[1] ABDEHKAKHA A, HAMMOND AL, PATEL TR, et al. Cerebral aneurysm flow diverter modeled as a thin inhomogeneous porous medium in hemodynamic simulations. Comput Biol Med. 2021;139:104988.
[2] BHARDWAJ A, DAGAR V, KHAN MO, et al. On the prevalence of flow instabilities from high-fidelity computational fluid dynamics of intracranial bifurcation aneurysms. J Biomech. 2021;127:110683.
[3] 刘召. 开颅夹闭对照介入栓塞对破裂性前交通动脉瘤患者预后的回顾性分析[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2021.
[4] GHOLAMPOUR S, MEHRJOO S. Effect of bifurcation in the hemodynamic changes and rupture risk of small intracranial aneurysm. Neurosurg Rev. 2021;44(3):1703-1712.
[5] 任国荣,祝树森,于良宁,等.颅内动脉瘤的血流动力学研究综述[J].医疗卫生装备,2020,41(6):99-102+105.
[6] 钟焕鑫. 颅内动脉瘤异常血流与形态的关系及破裂预测模型建立[D]. 汕头:汕头大学,2021.
[7] FRÖSEN J, CEBRAL J, ROBERTSON AM, et al.Flow-induced, inflammation-mediated arterial wall remodeling in the formation and progression of intracranial aneurysms.Neurosurg Focus. 2019;47(1):E21.
[8] YUAN J, HUANG C, LAI N, et al. Hemodynamic and Morphological Analysis of Mirror Aneurysms Prior to Rupture. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2020;16:1339-1347.
[9] MENICHINI C, XU XY.Mathematical modeling of thrombus formation in idealized models of aortic dissection: initial findings and potential applications.J Math Biol. 2016;73(5):1205-1226.
[10] MURAYAMA Y, FUJIMURA S, SUZUKI T,et al. Computational fluid dynamics as a risk assessment tool for aneurysm rupture. Neurosurg Focus. 2019;47(1):E12.
[11] 杨刚. 主动脉瓣置换血流动力学的PIV实验研究[D]. 北京:北京工业大学,2020.
[12] 梁晏宾,木合塔尔·克力木,买买提力·艾沙.个体化颈动脉瘤的血流动力学特性分析[J]. 医用生物力学,2021,36(3):396-401.
[13] QIAO Y, ZENG Y, DING Y, et al. Numerical simulation of two-phase non-Newtonian blood flow with fluid-structure interaction in aortic dissection. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2019;22(6):620-630.
[14] 曾宇杰,罗坤,樊建人,等.主动脉夹层血液两相流动数值模拟分析[J].工程热物理学报,2016,37(4):780-784.
[15] 乔永辉. 计算机辅助优化胸主动脉腔内修复术[D].杭州:浙江大学, 2020.
[16] 刘莹,张伟中,殷艳飞,等.双向流固耦合作用下狭窄左冠状动脉内两相血流分析[J]. 应用数学和力学,2016,37(5):501-509.
[17] 徐文涛,木合塔尔·克力木,高霞霞.颅内动脉瘤两相血流动力学分析及PIV实验研究[J]. 数学的实践与认识,2019,49(14):123-131.
[18] 郭炳忠,李毅锋,姜维喜,等.高分辨率磁共振成像技术评估颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的研究进展[J].中南大学学报(医学版),2020, 45(12):1476-1482.
[19] TAO WU, QING ZHU. Advancement in the haemodynamic study of intracranial aneurysms by computational fluid dynamics. Brain Hemorrhages. 2021;2(2): 71-75.
[20] WU X, GÜRZING S, SCHINKEL C, et al. Hemodynamic Study of a Patient-Specific Intracranial Aneurysm: Comparative Assessment of Tomographic PIV, Stereoscopic PIV, In Vivo MRI and Computational Fluid Dynamics. Cardiovasc Eng Technol. 2021 Nov 8. doi: 10.1007/s13239-021-00583-2.
[21] 邹燕萍,徐锋.壁面切应力与颅内动脉瘤的研究进展[J].临床神经外科杂志,2021,18(1):117-120.
[22] JOU LD, WONG G, DISPENSA B,et al. Correlation between lumenal geometry changes and hemodynamics in fusiform intracranial aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005;26(9):2357-2363.
[23] 马宏伟. 颅内动脉瘤的病理和计算流体力学研究[D].北京:中国人民解放军医学院,2014.
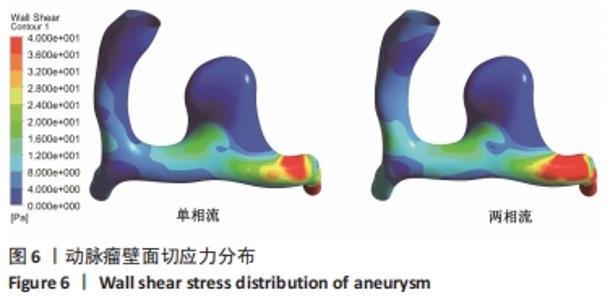
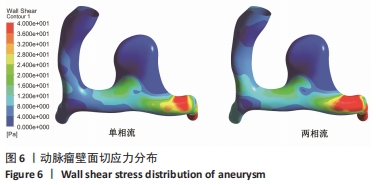
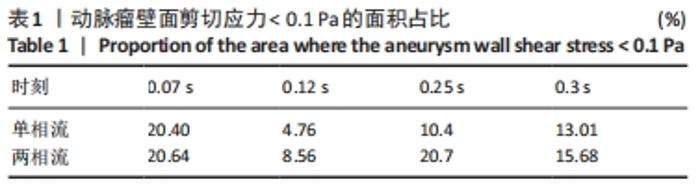
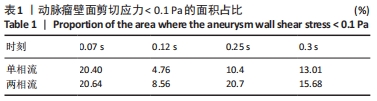
|