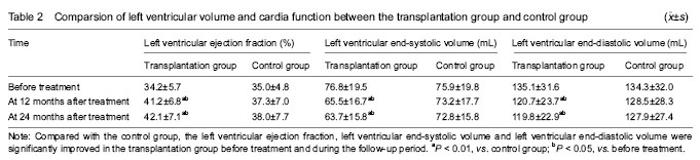
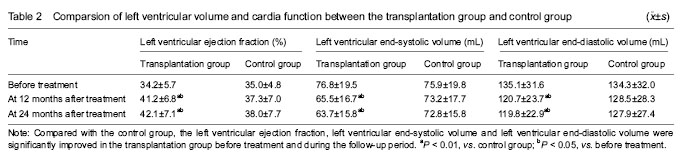
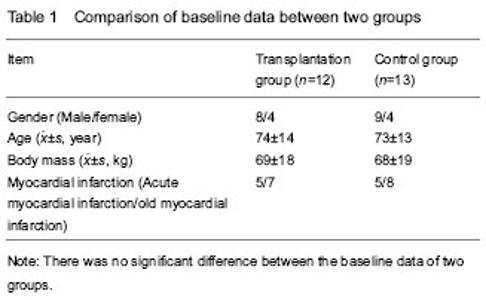
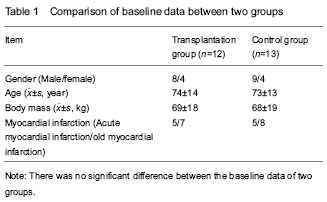
| [1] Pfister O, Della Verde G, Liao R, et al. Regenerative therapy for cardiovascular disease.Transl Res. 2014;163(4): 307-320.
[2] Sánchez LA, Guerrero-Beltrán CE, Cordero-Reyes AM, et al. Use of stem cells in heart failure treatment: where we stand and where we are going. Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc J. 2013;9(4):195-200.
[3] Sanganalmath SK, Bolli R. Cell therapy for heart failure: a comprehensive overview of experimental and clinical studies, current challenges, and future directions. Circ Res. 2013;113(6):810-834.
[4] Boyle AJ, Schulman SP, Hare JM, et al. Is stem cell therapy ready for patients? Stem cell therapy for cardiac repair. Ready for the next step. Circulation. 2006;114(4):339-352.
[5] Kajstura J, Urbanek K, Perl S, et al. Cardiomyogenesis in the adult human heart.Circ Res. 2010;107(2):305-315.
[6] Schächinger V, Erbs S, Elsässer A, et al. Improved clinical outcome after intracoronary administration of bone-marrow-derived progenitor cells in acute myocardial infarction: final 1-year results of the REPAIR-AMI trial. Eur Heart J. 2006;27(23):2775-2783.
[7] Assmus B, Rolf A, Erbs S, et al. Clinical outcome 2 years after intracoronary administration of bone marrow-derived progenitor cells in acute myocardial infarction. Circ Heart Fail. 2010;3(1):89-96.
[8] Sadat K, Ather S, Aljaroudi W, et al. The effect of bone marrow mononuclear stem cell therapy on left ventricular function and myocardial perfusion. J Nucl Cardiol. 2014; 21(2):351-367.
[9] Yousef M, Schannwell CM, Köstering M, et al. The BALANCE Study: clinical benefit and long-term outcome after intracoronary autologous bone marrow cell transplantation in patients with acute myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;53(24):2262-2269.
[10] Meyer GP, Wollert KC, Lotz J, et al. Intracoronary bone marrow cell transfer after myocardial infarction: 5-year follow-up from the randomized-controlled BOOST trial. Eur Heart J. 2009;30(24):2978-2984.
[11] Mielewczik M, Cole GD, Nowbar AN, et al. The C-CURE Randomized Clinical Trial (Cardiopoietic stem Cell therapy in heart failURE). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62(25):2453.
[12] Furfaro EM, Gaballa MA. Do adult stem cells ameliorate the damaged myocardium? Human cord blood as a potential source of stem cells. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2007;5(1): 27-44.
[13] Jaing TH, Hsia SH, Chiu CH, et al. Successful unrelated cord blood transplantation in a girl with malignant infantile osteopetrosis. Chin Med J (Engl). 2008;121(13):1245-1246.
[14] Martins AA, Paiva A, Morgado JM, et al. Quantification and immunophenotypic characterization of bone marrow and umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells by multicolor flow cytometry. Transplant Proc. 2009;41(3):943-946.
[15] Poliachenko IuV, Habriielian AV, Domans'ky? TM, et al. Effects of the umbilical blood stem cells in experimental injury of myocardium. Klin Khir. 2013;(7):56-60.
[16] Bewley S, Mercer J. Using umbilical cord blood stem cells for myocardial infarction and stroke is ethically challenging. Clin Med. 2010;10(1):97; author reply 97-98.
[17] Greco N, Laughlin MJ. Umbilical cord blood stem cells for myocardial repair and regeneration. Methods Mol Biol. 2010;660:29-52.
[18] Rabald S, Marx G, Mix B, et al. Cord blood cell therapy alters LV remodeling and cytokine expression but does not improve heart function after myocardial infarction in rats. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2008;21(5-6):395-408.
[19] Leor J, Guetta E, Feinberg MS, et al. Human umbilical cord blood-derived CD133+ cells enhance function and repair of the infarcted myocardium. Stem Cells. 2006;24(3):772-780.
[20] Henning RJ, Shariff M, Eadula U, et al. Human cord blood mononuclear cells decrease cytokines and inflammatory cells in acute myocardial infarction. Stem Cells Dev. 2008; 17(6):1207-1219.
[21] Zhang M, Yu L. Umbilical cord blood mononuclear cell transplantation is safe for treatment of coronary heart disease with heart failure. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2013;17(49):8557-8562.
[22] Hirata Y, Sata M, Motomura N,et al.Human umbilical cord blood cells improve cardiac function after myocardial infarction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005; 327(2): 609-614. |