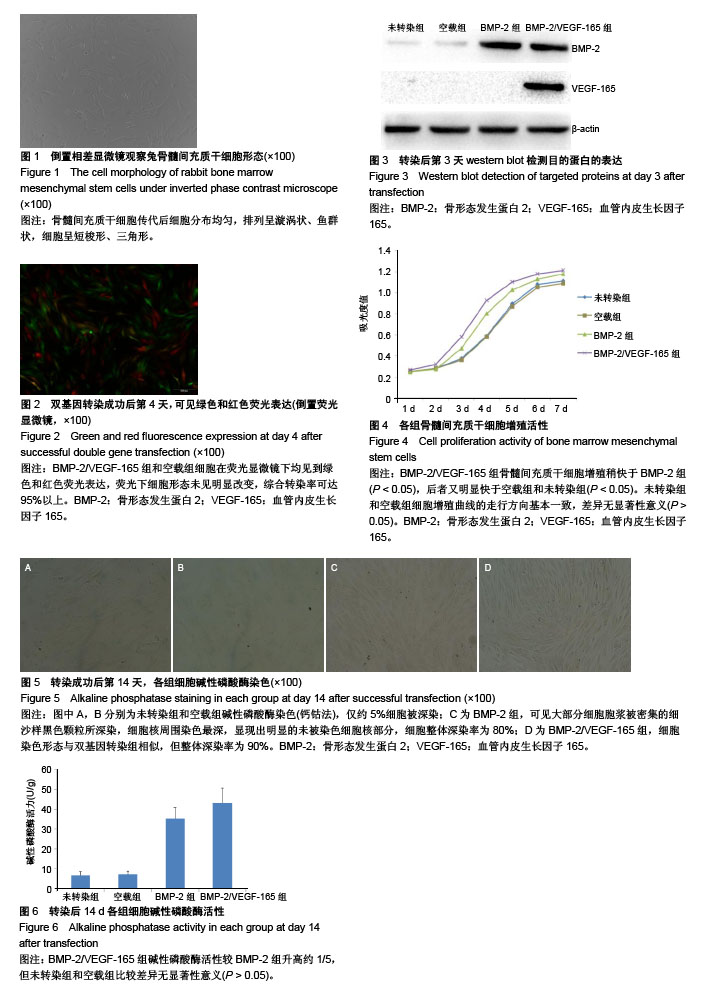
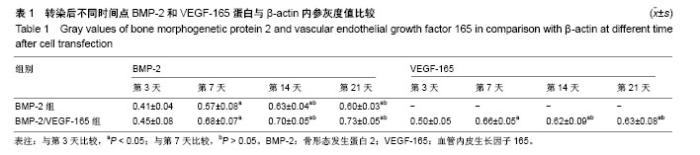
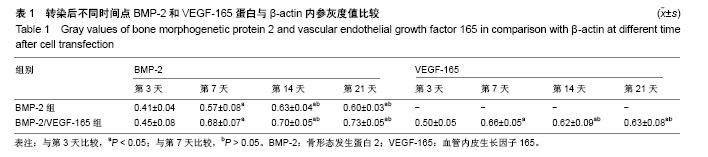
| [1] Miron RJ, Guillemette V, Zhang Y, et al. Enamel matrix derivative in combination with bone grafts: A review of the literature.Quintessence Int. 2014;45(6):475-487.[2] Poon B, Kha T, Tran S, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein-2 and bone therapy: successes and pitfalls.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2016;68(2):139-147.[3] Hu WW, Wang Z, Krebsbach PH.Virus immobilization on biomaterial scaffolds through biotin-avidin interaction for improving bone regeneration.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016; 10(2):E63-72.[4] KimelmanBleich N, Kallai I, Lieberman JR, et al. Gene therapy approaches to regenerating bone.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012; 64(12):1320-1330.[5] Evans CH.Gene therapy for bone healing.Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine. 2010; 12(6) :e18.[6] 李诗鹏,李强,石正松,等. 基因重组腺病毒载体与慢病毒载体转染兔骨髓间充质干细胞的对比[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2017,21(9): 1341-1345.[7] Jorgensen C,Gordeladze J,Noel D.Tissue engineering through autologous mesenchymal stem cells.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2004;15(5):406-410.[8] Arvidson K, Abdallah BM, Applegate LA, et al. Bone regeneration and stem cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2011;15(4): 718-746.[9] Manassero M, Viateau V, Deschepper M, et al. Bone regeneration in sheep using acropora coral, a natural resorbable scaffold, and autologous mesenchymal stem cells.Tissue Eng Part A. 2013;19(13-14):1554-1563.[10] Wang T, Xu Z, Jiang W, et al. Cell-to-cell contact induces mesenchymal stem cell to differentiate into cardiomyocyte and smooth muscle cell.Int J Cardiol. 2006;109(1):74-81.[11] Demeulemeester J, De Rijck J, Gijsbers R, et al. Retroviral integration: Site matters: Mechanisms and consequences of retroviral integration site selection.Bioessays. 2015;37(11): 1202-1214.[12] Mura M, Pisano F,Malpasso G, et al. Novel IRES-based lentivirus co-expressing IGF1 and BMP2 enhances both cardiomyogenesis and cytoprotection of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells.Eur Heart J. 2013;34(suppl 1) :P147.[13] Jiang J, Fan CY, Zeng BF.Osteogenic differentiation effects on rat bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells by lentivirus-mediated co-transfection of human BMP2 gene and VEGF165 gene.Biotechnol Lett. 2008;30(2):197-203.[14] Jeon O, Rhie JW, Kwon IK, et al. In vivo bone formation following transplantation of human adipose-derived stromal cells that are not differentiated osteogenically.Tissue Eng Part A. 2008;14(8):1285-1294.[15] Rivera JC, Strohbach CA, Wenke JC, et al. Beyond osteogenesis: an in vitro comparison of the potentials of six bone morphogenetic proteins.Front Pharmacol. 2013;4:125.[16] 石正松,李强,蔡伟良,等.腺病毒介导hBMP-2转染BMSCs复合DBM修复兔缺血性股骨头坏死的实验研究[J].天津医药, 2015, 43(10):1128-1132.[17] 宁寅宽,李强,蔡伟良,等.Ad-BMP-2/GFP转染兔骨髓间充质干细胞前后生物学特性的研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2014,20(12): 1387-1392.[18] Carlevaro MF, Cermelli S, Cancedda R, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in cartilage neovascularization and chondrocyte differentiation: auto-paracrine role during endochondral bone formation.J Cell Sci. 2000;113 ( Pt 1):59-69.[19] Gerber HP, Vu TH, Ryan AM, et al. VEGF couples hypertrophic cartilage remodeling, ossification and angiogenesis during endochondral bone formation.Nat Med. 1999;5(6):623-628.[20] Silvestre JS, Lévy BI.Angiogenesis therapy in ischemic disease.Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss. 2002;95(3):189-196.[21] Xiao C, Zhou H, Liu G, et al. Bone marrow stromal cells with a combined expression of BMP-2 and VEGF-165 enhanced bone regeneration.Biomed Mater. 2011;6(1):015013.[22] Jiang J, Fan CY, Zeng BF.Experimental construction of BMP2 and VEGF gene modified tissue engineering bone in vitro.Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12(3):1744-1755.[23] Zhang HX, Zhang XP, Xiao GY, et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of calcium phosphate composite scaffolds containing BMP-VEGF loaded PLGA microspheres for the treatment of avascular necrosis of the femoral head.Mater SciEng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;60:298-307.[24] Kakudo N, Kusumoto K, Wang YB, et al. Immunolocalization of vascular endothelial growth factor on intramuscular ectopic osteoinduction by bone morphogenetic protein-2.Life Sci. 2006; 79(19):1847-1855. |