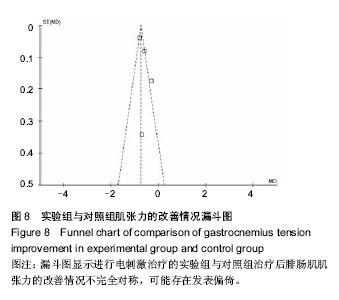
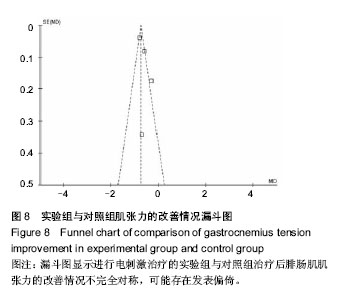
| [1] 曲志峰,刘欣,牛栋,等.脑性瘫痪260例病因分析[J].武警医学, 2013,24(12):1077-1079.
[2] 尤登攀,王冬,王兴宏,等.小儿脑性瘫痪的病因学研究进展[J].中国现代药物应用,2012,06(19):116.
[3] 吴云.小儿脑性瘫痪的发病机制及诊治进展[J].安徽医学,2011, 32(6):859-862.
[4] 林庆,李松,刘建蒙,等.我国六省(区)小儿脑性瘫痪患病率及临床类型的调查分析[J].中华儿科杂志,2001,39(10):613-615.
[5] Yeargin M, Van Naarden Braun K, Doernberg NS, et al. Prevalence of cerebral palsy in 8-year-old children in three areas of the United States in 2002: a multisite collaboration. Pediatrics. 2008;121(3):547-554.
[6] 冯利东,王建良,吴湘玲,等.显微神经外科手术治疗脑性瘫痪临床研究[J].医学研究杂志,2006(4):38-40.
[7] 于炎冰,张黎,伍成奇,等.显微神经外科手术治疗痉挛型脑性瘫痪738例临床观察[J].中华神经外科杂志,2004(1)59-62.
[8] 林庆.小儿脑性瘫痪的定义、诊断条件及分型[J].中华儿科杂志, 2005,43(4):262-262.
[9] Alderson P, Green S, Higgins JPT. Assessment of study quality: Cochran Reviewers’ handbook 4.2.2. Chichester, UK. 2004.
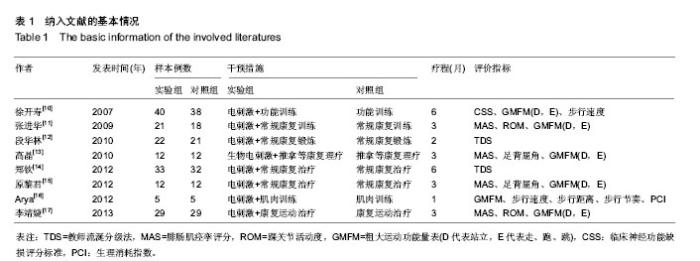
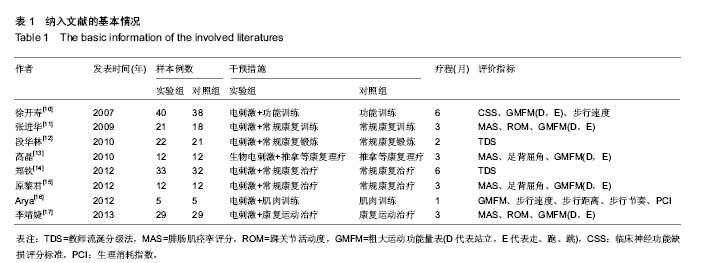
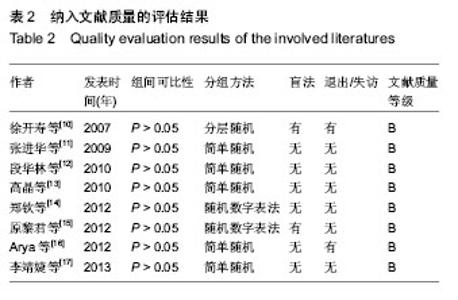
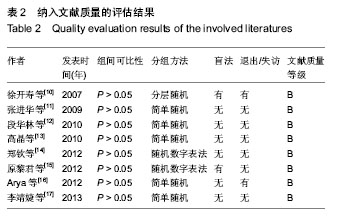
[10] 徐开寿,何璐,李金玲,等.经皮电神经刺激对痉挛型脑性瘫痪患儿运动功能影响的对照研究[J].中华儿科杂志,2007,45(8): 564-567.
[11] 张进华,杨正,韩玉玲,等.功能性电刺激对痉挛型脑性瘫痪儿童下肢功能的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志,2009,24(4):328-330.
[12] 段华林,张惠佳,颜华,等.神经肌肉电刺激治疗脑性瘫痪患儿流涎症的临床研究[J].中国康复理论与实践,2010,16(5): 453-454.
[13] 高晶,岳虹霓,毛红梅,等.肌电生物反馈综合治疗促进痉挛性双瘫型脑性瘫痪患儿下肢运动功能的疗效观察[J].中国康复医学杂志,2010,25(1):42-45.
[14] 郑钦,沈敏,何文龙,等.低频电刺激治疗脑性瘫痪儿童流涎症的疗效观察[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2012,34(11):848-849.
[15] 原黎君.肌电生物反馈刺激对痉挛型脑性瘫痪患儿下肢功能的影响[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2012,34(11):850-851.
[16] Arya BK, Mohapatra J, Subramanya K, et al. Surface EMG analysis and changes in gait following electrical stimulation of quadriceps femoris and tibialis anterior in children with spastic cerebral palsy. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2012;2012: 5726-5729.
[17] 李靖婕,尚清,马彩云,等.肌电生物反馈疗法在痉挛型脑性瘫痪儿童康复中的疗效[J].中华实用儿科临床杂志,2013,28(10):796-797.
[18] 傅克礼,吴春容.脑性瘫痪儿童康复现状与对策[J].中国全科医学, 2003,6(8):672-673.
[19] 李威,章荣,罗亚玲,等.步态诱发功能性电刺激改善痉挛型双瘫型脑性瘫痪患儿下肢运动功能的疗效观察[J].中国康复医学杂志, 2013,28(12):1126-1130.
[20] Wright PA, Granat MH. Therapeutic effects of functional electrical stimulation of the upper limb of eight children with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2000;42(11):724-727.
[21] 张进华,杨正,韩玉玲,等.功能性电刺激对痉挛型脑性瘫痪儿童下肢功能的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志,2009,24(4):328-330.
[22] 燕铁斌.积极推广神经肌肉电刺激技术在中枢神经损伤中的应用[J].中国康复医学杂志,2007,22(10):865-866.
[23] Cho SH, Shin HK, Yong HK, et al.Cortical activation changes induced by visual biofeedback tracking training in chronic stroke patients.NenroRehabilitation. 2007;22(2):77-84.
[24] Pierce SR, Orlin MN, Lauer RT, et al. Comparison of percutaneous and surface functional electrical stimulation during gait in a child with hemiplegic cerebral palsy. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2004;83:798-805.
[25] Yan T, Hui-Chan CW, Li LS. Functional electrical stimulation improves motor recovery of the lower extremity and walking ability of subjects with first acute stroke: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Stroke. 2005;36(1):80-85.
[26] Kerr C, McDowell B, McDonough S.Electrical stimulation in cerebral palsy:a review of effects on strength and motor function. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2004;46(2):205-213.
[27] 李晓捷.关注不同年龄段脑性瘫痪儿童康复治疗特点[J].中国康复医学杂志,2011,26(4):301-302.
[28] 侯梅,王海桥,孙殿荣.脑性瘫痪患者神经肌肉和骨骼系统继发性病变及康复策略[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2011, 33(3):238-240.
[29] 史艳,王飞,李跃峰,等.康复训练结合家庭康复指导对痉挛型脑性瘫痪患儿的效果[J].中国康复理论与实践,2014(5):420-422.
[30] Freeman M. Cerebral Palsy. 1st ed. New York. Springer. 2005. |