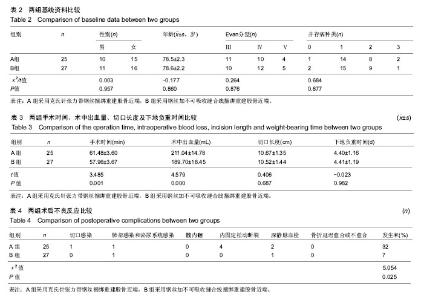
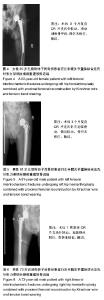
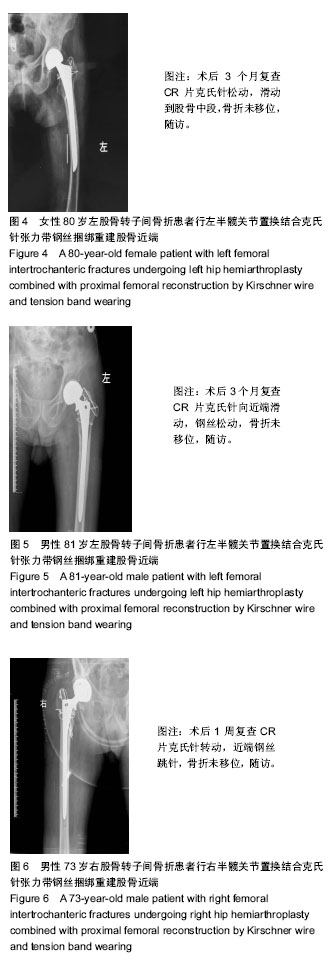
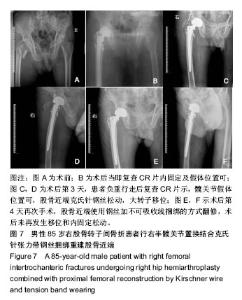
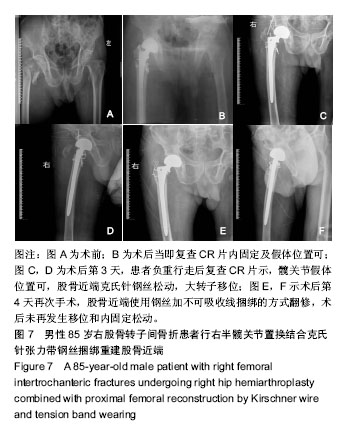
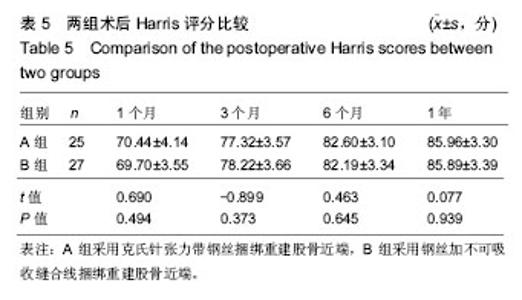
| [1] 叶少腾,陈凯宁,蓝创新,等.半髋置换在高龄不稳定型股骨转子间骨折治疗中的价值[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2013,12(8): 574-576.[2] 陈雁西,强敏菲.股骨转子间骨折的治疗策略与数字化临床路径[J].中华骨科杂志,2017,37(17):1111-1117.[3] Kim JY, Kong GM. Subcapital femoral neck fracture after treatment of an intertrochanteric fracture with proximal femoral intramedully nail. Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2016; 26(1):78-79.[4] 卢晓,罗斌.双极股骨头半髋置换与股骨近端防旋髓内钉固定治疗老年非稳定股骨粗隆间骨折的疗效比较研究[J].浙江创伤外科,2018, 23(1):89-91.[5] 汤宇宏,赵丹红.人工股骨头置换与动力髋螺钉治疗高龄股骨粗隆间骨折的疗效比较[J].浙江创伤外科,2015,20(6):1227-1228.[6] 徐风瑞, 何明武, 姚忠军, 等. PFNA内固定与人工股骨头置换术治疗高龄骨质疏松性股骨粗隆间骨折的比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2016,31(2):130-133.[7] 董建彬,王智勇,芦浩,等.内固定术与髋关节置换术治疗股骨粗隆间骨折疗效的Meta分析[J].中国骨伤,2015,28(3):245-251.[8] Makinen TJ,Gunton M,Fichman SG,et al.Arthroplasty for pertrochanterie hip fractures. Orthop Clin North Am. 2015; 46(4):433-444.[9] Vermesan D, Prejbeanu R, Poenaru DV, et al.Do intramedullary implants improve survival in elderly patients with trochanteric fractures? A retrospective study.Clin Ter. 2015;166(3): e140-e145.[10] 赵卓,周学颖,张艳秋,等.高分子体位垫在双髋关节置换术中应用价值的研究[J]. 中国实验诊断学,2015,6(4):667-668.[11] 张飞,彭吾训.髋关节置换术在治疗老年股骨转子间骨折中的应用现状[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2016,32(21):3486-3488.[12] Tomonori B,Katsuo S,Kazuo K. Bipolar hemiarthroplasty for femoral neck fracture using the direct anterior approach. World J Orthop. 2013;4(2):85-89.[13] Colais P,Pinnarelli L,Fusco D,et al. The impact of a pay for performance system on timing to hip fracture surgery:experience from the Lazio Region(Italy). BMC Health Serv Res. 2013;13(1):393.[14] 姚绍平,孙先润,李维朝,等.不稳定型股骨转子间骨折人工股骨头置换和股骨近端髓内钉内固定疗效分析[J].创伤骨科杂志, 2015, 17(2):131-133.[15] 张殿英,姜保国,付中国.防旋股骨近端髓内钉治疗转子间骨折的初步疗效分析[J].中华创伤杂志,2007,23(2):91-93.[16] Kiran Kumar GN, Meena S, Vijaya Kumar N, et al. Bipolar hemiarthroplasty in unstable intertrochanteric fractures in elderly: a prospective study.J Clin Diagn Res. 2013;7(8): 1669-1671.[17] 黄晓微,禹宝庆,李泽湘,等.动力髋螺钉和Gamma钉置入固定不稳定股骨转子间骨折的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(53):8603-8608.[18] 王加刚,沈鹏程,朱立帆,等.三种治疗老年股骨转子间骨折内固定法的临床疗效对比研究[J].实用骨科杂志, 2017,23(11): 1032-1035.[19] 刘潮坚,蔡拉加,石昭宏,等.半髋置换加钢丝环扎术在高龄不稳定粗隆间骨折的应用[J].创伤外科杂志,2016, 18(5):281-283.[20] 唐佩福,王岩,卢世璧, 等.坎贝尔骨科手术学[M].13版.北京:北京大学出版社,2018:2648.[21] 袁志,毕龙.老年股骨转子间骨折的治疗趋势[J].中华骨科杂志, 2017,37(17):1057-1060.[22] 陈剑虹,李顺东,童培建, 等.人工股骨头置换术与股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗高龄股骨转子间骨折的对比研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2016, 24(2):18-28.[23] Cui Q, Liu YS, Li DF, et al. Cemented hip hemiarthroplasty clinical observations on unstable intertrochanteric fracture in elderlies. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2016;42: 651-656.[24] 吕荷荣,项少梅,王艮存,等. 老年股骨颈及股骨粗隆间骨折治疗方法的选择[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2015,3(6):628-629.[25] 冯暘,陈斌,张焱,等.半髋置换与股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗股骨粗隆间骨折的比较[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2017,25(12): 1081-1085.[26] 张兵.不同方案治疗老年严重骨质疏松股骨转子间骨折的疗效和安全性的对比[J].检验医学与临床,2014,11(16):2222-2225.[27] 陈述祥,刘彦,陈丽君.老年股骨转子间骨折不同治疗方法的评价[J].暨南大学学报,2014, 35(2): 178-181.[28] Shi H, Xiao L, Wang Z. Curative effect of artificial femoral head replacement and its effect on hip joint function and complications of senile patients with femoral intertrochanteric fracture. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16(2): 623-628.[29] 汪洋,彭家全,唐春江.防旋转股骨近端髓内钉与人工关节置换治疗老年股骨转子间骨折的比较[J].重庆医学, 2017,6(2): 2706-2707.[30] 王建年.双极股骨头半髋置换治疗老年不稳定粗隆间骨折的疗效及预后影响因素[J].实用临床医药杂志,2016,20(11):116-117.[31] Zhao R, Cai H, Liu Y, et al. Risk factors for intraoperative proximal femoral fracture during primary cementless THA. Orthopedics. 2017; 40(2): e821-e287.[32] 谢庆云,张波,权毅,等.人工双极股骨头置换中大转子不同固定方法的比较[J].中国组织工程研究及临床康复, 2011,15(26): 4781-4784.[33] Sancheti KH, Sancheti P, Shyam A, et al. Primary hemiarthroplasty for unstable osteoporotic intertrochanteric fractures in the elderly: A retrospective case series. Indian J Orthop. 2010;44(4):428-434. |