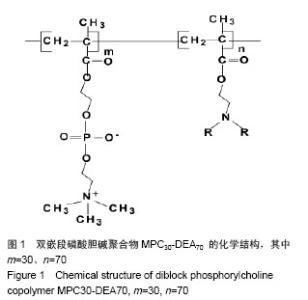
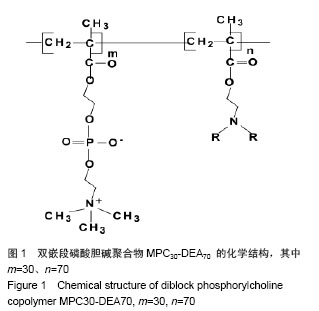
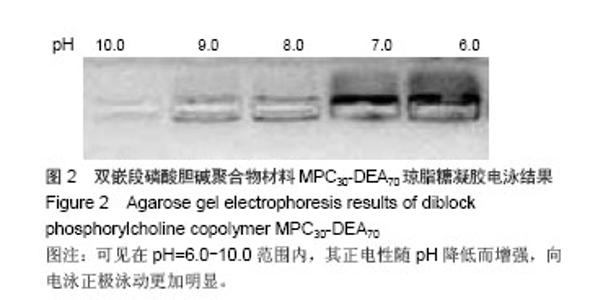
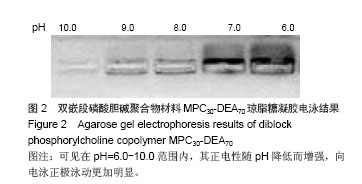
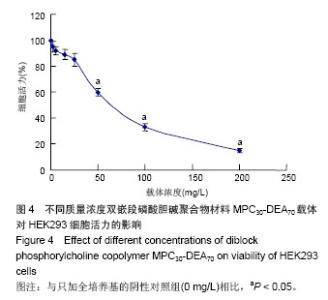
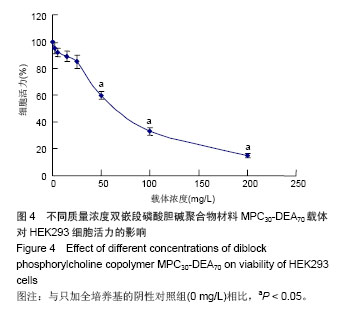
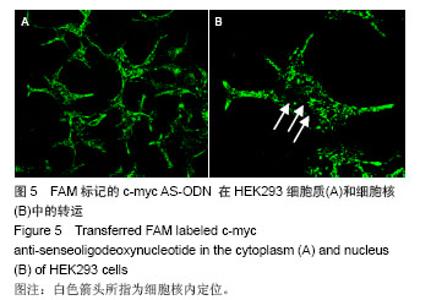
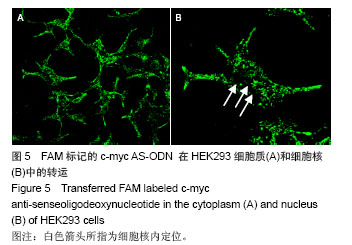
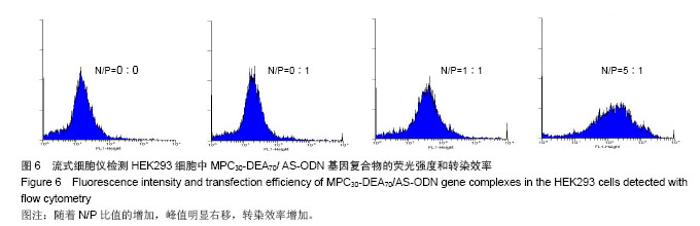
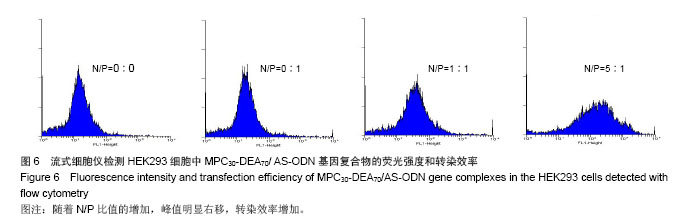
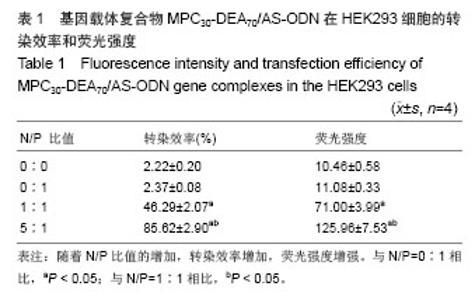
| [1] |
Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao.
Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445.
|
| [2] |
Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan.
Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087.
|
| [3] |
Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian.
Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650.
|
| [4] |
Xiang Feifan, Ye Junwu, Zhang Xihai, Ge Jianhua, Tang Lian, Yang Yunkang.
Comparison of three different internal fixation methods in treatment of ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fracture
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 403-408.
|
| [5] |
Lang Limin, He Sheng, Jiang Zengyu, Hu Yiyi, Zhang Zhixing, Liang Minqian.
Application progress of conductive composite materials in the field of tissue engineering treatment of myocardial infarction
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3584-3590.
|
| [6] |
Fu Panfeng, Shang Wei, Kang Zhe, Deng Yu, Zhu Shaobo.
Efficacy of anterolateral minimally invasive approach versus traditional posterolateral approach in total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3409-3415.
|
| [7] |
Ren Xingyu, Zhang Yi, Xu Haoran, Fan Bin, Dai Shifeng, Liang Chunyu.
Meta-analysis of the postoperative effects of robot-assisted unicompartmental knee arthroplasty versus conventional surgery
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3416-3422.
|
| [8] |
Ma Dujun, Peng Liping, Chen Feng, Jiang Shunwan, Jiang Jinting, Gao Kun, Lin Zhanpeng.
Research strategy of gene editing technology in the gene treatment of osteoarthritis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 298-303.
|
| [9] |
Song Kaikai, Du Gangqiang, Li Peng, Jiang Shengyuan, Gong Zhihao, Zhang Zhiwei, Zhang Kai .
Application of head-neck ratio in the treatment of femoral neck fracture in aged patients with artificial femoral head replacement
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2805-2809.
|
| [10] |
Li Haifeng, Liu Yu, Yin Qudong, Sun Zhenzhong, Rui Yongjun, Gu Sanjun.
Risk of complications of early postoperative weight-bearing after internal fixation of intracapsular femoral neck fractures: 2-year follow-up
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2875-2880.
|
| [11] |
Yuan Jiaqin, Luan Fujun, Chen Yangfan, Deng Yi, Li Bo.
Meta-analysis of bipolar and unipolar hemiarthroplasties for displaced femoral neck fracture in the elderly patients
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2915-2922.
|
| [12] |
Gao Fenghe, Chen Tongying, Lin Jiebin, Liang Zujian.
Efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid combined with rivaroxaban in primary total knee and hip arthroplasties: a meta-analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2453-2460.
|
| [13] |
Zhang Tengfei, Wang Kun, Zhu Yanyu, Mei Wei, Wang Qingde.
Meta-analysis of risk factors associated with adjacent segment degeneration after lumbar posterior fusion
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(12): 1936-1943.
|
| [14] |
Milalimmu•Multiza, Zhao Wei, Varesjiang•Nyyaz, Yuan Hong, Wang Li.
Direct anterior approach versus anterolateral approach in total hip arthroplasty: comparison of early
postoperative patient’s perception
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1318-1323.
|
| [15] |
Yin Jiandong, Wang Xinling, Zuo Biao, Li Nongyi.
Relationship of extrusion and elevation of blood-expelling methods during
total knee arthroplasty with postoperative complications
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1331-1336.
|