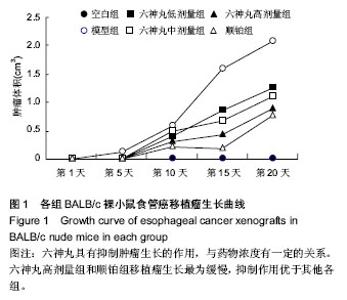
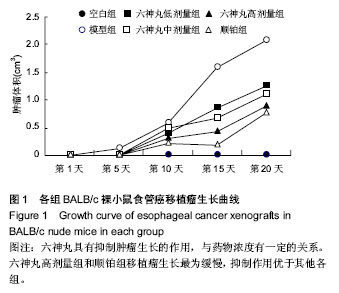
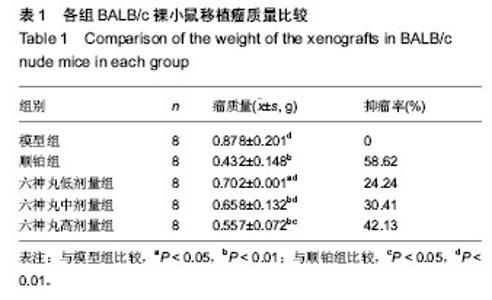
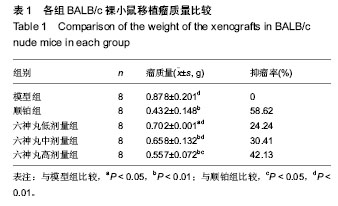
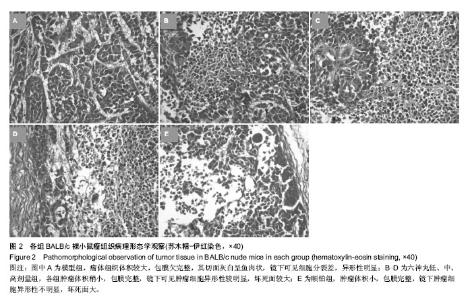
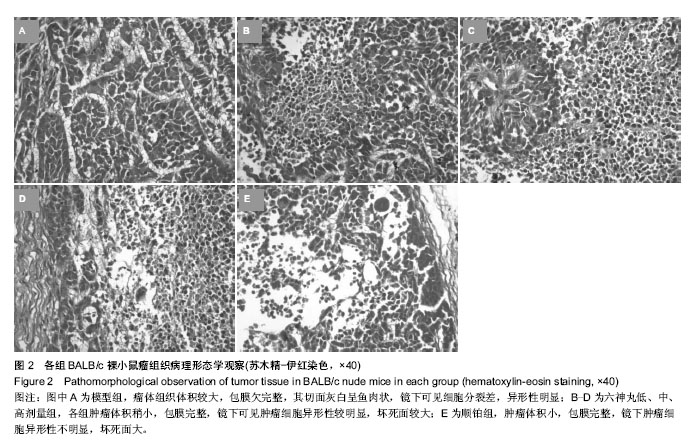
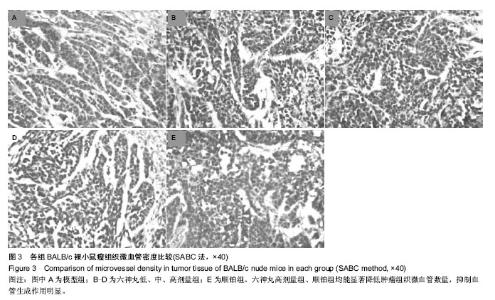
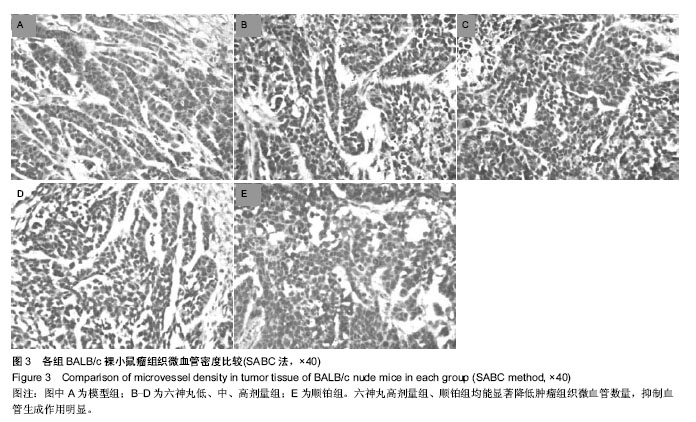
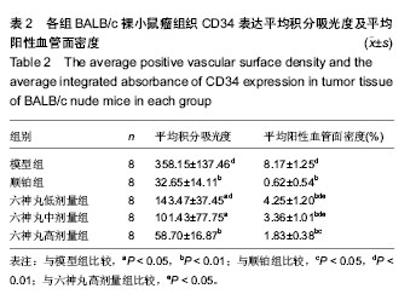
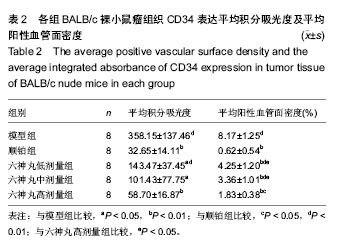
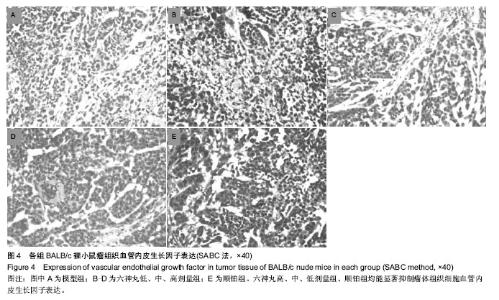
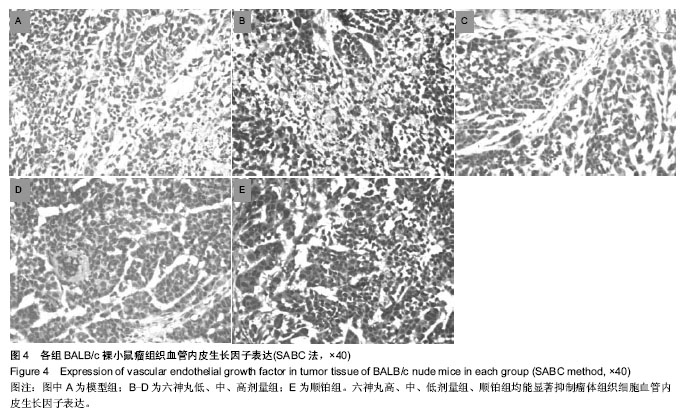
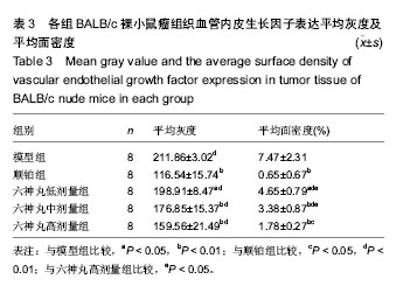
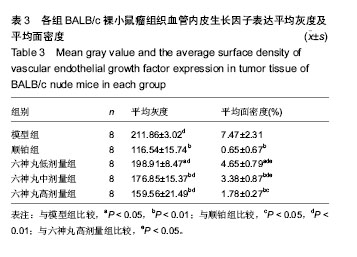
| [1] 肖国红.六神丸治疗急性化脓性扁桃腺炎的临床疗效观察[J].内蒙古中医药,2013,32(17):26-27.
[2] 李伟,王莉,侯寿安. 六神丸治疗智齿冠周炎的临床研究[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2003,19(5):294.
[3] 贾小靖.六神丸治疗带状疱疹22例疗效分析[J].临床医药实践, 2013,22(5):391-392.
[4] Guan B, Li H, Yang Z,et al.Inhibition of farnesoid X receptor controls esophageal cancer cell growth in vitro and in nude mouse xenografts.Cancer. 2013;119(7):1321-1329.
[5] Moens S, Goveia J, Stapor PC,et al.The multifaceted activity of VEGF in angiogenesis - Implications for therapy responses.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014 Jul 23. [Epub ahead of print]
[6] Jiang JT, Zhang LF, Zhou B,et al.Relationships of uPA and VEGF expression in esophageal cancer and microvascular density with tumorous invasion and metastasis.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012;13(7):3379-3383.
[7] Toi M, Matsumoto T, Bando H.Vascular endothelial growth factor: its prognostic, predictive, and therapeutic implications. Lancet Oncol. 2001;2(11):667-673.
[8] Xu XL, Ling ZQ, Chen W,et al.The overexpression of VEGF in esophageal cancer is associated with a more advanced TMN stage: a meta-analysis.Cancer Biomark. 2013;13(2):105-113.
[9] 方立峰,陈宏超,梁倩萍.细胞色素p450 2E1和血管内皮生长因子在食管鳞癌中的表达及临床意义[J].医药论坛杂志,2008,29(16): 6-8.
[10] 曹洋,施瑞华,朱宏.食管鳞癌组织中CTGF和VEGF的表达及其临床意义[J].南京医科大学学报:自然科学版,2008,28(9):1146- 1148.
[11] Su CM, Su YH, Chiu CF,et al.Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-C Upregulates Cortactin and Promotes Metastasis of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Ann Surg Oncol. 2014 Sep 12. [Epub ahead of print]
[12] Peng J, Shao N, Peng H, et al.Prognostic significance of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in esophageal carcinoma: a meta-analysis.J BUON. 2013; 18(2):398-406.
[13] Cheng AS, Chan HL, To KF,et al.Cyclooxygenase-2 pathway correlates with vascular endothelial growth factor expression and tumor angiogenesis in hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma.Int J Oncol. 2004;24(4):853-860.
[14] Hong YM, Gan WG, Xu ZH.Significance of the expression of integrin β1, VEGF and MVD in hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma.Genet Mol Res. 2014;13(3):6455-6465.
[15] Triratanachat S, Niruthisard S, Trivijitsilp P,et al.Angiogenesis in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and early-staged uterine cervical squamous cell carcinoma: clinical significance.Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2006;16(2):575-580.
[16] Bremnes RM, Camps C, Sirera R.Angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer: the prognostic impact of neoangiogenesis and the cytokines VEGF and bFGF in tumours and blood. Lung Cancer. 2006;51(2):143-158.
[17] 陶识博,张蕾,张云汉,等. 食管鳞癌中MTAl、MMP-9和MVD的表达及其临床病理意义[J].河南大学学报:医学版,2010,29(1): 29-33.
[18] 齐元富,郑祎,侯倩倩.六神丸以毒攻毒治疗非小细胞肺癌临床研究[J].辽宁中医杂志,2013,40(1):6-7.
[19] 高国青.三七粉冲服六神丸治疗晚期食道癌咽下困难32例[J].陕西中医, 2011,32(9):1123-1124.
[20] 张顺湧.食道癌的中医治疗体会[J].中国实用乡村医生杂志,2009, 16(6):43.
[21] 齐元富,李慧杰,李静.六神丸对H22肝癌腹水移植瘤PDGF与VEGF表达的影响及相关机制探讨[J].世界中医药,2013,8(1): 69-71.
[22] 丁诗语,孙莉,田项楠,等.六神丸对H22肝癌抑瘤及减毒效果的实验研究[J].实用医药杂志,2005,22(7):619-620.
[23] 张春荣,姜伟,齐元富.六神丸对鼠S180生长的抑制作用与抑制血管生成的关系[J].中国预防医学杂志,2005,6(4):327-330.
[24] 刘丹,祝林,奉建芳.蟾酥中蟾毒配基类成分的分离纯化及其体外抗肿瘤活性的研究[J]中成药,2010,32(6):937-940.
[25] 李宗云,高慧敏,王金华.蟾酥总蟾蜍甾烯对H22荷瘤小鼠的抗肿瘤作用及组织中代谢物的初步分析[J]中国中药杂志,2011, 36(21):2987-2993.
[26] 席晓霞,范临兰,田永刚.纳米雄黄的抗小鼠原位乳腺癌作用及其机制[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2013,18(9):981-987.
[27] 张亚兰,罗燕,刘春兰,等.中药麝香抗肿瘤研究进展[J].畜牧与饲料科学,2009,30(4):191-192.
[28] 吴志远,李芳芳,张昆.人工牛黄对小鼠乳腺癌肺转移的影响[J]中草药,2012,43(10):2013-2016. |