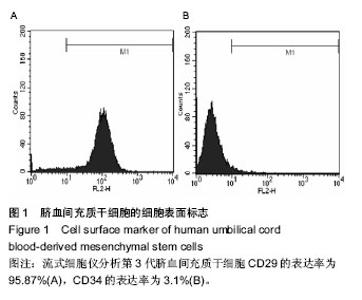
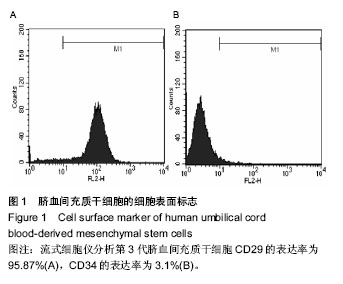
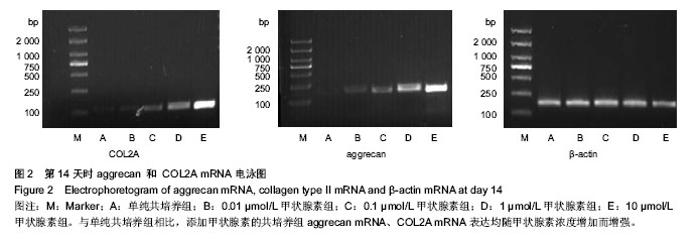
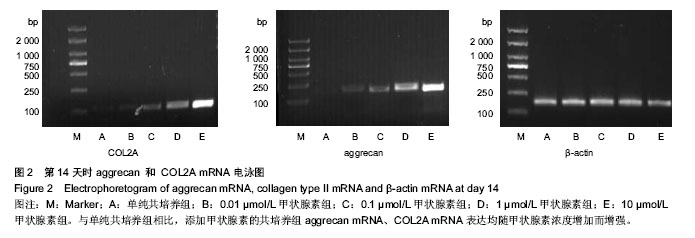
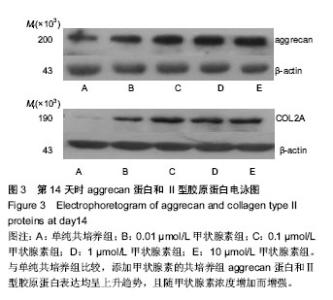
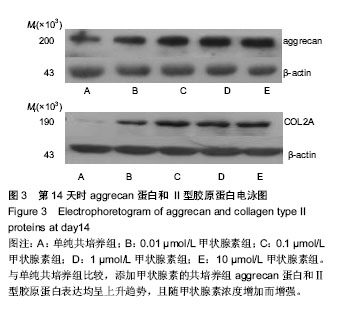
| [1] Yu Y, Ren H, Yun W, et al. Differentiation of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells into chondroblast and osteoblasts.Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2008;25(6):1385-1389.
[2] Laco F, Kun M, Weber HJ,et al.The dose effect of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells on epidermal development in organotypic co-culture.J Dermatol Sci. 2009; 55(3):150-160.
[3] Habisch HJ, Liebau S, Lenk T, et al. Neuroectodermally converted human mesenchymal stromal cells provide cytoprotective effects on neural stem cells and inhibit their glial differentiation.Cytotherapy. 2010;12(4):491-504.
[4] Aung A, Gupta G, Majid G,et al. Osteoarthritic chondrocyte-secreted morphogens induce chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells.Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(1):148-158.
[5] Luo Q, Song G, Song Y, et al. Indirect co-culture with tenocytes promotes proliferation and mRNA expression of tendon/ligament related genes in rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells.Cytotechnology. 2009;61(1-2):1-10.
[6] Hoff P, Buttgereit F, Burmester GR,et al. Osteoarthritis synovial fluid activates pro-inflammatory cytokines in primary human chondrocytes.Int Orthop. 2013;37(1):145-151.
[7] Tan AR, Dong EY, Andry JP,et al. Coculture of engineered cartilage with primary chondrocytes induces expedited growth.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(10):2735-2743.
[8] Broxmeyer HE.Biology of cord blood cells and future prospects for enhanced clinical benefit. Cytotherapy. 2005; 7(3):209-218.
[9] Koch TG, Heerkens T, Thomsen PD, et al. Isolation of mesenchymal stem cells from equine umbilical cord blood. BMC Biotechnol. 2007;7:26.
[10] Lu X, Alshemali S, de Wynter EA, et al.Mesenchymal stem cells from CD34(-) human umbilical cord blood.Transfus Med. 2010;20(3):178-184.
[11] Yu J, Cao H, Yang J,et al. In vivo hepatic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord blood after transplantation into mice with liver injury.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;422(4):539-545.
[12] Qian H, Wang J, Wang S, et al. In utero transplantation of human hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells partially repairs injured liver in mice.Int J Mol Med. 2006;18(4):633-642.
[13] Ghen MJ, Roshan R, Roshan RO, et al. Potential clinical applications using stem cells derived from human umbilical cord blood. Reprod Biomed Online. 2006;13(4):562-572.
[14] Gennery AR, Cant AJ. Cord blood stem cell transplantation in primary immune deficiencies. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;7(6):528-534.
[15] 郑朋飞,陈雷,董展,等.共培养诱导人脐血间充质干细胞向软骨细胞分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(23):4196-4203.
[16] Zhu S, Zhang T, Sun C, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells combined with calcium alginate gel modified by hTGF-β1 for the construction of tissue-engineered cartilage in three-dimensional conditions. Exp Ther Med. 2013;5(1): 95-101.
[17] Qing C, Wei-ding C, Wei-min F.Co-culture of chondrocytes and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro enhances the expression of cartilaginous extracellular matrix components.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2011;44(4):303-310.
[18] Hidaka K, Kanematsu T, Takeuchi H, et al. Involvement of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B signaling pathway in insulin/IGF-I-induced chondrogenesis of the mouse embryonal carcinoma-derived cell line ATDC5.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2001;33(11):1094-1103.
[19] Liu G, Kawaguchi H, Ogasawara T, et al. Optimal combination of soluble factors for tissue engineering of permanent cartilage from cultured human chondrocytes.J Biol Chem. 2007;282(28):20407-20415.
[20] Qian H, Wang J, Wang S, et al. In utero transplantation of human hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells partially repairs injured liver in mice.Int J Mol Med. 2006;18(4):633-642.
[21] Meretoja VV, Dahlin RL, Kasper FK, et al. Enhanced chondrogenesis in co-cultures with articular chondrocytes and mesenchymal stem cells.Biomaterials. 2012;33(27):6362- 6369.
[22] Wu L, Prins HJ, Helder MN,et al. Trophic effects of mesenchymal stem cells in chondrocyte co-cultures are independent of culture conditions and cell sources.Tissue Eng Part A. 2012;18(15-16):1542-1551.
[23] Tsuchiya K, Mori T, Chen G, et al. Custom-shaping system for bone regeneration by seeding marrow stromal cells onto a web-like biodegradable hybrid sheet.Cell Tissue Res. 2004; 316(2):141-153.
[24] Johnstone B, Hering TM, Caplan AI,et al. In vitro chondrogenesis of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal progenitor cells.Exp Cell Res. 1998;238(1):265-272.
[25] King DB, May JD.Thyroidal influence on body growth.J Exp Zool. 1984;232(3):453-460.
[26] Lewinson D, Harel Z, Shenzer P, et al. Effect of thyroid hormone and growth hormone on recovery from hypothyroidism of epiphyseal growth plate cartilage and its adjacent bone.Endocrinology. 1989;124(2):937-945.
[27] Hidaka K, Kanematsu T, Takeuchi H, et al. Involvement of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B signaling pathway in insulin/IGF-I-induced chondrogenesis of the mouse embryonal carcinoma-derived cell line ATDC5.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2001;33(11):1094-1103.
[28] Liu G, Kawaguchi H, Ogasawara T, et al. Optimal combination of soluble factors for tissue engineering of permanent cartilage from cultured human chondrocytes.J Biol Chem. 2007;282(28):20407-20415.
[29] Tan AR, Dong EY, Andry JP,et al.Coculture of engineered cartilage with primary chondrocytes induces expedited growth.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(10):2735-2743.
[30] Hoff P, Buttgereit F, Burmester GR,et al. Osteoarthritis synovial fluid activates pro-inflammatory cytokines in primary human chondrocytes.Int Orthop. 2013;37(1):145-151.
[31] 郑敏,潘莉珍,谭建强,等.先天性甲状腺功能减低症治疗前后TSH、FT4、IGF-1水平的变化及与体格生长的关系[J]. 中国儿童保健杂志,2013,21(8):793-795.
[32] Silvestro L, Chiorboli E. IGF-1 and IGFBP in congenital and acquired hypothyroidism after long-term replacement treatment.Minerva Endocrinol. 1999;24(2):51-55.
[33] Purandare A, Co Ng L, Godil M, et al. Effect of hypothyroidism and its treatment on the IGF system in infants and children.J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2003;16(1):35-42. |