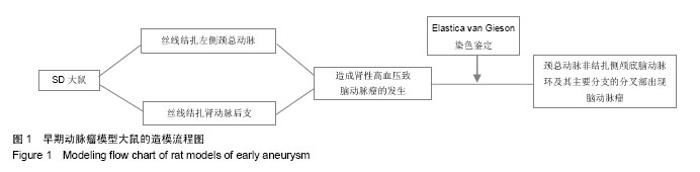
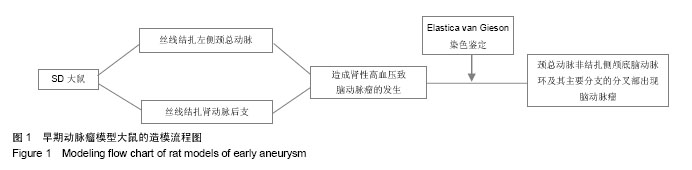
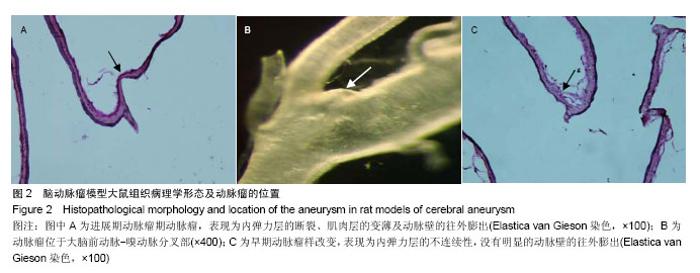
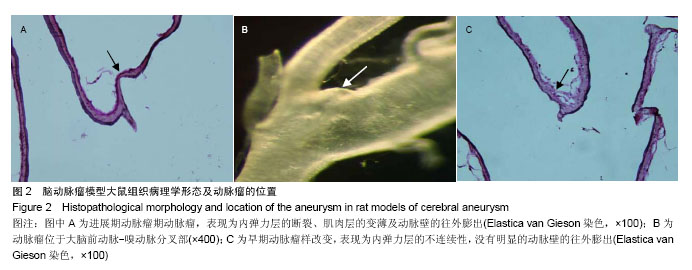
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (5): 745-751.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.05.016
Previous Articles Next Articles
Expression of matrix structural proteins in the vessel wall of rat models during the early aneurysm formation
Wang Zeng-liang, Li Shao-shan, Sailike Duishanbai, Wang Yong-xin, Cheng Xiao-jiang, Zhou Qing-jiu, Zhou Kai, Du Guo-jia, Wang Xin, Geng Dangmurenjiafu
- Department of Neurosurgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Revised:2014-12-19Online:2015-01-30Published:2015-03-02 -
Contact:Sailike Duishanbai, M.D., Chief physician, Associate professor, Department of Neurosurgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Wang Zeng-liang, Studying for doctorate, Attending physician, Department of Neurosurgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, No. 2011211A076
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Zeng-liang, Li Shao-shan, Sailike Duishanbai, Wang Yong-xin, Cheng Xiao-jiang, Zhou Qing-jiu, Zhou Kai, Du Guo-jia, Wang Xin, Geng Dangmurenjiafu. Expression of matrix structural proteins in the vessel wall of rat models during the early aneurysm formation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(5): 745-751.
share this article
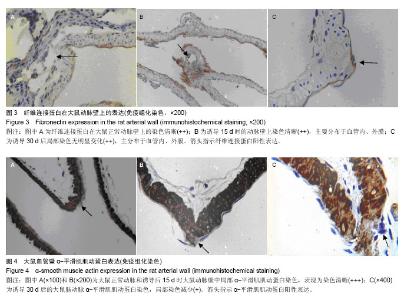
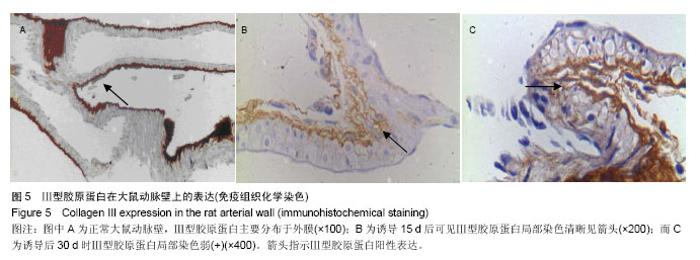
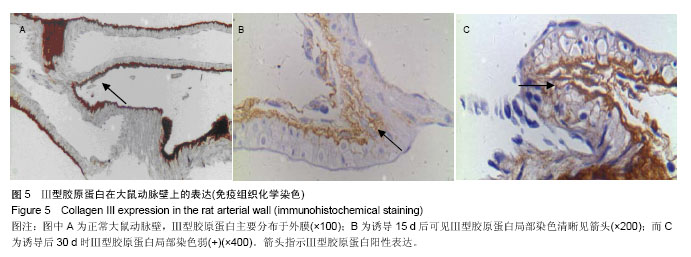
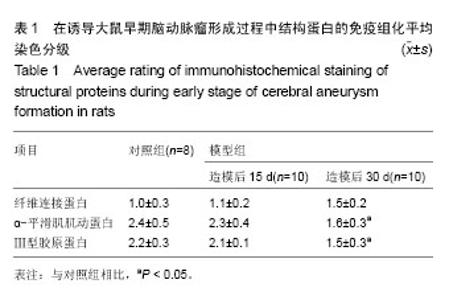
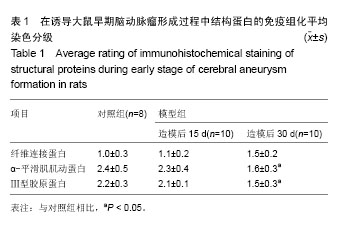
2.3 脑动脉瘤模型大鼠动脉瘤形成部位中相关基质蛋白的表达 2.3.1 纤维连接蛋白 纤维连接蛋白在正常血管壁和动脉瘤形成动脉诱导15 d时血管壁上有表达,其中在1个正常脑动脉标本中染色强,另外6个中较明显染色,而在诱导动脉瘤形成15 d时,10个脑动脉标本中7个中染色清晰,另外3个中染色弱。到30 d时在检测的10个脑动脉标本中表达阳性率为100%,2个标本中染色弱,8个标本中呈染色清晰,模型组大鼠脑动脉标本中纤维连接蛋白平均染色级别与对照组相比差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05;图3,表1)。 2.3.2 α-平滑肌肌动蛋白 在检测的8个正常标本中α-平滑肌肌动蛋白呈全阳性,其中在6个正常脑动脉标本中呈强染色,另外2个中为染色清晰,而在诱导动脉瘤形成15 d时的10个脑动脉标本中8个中染色清晰,另外2个中染色弱,到30 d时在检测的10个脑动脉标本中α-平滑肌肌动蛋白的阳性表达率为100%,在7个标本中染色弱,3个标本中染色清晰,模型组大鼠脑动脉标本中α-平滑肌肌动蛋白平均染色级别与对照组相比差异有显著性意义(P=0.005;图4,表1)。 2.3.3 Ⅲ型胶原蛋白 在检测的8个正常标本和诱导动脉瘤形成第15天时的10个脑动脉标本中Ⅲ型胶原蛋白呈阳性,主要分布于外膜。其中在5个正常脑动脉标本中染色强,另外3个中为染色清晰,而在诱导动脉瘤形成第15天时的10个脑动脉标本中8个中染色清晰,另外2个染色弱。 到诱导动脉瘤形成30 d时在检测的10个脑动脉标本中Ⅲ型胶原蛋白的阳性表达率为100%,在7个标本中染色清晰,3个标本中染色弱。模型组大鼠脑动脉标本中Ⅲ型胶原蛋白平均染色级别与对照组相比差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05;图5,表1)。"
| [1] Vlak MH, Algra A, Brandenburg R, et al. Prevalence of unruptured intracranial aneurysms, with emphasis on sex, age, comorbidity, country, and time period: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2011;10(7):626-636. [2] Juvela S, Poussa K, Lehto H, et al. Natural history of unruptured intracranial aneurysms: a long-term follow-up study. Stroke. 2013;44(9):2414-2421. [3] Xiang J, Natarajan SK, Tremmel M, et al. Hemodynamic- morphologic discriminants for intracranial aneurysm rupture. Stroke. 2011;42(1):144-152. [4] 沈建康.颅内动脉瘤手术治疗的现状和前景[J].中华神经外科杂志,2005,21(11):641-642. [5] Frösen J, Tulamo R, Paetau A, et al. Saccular intracranial aneurysm: pathology and mechanisms. Acta Neuropathol. 2012;123(6):773-786. [6] 袁陆涛.颅内动脉瘤的流行病学研究现状[J].国际神经病学神经外科学杂志,2011,38(6):587-590. [7] Brown RD Jr, Broderick JP. Unruptured intracranial aneurysms: epidemiology, natural history, management options, and familial screening. Lancet Neurol. 2014;13(4): 393-404. [8] Caranci F, Briganti F, Cirillo L, et al. Epidemiology and genetics of intracranial aneurysms. Eur J Radiol. 2013;82(10): 1598-1605. [9] 张万宏,吴恒浩,田卫平,等.颅内动脉瘤性蛛网膜下腔出血患者不同时间点GCS 评分与预后相关性研究[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2013,15(22):36-39. [10] 黄清海,杨鹏飞.颅内动脉瘤血管内介入治疗中国专家共识(2013) [J].中国脑血管病杂志,2013,10(11):12. [11] 秦尚振,马廉亭,徐国政,等.颅内动脉瘤治疗十年回顾(附1372例治疗及随访)[J].中国临床神经外科杂志,2012,17(1):1-4. [12] 康慧斌,彭汤明,钱增辉,等.颅内动脉瘤破裂风险因素分析[J].中华神经医学杂志,2014,13(4). [13] 马宏伟,许百男.未破裂颅内动脉瘤的破裂风险评估与治疗决策[J].中国微侵袭神经外科杂志,2014(7). [14] 赛力克•对山拜,周凯,阿尔达克•胡那匹亚,等.血管生长因子和结构蛋白在新疆哈萨克族破裂和未破裂颅内动脉瘤中的表达[J].中华神经外科杂志,2011,27(11):1157-1159. [15] Yasargil MG. Microneurosurgery. Stuttgart: Thieme Medical Publishers, 2013. [16] Kole MK, Pelz DM, Kalapos P, et al. Endovascular coil embolization of intracranial aneurysms: important factors related to rates and outcomes of incomplete occlusion. J Neurosurg. 2005;102(4):607-615. [17] Deniz ML, Kiliç T, Almaata I, et al. Expression of growth factors and structural proteins in chordomas: basic fibroblast growth factor, transforming growth factor alpha, and fibronectin are correlated with recurrence. Neurosurgery. 2002;51(3):753-760. [18] Kuivaniemi H, Prockop DJ, Wu Y, et al. Exclusion of mutations in the gene for type III collagen (COL3A1) as a common cause of intracranial aneurysms or cervical artery dissections: results from sequence analysis of the coding sequences of type III collagen from 55 unrelated patients. Neurology. 1993; 43(12):2652-2658. [19] Bor AS, Rinkel GJ, van Norden J, et al. Long-term, serial screening for intracranial aneurysms in individuals with a family history of aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage: a cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2014;13(4):385-392. [20] Lebland R. De novo formation of familial cerebral aneurysms: case report. Neurosurgery. 1999;44(4):871-877. [21] Stehbens WE. Aneurysms and anatomical variation of cerebral arteries. Arch Pathol. 1963;75:45-64. [22] 赛力克•对山拜,胡那皮亚阿尔达克,杨振村,等.纤维连接蛋白在颅内脑动脉瘤中的表达及动脉瘤壁纤维结构的特殊染色[J].中华神经外科杂志,2013,29(12):1256-1259. [23] 齐巍,赵继宗,王硕,等.免疫炎性反应与颅内囊性动脉瘤基质重塑的组织病理学研究[J].首都医科大学学报,2005,25(4):461-463. [24] Ramachandran M, Laakso A, Harbaugh RE, et al. On the role of modeling choices in estimation of cerebral aneurysm wall tension. J Biomech. 2012;45(16):2914-2919. [25] 凌峻,熊秋迎,聂艳良,等.肾性高血压诱导的大鼠脑动脉瘤模型的建立[J].中华实验外科杂志,2010,27(9):1352-1353. [26] 包新杰,赵浩,赵英杰,等.线栓法插线深度对大鼠脑梗死模型制备的影响[J].中国实验动物学报,2011,19(3):233-236. [27] 马良,付强,关俊宏.实验性大鼠脑动脉瘤形成过程中MMP-2, MMP-9表达的动态变化[J].中华神经外科疾病研究杂志, 2013, 12(3):197-200. [28] 康涛,张洪.经颈总动脉和经颈外动脉制作大鼠MCAO模型的比较[J].中华脑血管病杂志(电子版),2013,7(3):29-33. [29] 张贤华.Src 激酶抑制剂 PP2 抑制颅内动脉瘤形成的初步研究[D].南昌:南昌大学,2013. [30] Kilic T, Sohrabifar M, Kurtkaya O, et al. Expression of structural proteins and angiogenic factors in normal arterial and unruptured and ruptured aneurysm walls. Neurosurgery. 2005;57(5):997-1007. [31] Chien A, Liang F, Sayre J, et al. Enlargement of small, asymptomatic, unruptured intracranial aneurysms in patients with no history of subarachnoid hemorrhage: the different factors related to the growth of single and multiple aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 2013;119(1):190-197. [32] Schievink WI. Intracranial aneurysms. N Engl J Med. 1997; 336(1):28-40. [33] Bulters DO, Birch AA, Hickey E, et al. A randomized controlled trial of prophylactic intra-aortic balloon counterpulsation in high-risk aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke. 2013;44(1):224-226. [34] Hop JW, Rinkel GJ, Algra A, et al. Case-fatality rates and functional outcome after subarachnoid hemorrhage: a systematic review. Stroke. 1997;28(3):660-664. [35] Schweizer TA, Macdonald L. The Behavioral Consequences of Stroke. Berlin: Springer, 2014:177-197. [36] Kilbourn KJ, Levy S, Staff I, et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of neurogenic stress cadiomyopathy in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2013; 115(7):909-914. [37] van den Berg JS, Pals G, Arwert F, et al. Type III collagen deficiency in saccular intracranial aneurysms. Defect in gene regulation? Stroke. 1999;30(8):1628-1631. [38] Kuivaniemi H, Prockop DJ, Wu Y, et al. Exclusion of mutations in the gene for type III collagen (COL3A1) as a common cause of intracranial aneurysms or cervical artery dissections: results from sequence analysis of the coding sequences of type III collagen from 55 unrelated patients. Neurology. 1993; 43(12):2652-2658. [39] Schievink WI, Schaid DJ, Michels VV, et al. Familial aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a community-based study. J Neurosurg. 1995;83(3):426-429. [40] Coutard M, Osborne-Pellegrin M. Genetic susceptibility to experimental cerebral aneurysm formation in the rat. Stroke. 1997;28(5):1035-1042. [41] Aalto-Setälä K, Laitinen K, Erkkilä L, et al. Chlamydia pneumoniae does not increase atherosclerosis in the aortic root of apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2001;21(4):578-584. [42] 赛力克,鲍遇海,更•党木仁加甫,等.选择性血管结扎法建立大鼠脑动脉瘤模型[J].中华神经外科杂志,2010,26(5):419-421. [43] Peters DG, Kassam AB, Feingold E, et al. Molecular anatomy of an intracranial aneurysm: coordinated expression of genes involved in wound healing and tissue remodeling. Stroke. 2001; 32(4):1036-1042. [44] Futami K, Yamashita J, Tachibana O, et al. Immunohistochemical alterations of fibronectin during the formation and proliferative repair of experimental cerebral aneurysms in rats. Stroke. 1995;26(9):1659-1664. [45] Morimoto M, Miyamoto S, Mizoguchi A, et al. Mouse model of cerebral aneurysm: experimental induction by renal hypertension and local hemodynamic changes. Stroke. 2002; 33(7):1911-1915. [46] Hashimoto N, Kim C, Kikuchi H, et al. Experimental induction of cerebral aneurysms in monkeys. J Neurosurg. 1987;67(6): 903-905. [47] Skirgaudas M, Awad IA, Kim J, et al. Expression of angiogenesis factors and selected vascular wall matrix proteins in intracranial saccular aneurysms. Neurosurgery. 1996;39(3):537-547. [48] Omodaka S, Sugiyama S, Inoue T, et al. Local hemodynamics at the rupture point of cerebral aneurysms determined by computational fluid dynamics analysis. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2012; 34(2):121-129. [49] Fukazawa K, Ishida F, Umeda Y, et al. Using Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis to Characterize Local Hemodynamic Features of Middle Cerebral Artery Aneurysm Rupture Points. World Neurosurg. 2013. in press. [50] Wong GK, Poon WS. Current status of computational fluid dynamics for cerebral aneurysms: the clinician's perspective. J Clin Neurosci. 2011;18(10):1285-1288. [51] Jeong W, Rhee K. Hemodynamics of cerebral aneurysms: computational analyses of aneurysm progress and treatment. Comput Math Methods Med. 2012;2012:782801. [52] 张建忠,吴曦,黄清海,等.血流动力学诱导炎性反应对颅内动脉瘤形成机制的研究进展[J].中国脑血管病杂志,2014(7):56. [53] 彭汤明,刘爱华,吴中学.血管壁剪切力相关易感基因对颅内动脉瘤形成早期的作用[J].中华神经医学杂志,2013,12(4):419-421. [54] 赖小彪.前交通动脉瘤形成、破裂和复发的危险因素及破裂的血流动力学机制研究[D].杭州:浙江大学,2013. [55] Rothbart D, Awad IA, Lee J,et al. Expression of angiogenic factors and structural proteins in central nervous system vascular malformations. Neurosurgery. 1996;38(5):915-925. [56] Abdulrauf SI, Malik GM, Awad IA. Spontaneous angiographic obliteration of cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery. 1999;44(2):280-288. [57] Brown LF, Detmar M, Claffey K, et al. Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor: a multifunctional angiogenic cytokine. EXS. 1997;79:233-269. [58] Reynolds LP, Redmer DA. Expression of the angiogenic factors, basic fibroblast growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor, in the ovary. J Anim Sci. 1998;76(6):1671-1681. [59] Stalmans I. Role of the vascular endothelial growth factor isoforms in retinal angiogenesis and DiGeorge syndrome. Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 2005;67(4):229-276. [60] 李东升,潘伟生,夏家辉,等.颅内动脉瘤患者 Ⅲ 型胶原蛋白基因的限制性片段长度多态性分析[J].中华神经外科杂志,1996, 12(2): 84-87. |
| [1] | Wu Chuang, Muhetaer · Kelimu, Maimaitili · Aisha, Yang Hang. Influence of blood components on blood flow characteristics of individualized communicating aneurysm [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1219-1223. |
| [2] | Li Fang, Wu Ketong, Zhao Jun, Li Gang. Advances of endovascular stent and its treatment for aneurysms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(34): 5561-5569. |
| [3] | Xu Weilong, Zuo Yuan, Xin Daqi, He Chenyang, Zhao Peng, Shi Ming, Zhou Boyuan, Liu Yating, Zhao Yan. Selection of modeling methods for acute compressive spinal cord injury: a network Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3767-3772. |
| [4] | Zhao Xin, Shi Xin, Chen Bei, Cao Yanpeng, Chen Yaowu, Liu Xiaoren, He Yusheng, He Liyun, Li Xiying, Liu Jun. Vacuum sealing drainage enhances wound healing by up-regulating collagen type I/III ratio in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(32): 5122-5127. |
| [5] | Zhang Yaochun, Zheng Lifang, Liu Rong. Prospects for 3D printing in the treatment of cerebral aneurysm [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(32): 5243-5248. |
| [6] | Gong Hewei, Liu Chengwei, Liang Bingsheng, Li Gang. Lentiviral vector-mediated overexpression of miRNA-1 in L6 myoblasts: cell proliferation, differentiation and histone deacetylase expression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(13): 2075-2080. |
| [7] | Luo Yin-yue, Li Hong-yan, Bao Guang-jie, Kang Hong. Mechanisms of staurosporine intervention in tissue-engineered self-assembly construct contraction of the temporomandibular joint disc [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(30): 4888-4893. |
| [8] | Hou Tian, An Mei-wen, Wang Li . Changes in cytoskeleton proteins and mechanical properties of the cells on soft substrates [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(22): 3461-3466. |
| [9] | Han Xue-jie1, 2, Halleda•Balikarthan2, Gao Hua3, Yang Xin-ling2. Baicalin increases connexin 43 expression in striatal astrocytes of rats with Parkinson’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(16): 2542-2548. |
| [10] |
Zhao Yu-long, Zhang Hai-feng, Dong Yu-shu, Jiang Wei, Hao Guang-zhi, Liang Guo-biao, Gao Xu.
Complications associated with stent-assisted coil embolization of wide-neck intracranial aneurysms
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(34): 5506-5512.
|
| [11] | Liu Ming-yuan, Liu Bing, Wang Hao-fu. A novel domestic-made stent-graft in endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: outcome of short- and medium-term follow-up and experience summary of a single-center controlled clinical trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(47): 7097-7105. |
| [12] | Liu Ying-wei, Zhang Wan-li, Chi Cheng-tao, Xu Qing-yu, Lu De-zhi. Effects of hyaluronic acid on scar formation in the acellular nerve allograft [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(42): 6317-6323. |
| [13] | Sun Gui-fang, Zhang Xiao-fen, Li Hong-chang, Pan Li-yun, Chen Ya-feng, Xu Ke, Feng Dian-xu. Shengjiyuhong ointment inhibits hypertrophic scar formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(33): 4890-4898. |
| [14] | Yan Ping, Hou Jing-ying, Zheng Shao-xin, Long Hui-bao, Zhong Ting-ting, Zhou Chang-qing, Guo Tian-zhu, Wu Quan-hua, Wang Tong. Cardiac stem cells improve the electrophysiological stability and ventricular fibrillation threshold via ANGII/AT1R/TGF-beta1/SMAD/CX43 signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(28): 4226-4233. |
| [15] | Yan Ping, Hou Jing-ying, Zheng Shao-xin, Long Hui-bao, Zhou Chang-qing, Guo Tian-zhu, Wu Quan-hua, Zhong Ting-ting, Wang Tong. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma promotes exogenous mesenchymal stem cells to express connexin 43: its role and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(23): 3357-3365. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||