, Kucuk L, Karapinar L, et al. Retrospective comparison of external fixation versus volar locking plate in the treatment of unstable intra-articular distal radius fractures. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014;24(2):173-178. [35] Kasapinova K, Kamiloski V. Open reduction and internal fixation versus external fixation and/or kirschner wires for distal radius fractures. A systematic review. Pril. 2014;35(1): 225-237. [36] Roh YH, Lee BK, Baek JR, et al. A randomized comparison of volar plate and external fixation for intra-articular distal radius fractures. J Hand Surg. 2015;40(1):34-41. [37] Dong W, Lei S, Zhou JL. Locking plate versus external fixation for type C distal radius fractures: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Chin J Traumatol. 2018;21(2):113-117. [38] Tang Z, Liu J, Yang H. Comparison of outcome of VLCP versus PKEF in the treatment of AO type C2-3 distal radial fractures. Ann Med Surg. 2017;18(C):28-32. [39] 胥少汀,葛宝丰,徐印坎.实用骨科学[M]. 3版.北京:人民军医出版社,2005.[40] Eschweiler J, Allmendinger F, Stromps JP, et al. Biomechanical modelling of the wrist joint. Z Orthop Unfall. 2014;152(2):161-169. |
| [1] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [2] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [3] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [4] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [5] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [6] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [7] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [8] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [9] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [10] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [11] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [12] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [13] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [14] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [15] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||