Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (1): 101-107.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.01.018
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of paeoniflorin on the proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
Chao Er-tao1, Bai Hai2, Wang Cun-bang2, Xi Rui2, Ou Jian-feng2, Zhao Qiang2
- 1Gansu College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730050, Gansu Province, China
2Hematology Center, General Hospital of Lanzhou Military Region, Lanzhou 730050, Gansu Province, China
-
Revised:2014-11-19Online:2015-01-01Published:2015-01-01 -
Contact:Bai Hai, M.D., Chief physician, Professor, Hematology Center, General Hospital of Lanzhou Military Region, Lanzhou 730050, Gansu Province, China -
About author:Chao Er-tao, Studying for master’s degree, Gansu College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730050, Gansu Province, China -
Supported by:the Major Science and Technology Project of Gansu Province, No. 1102FKDA005
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chao Er-tao, Bai Hai, Wang Cun-bang, Xi Rui, Ou Jian-feng, Zhao Qiang. Effects of paeoniflorin on the proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(1): 101-107.
share this article
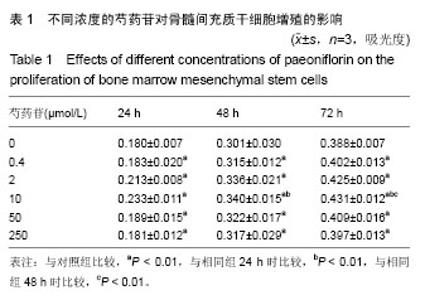
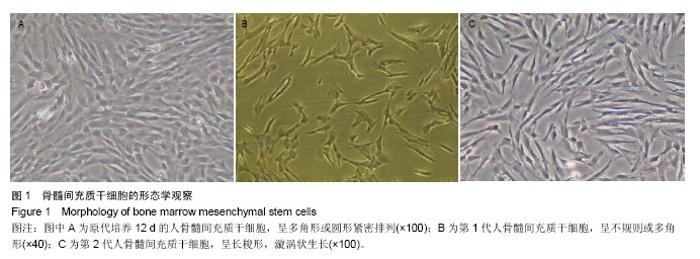
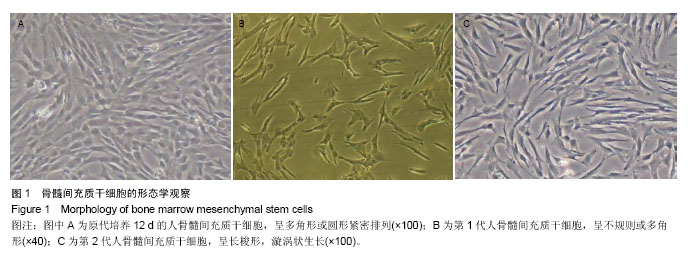
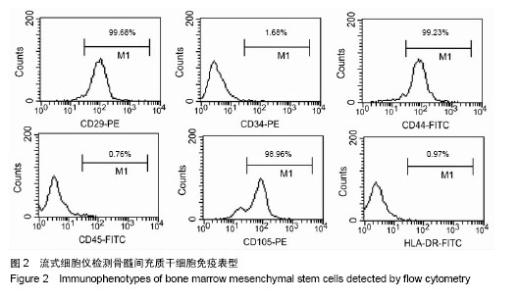
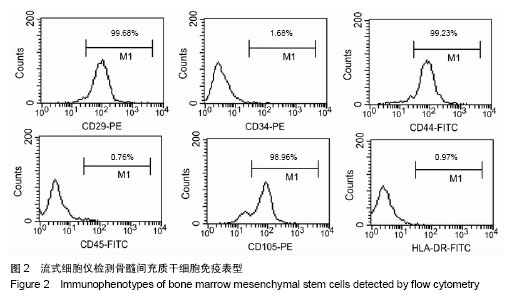
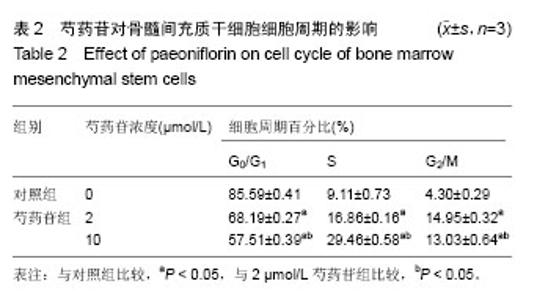
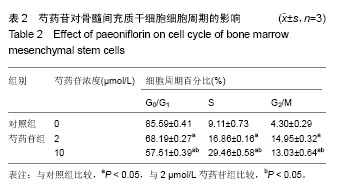
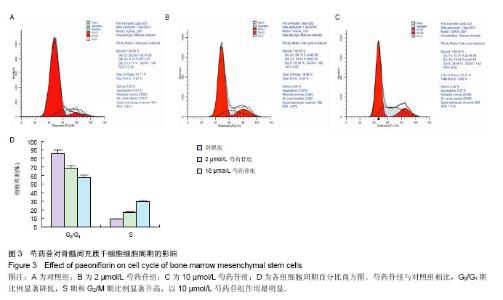
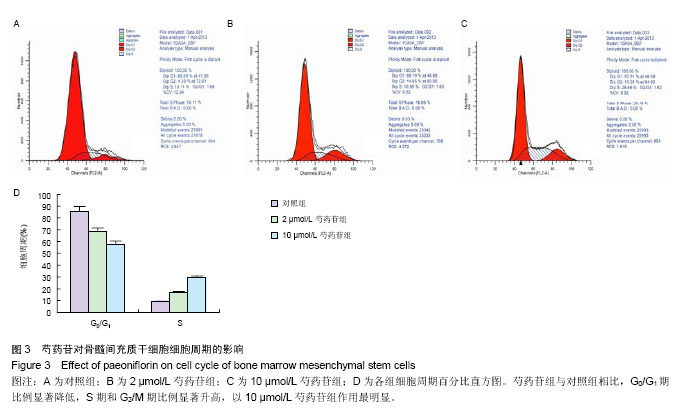
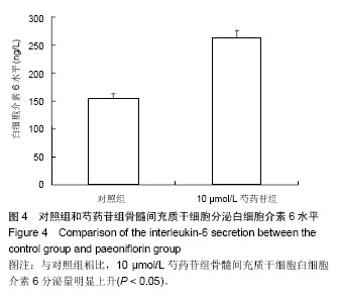
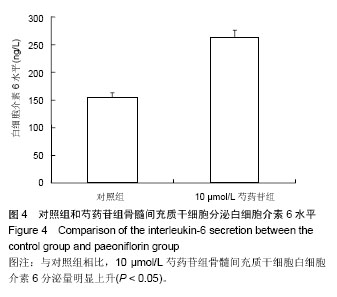
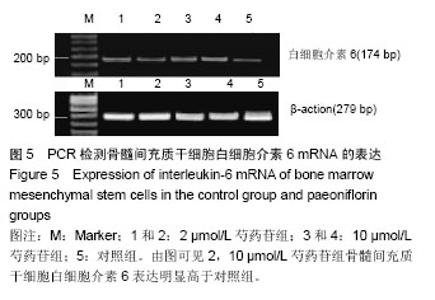
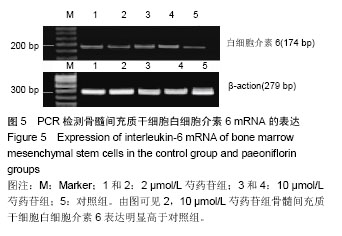
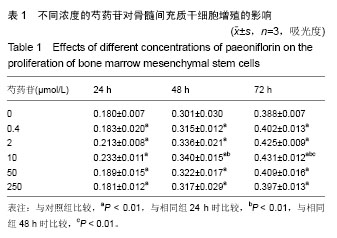
2.3 成骨成脂诱导分化 骨髓间充质干细胞具有成骨分化潜能,在成骨诱导液中培养骨髓间充质干细胞,随着培养时间的延长,细胞形态逐渐变为短梭形、多边形,持续诱导28 d后行茜素红染色,可见红色矿化的钙结节形成。成脂诱导21 d后行油红O染色,细胞胞浆内出现大量的脂质颗粒。 2.4 芍药苷对骨髓间充质干细胞增殖的影响 MTT检测结果表明,芍药苷与骨髓间充质干细胞共培养后,骨髓间充质干细胞的吸光度值增加明显,2 μmol/L和10 μmol/L浓度的实验组与对照组相比差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.01),2 μmol/L和10 μmol/L两个浓度间比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),0.4,50,250 μmol/L浓度对骨髓间充质干细胞促增殖作用不明显(P > 0.05)。10 μmol/L芍药苷培养24,48,72 h后,各个时间段增殖率相比较差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.01)。由此说明,芍药苷对骨髓间充质干细胞的促增殖作用呈时间依赖性但无剂量依赖性,达到一定的药物浓度后骨髓间充质干细胞增殖率不再增加,见表1。"
| [1] Gordon MY, Goldman JM, Gordon-Smith EC.Spatial and functional relationships between human hemopoietic and marrow stromal cells in vitro.Int J Cell Cloning. 1983;1(6): 429-439. [2] Gordon MY, Kearney L, Hibbin JA.Effects of human marrow stromal cells on proliferation by human granulocytic (GM-CFC), erythroid (BFU-E) and mixed (Mix-CFC) colony-forming cells.Br J Haematol. 1983;53(2):317-325. [3] Le Blanc K, Rasmusson I, Sundberg B,et al.Treatment of severe acute graft-versus-host disease with third party haploidentical mesenchymal stem cells.Lancet. 2004;363 (9419):1439-1441. [4] Orlic D, Kajstura J, Chimenti S,et al.Bone marrow cells regenerate infarcted myocardium.Nature. 2001;410(6829): 701-705. [5] Toma C, Pittenger MF, Cahill KS,et al.Human mesenchymal stem cells differentiate to a cardiomyocyte phenotype in the adult murine heart.Circulation. 2002;105(1):93-98. [6] Yoon YS, Wecker A, Heyd L,et al.Clonally expanded novel multipotent stem cells from human bone marrow regenerate myocardium after myocardial infarction.J Clin Invest. 2005; 115(2):326-338. [7] Catenacci DV, Schiller GJ.Myelodysplasic syndromes: a comprehensive review.Blood Rev. 2005;19(6):301-319. [8] Garayoa M, Garcia JL, Santamaria C,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells from multiple myeloma patients display distinct genomic profile as compared with those from normal donors. Leukemia. 2009;23(8):1515-1527. [9] Semple JW, Milev Y, Cosgrave D,et al.Differences in serum cytokine levels in acute and chronic autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura: relationship to platelet phenotype and antiplatelet T-cell reactivity.Blood. 1996;87(10):4245-4254. [10] 郭平,宋卓彦,王升启. 芍药苷对辐射致血虚小鼠骨髓蛋白质表达的影响[J].中药药理与临床,2007,23(4):17-19. [11] 高月,马增春,谭洪玲,等.四物汤及其提取物对辐射致血虚证小鼠造血作用的研究[J].天津中医药,2003,20(6):47-51. [12] 郭平,郭霞. 芍药苷对辐射致血虚证小鼠骨髓细胞白介素及其受体基因表达的作用[J].中药药理与临床, 2009,25(5): 25-27. [13] Carrancio S, Blanco B, Romo C,et al.Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells for improving hematopoietic function: an in vitro and in vivo model. Part 2: Effect on bone marrow microenvironment.PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e26241. [14] Casiraghi F, Azzollini N, Cassis P,et al.Pretransplant infusion of mesenchymal stem cells prolongs the survival of a semiallogeneic heart transplant through the generation of regulatory T cells.J Immunol. 2008;181(6):3933-3946. [15] Krampera M, Glennie S, Dyson J,et al.Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells inhibit the response of naive and memory antigen-specific T cells to their cognate peptide. Blood. 2003;101(9):3722-3729. [16] Benvenuto F, Ferrari S, Gerdoni E,et al.Human mesenchymal stem cells promote survival of T cells in a quiescent state. Stem Cells. 2007;25(7):1753-1760. [17] Li H, Guo Z, Jiang X,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells alter migratory property of T and dendritic cells to delay the development of murine lethal acute graft-versus-host disease. Stem Cells. 2008;26(10):2531-2541. [18] Selmani Z, Naji A, Zidi I,et al.Human leukocyte antigen-G5 secretion by human mesenchymal stem cells is required to suppress T lymphocyte and natural killer function and to induce CD4+CD25highFOXP3+ regulatory T cells.Stem Cells. 2008;26(1):212-222. [19] Corcione A, Benvenuto F, Ferretti E,et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate B-cell functions.Blood. 2006;107(1):367-372. [20] Tabera S, Pérez-Simón JA, Díez-Campelo M,et al.The effect of mesenchymal stem cells on the viability, proliferation and differentiation of B-lymphocytes.Haematologica. 2008;93(9): 1301-1309. [21] Asari S, Itakura S, Ferreri K,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells suppress B-cell terminal differentiation.Exp Hematol. 2009; 37(5):604-615. [22] Corcione A, Benvenuto F, Ferretti E,et al.Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate B-cell functions.Blood. 2006;107(1):367-372. [23] Spaggiari GM, Capobianco A, Becchetti S,et al.Mesenchymal stem cell-natural killer cell interactions: evidence that activated NK cells are capable of killing MSCs, whereas MSCs can inhibit IL-2-induced NK-cell proliferation.Blood. 2006;107(4):1484-1490. [24] Spaggiari GM, Capobianco A, Abdelrazik H, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit natural killer-cell proliferation, cytotoxicity, and cytokine production: role of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and prostaglandin E2.Blood. 2008;111(3): 1327-1333. [25] Jiang XX, Zhang Y, Liu B,et al.Human mesenchymal stem cells inhibit differentiation and function of monocyte-derived dendritic cells.Blood. 2005;105(10):4120-4126. [26] Spaggiari GM, Abdelrazik H, Becchetti F,et al.MSCs inhibit monocyte-derived DC maturation and function by selectively interfering with the generation of immature DCs: central role of MSC-derived prostaglandin E2.Blood. 2009;113(26): 6576-6583. [27] Zhang B, Liu R, Shi D,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells induce mature dendritic cells into a novel Jagged-2-dependent regulatory dendritic cell population.Blood. 2009;113(1):46-57. [28] English K, Barry FP, Mahon BP.Murine mesenchymal stem cells suppress dendritic cell migration, maturation and antigen presentation.Immunol Lett. 2008;115(1):50-58. [29] Le Blanc K, Tammik C, Rosendahl K,et al.HLA expression and immunologic properties of differentiated and undifferentiated mesenchymal stem cells.Exp Hematol. 2003;31(10):890-896. [30] Hirano T.Interleukin 6 and its receptor: ten years later.Int Rev Immunol. 1998;16(3-4):249-284. [31] Levy Y, Tsapis A, Brouet JC.Interleukin-6 antisense oligonucleotides inhibit the growth of human myeloma cell lines.J Clin Invest. 1991;88(2):696-699. [32] Landgraf K, Brunauer R, Lepperdinger G,et al.The suppressive effect of mesenchymal stromal cells on T cell proliferation is conserved in old age.Transpl Immunol. 2011; 25(2-3):167-172. [33] Djouad F, Charbonnier LM, Bouffi C,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit the differentiation of dendritic cells through an interleukin-6-dependent mechanism.Stem Cells. 2007;25(8): 2025-2032. [34] Shi D, Ma A, Zheng H,et al.Paeoniflorin inhibits the maturation and immunostimulatory function of allergen-induced murine dendritic cells.Int Immunopharmacol. 2014;19(2):221-232. [35] Li CR, Zhou Z, Zhu D,et al. Protective effect of paeoniflorin on irradiation-induced cell damage involved in modulation of reactive oxygen species and the mitogen-activated protein kinases.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007;39(2):426-438. [36] Wu H, Li W, Wang T,et al.Paeoniflorin suppress NF-kappaB activation through modulation of I kappaB alpha and enhances 5-fluorouracil-induced apoptosis in human gastric carcinoma cells.Biomed Pharmacother. 2008;62(9):659-666. [37] 郭平,王升启.芍药苷对人骨髓基质细胞HFCL蛋白质表达的作用[J].中草药,2006, 37(8):1206-1210. [38] 陈少清,林建平,王诗忠,等.芍药苷促椎间盘纤维环细胞增殖的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(2):254-258. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [4] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [5] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [6] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [7] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [8] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [9] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [10] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [11] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [12] | Li Cai, Zhao Ting, Tan Ge, Zheng Yulin, Zhang Ruonan, Wu Yan, Tang Junming. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB promotes proliferation, differentiation and migration of skeletal muscle myoblast [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1050-1055. |
| [13] | Liu Cong, Liu Su. Molecular mechanism of miR-17-5p regulation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α mediated adipocyte differentiation and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1069-1074. |
| [14] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [15] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||